Forms of pseudoscience. Methodology of pseudoscience How to distinguish a scientific theory from a pseudoscientific one? Are there any instructions
Article 2, supplemented and corrected.
This article is devoted to such a phenomenon in cognition as pseudoscience.
An interdisciplinary, systemic analysis of the phenomenon of pseudoscience was carried out in order to determine the methodology of pseudoscience, the main characteristics and classification of pseudoscientific concepts. Generalizing the concept of pseudoscience will allow us to rationalize
measures to control and limit the development and spread of pseudoscience.
1. FUNDAMENTALS OF Pseudosciences.
1.1 Pseudoscience is everything that does not correspond to modern official science, and this is knowledge that is unprovable or refuted. Pseudoscience refers to a wide range of pseudosciences and other false concepts that do not develop knowledge and have no such value, but strive to take the place of science. Most pseudosciences have as their goal certain benefits, either money taken from people, or power over people. Pseudoscientists, for example astrologers and psychics, realize that they are engaged in pseudoscience; they are engaged meaningfully, or rather, they imitate the scientific process, because they do not want to lose easy income. That is why all pseudosciences are characterized by the fact that their theses are aimed at social and personal processes, since they are designed for people, and not for knowledge of the world. Classic pseudosciences have much in common with fraud, and perhaps are such in the sense that, masquerading as “scientific” or truth, they gain the trust of people, and receive income from empty services and goods. In addition to crime, pseudoscience seeks to equalize science or even crush science, since only in this case will they gain the significance of truth in society, and the falsity of their scams will be hidden. Pseudosciences create technologies and other things that will become a reason for the seizure of large funds and public money. Such variants of pseudoscience especially seek to suppress science and influence politicians and scientific institutions, from which these pseudosciences can receive recognition, and then large profits.
Any society is replete with stupid and gullible people and ignoramuses, the number of which is inversely proportional to the enlightenment of the society, but in any case their number is incomparably greater than the number of thinking and independent people. Pseudoscience uses this contingent of less enlightened people and penetrates their consciousness in order to obtain easy income from them. Little enlightened people, as a rule, are gullible people who, without knowledge of the world, are at the level of medieval development, believing in gods and the supernatural. During the Middle Ages, pseudoscience and false teachings, such as religion, were in opposition to science, and with the help of the Inquisition they suppressed knowledge; at the present time, science has developed so much that it has acquired a well-deserved dominant place in humanity’s understanding of the world. Modern science has acquired a dominant position not only due to the proof of its theses, but also due to its special significance for the development of technology and living standards, which in turn determines the level of development of civilization, that is, it is the basis of civilization. Modern science has achieved an authority that religion will never achieve, therefore religion, apart from small attempts, is not able to confront the facts. Pseudoscience has chosen a different path of development: not in opposition, but in adaptation and integration with science, creating theses similar to scientific ones, but having the meaning and goals of religion - influencing the consciousness of people and their trust.
1.2 The danger of pseudoscience lies in the fact that it seeks to equalize or take the place of science, in which case the public’s trust in them will be unlimited, and the fraud of pseudoscience will be as effective as possible. The danger of pseudoscience is also that it destroys the solid foundation of the provability of sciences, introducing false knowledge and disrupting the understanding of reality. Pseudoscience enters into the confidence of people when it is difficult for people to understand or accept scientific truths, when science has limitations in development, and when science denies something, in this case pseudoscience occupies this vacancy in the minds of these people, and makes it easy to understand the world through the supernatural, gives people “knowledge” that is more easily accepted (about the exclusivity of people and the Earth in the universe). Pseudoscience, based on fiction, “easily” explains and “does” what science cannot, for example, treat cancer, and of course pseudoscience does not deny anything that ordinary people do not deny, pseudoscience does not deny Darwinism, the existence of the soul and other things.
1.3 The human species, having gained independence from nature and reached the level of self-awareness, has archaic characteristics, for example, man unconsciously ascribes to himself chosenness and perfection in comparison with the animal world, man recognizes himself as the center of the universe - this self-awareness was fully realized in the religious teachings in which man originated in the likeness of God, is the ruler of the Earth, “The Earth is at the center of the universe,” and “the entire universe is a solid shell with stars attached,” “man’s thoughts are manifestations of his soul, which animals do not have.” Science, through irrefutable evidence, refuted each of these theses: Copernicus created the heliocentric system and overthrew the myth about the chosenness of the Earth, Darwin proved the origin of man from animals, this was also confirmed by geneticists - this is how the myth about the chosenness of man in living nature was refuted, Pavlov proved the reflex mechanism of thinking and exposed the mythical soul of man. Pseudoscience and religion rely on this archaic self-awareness, and develop within their framework - those directions that were recently refuted by science or that are too objectionable to people’s pride, such as, for example, Darwin’s theory and the theory of evolution in general, reappear; pseudoscience develops ideas about a certain world supernatural, in which there may be a soul and so on - thus, an unsuccessful alternative to knowledge develops, but in return pseudoscience receives greater approval from people whose pride has been consoled.
1.4 Human psychology has another feature that pseudoscience uses to penetrate consciousness - this is the subjective thinking of gullible people. Trusting and impressionable people see what is not there, but what they want to see, and do not see what they do not want to see, do not see obvious contradictions. Religious people are exactly like this; they don’t even want to hear anything against God and religion, be it even obvious denials; at the same time, in ordinary phenomena they see signs, appearances of angels, God’s will or God’s punishment. Trusting people are limited in their critical thinking, since their own thoughts are replaced by a set of conjectures formed by faith in something. It is almost impossible to convince such people, no matter how proven the refuting facts may be.
1.5 One of the means of developing and popularizing pseudoscience is falsification, when fictitious phenomena are presented as real. In case of falsification, pseudosciences try to strengthen their positions with false evidence, experimental data, falsified. Frauds are promoted by pseudoscience through the media and literature, and serve as “proof” of pseudoscientific positions. In addition to falsifications, pseudoscience spreads fiction about the manifestations of superpowers and healing properties of something, while pseudoscience does not bother itself with evidence and connection with science, their “evidence” goes parallel and independently of science, thereby demonstrating its isolation and independence from the enemy - Sciences. In terms of the use of falsifications by pseudoscience, it is worth noting that all kinds of supernatural phenomena are demonstrated, as a rule, publicly, or in laboratory-like conditions of any room in the presence of certain third-party people who give the impression of experts or scientists, and all these demonstrations are no different, and even inferior in entertainment tricks of illusionists. It is not difficult to find a connection between the demonstration of pseudoscientific “evidence” and the illusions being produced. Any experienced prestidigitator will easily expose such demonstrations, but they are designed for ordinary people who, seeing the tricks of illusionists, marvel at them, but seeing the same tricks called “superpowers.” It can be assumed that Jesus Christ existed and performed miracles, but only these miracles were ordinary tricks, today’s illusionists do such things that Jesus fades in their light: illusionists fly (Copperfield) - Jesus did not fly, he only ascended once (according to the testimony of 12 disciples , against thousands of witnesses of Copperfield’s flights), disappear, pass through walls, make objects and even structures disappear (Statue of Liberty), repeat tricks with “multiplying loaves”, resurrect the dead (Longo, Grabovoi), heal entire stadiums from a distance (Kashpirovsky, Chumak ).
The miracles of Jesus were limited: he did not fly in everyday life, did not extinguish the Sun, did not extinguish the stars, did not send earthquakes, because no one can do such tricks.
Biblical stories and miracles are most likely fiction, since they have not been proven, but they can also be real phenomena, only distorted, exaggerated and interpreted with a religious connotation, which is characteristic of believers, for example, the ebb of the sea could be represented by believers as the divergence of the waters of the sea before Moses; “manna from heaven” could be the same phenomenon as “fish” or frog rains,” when hurricanes and tornadoes raise various objects from the surface; the dissolution of red clay in river water can be perceived as a “bloody river”; the heated land creates an optical effect of a mirror - the illusion of the surface of the water, which could have taken place on a spit in the bay, hiding this spit from observers, and disguising it as the surface of the sea, anyone walking on it creates the impression of “walking on water” - after all, Jesus walked on water, but not flying over the water. Many people tend to worship something, most often these are fictional gods, but these can also be other people, for example, adepts deify the leaders of their religious sects, fans deify famous singers, people who believe Kashpirovsky, Grabovoy and other magicians will form a crowd of people who will be convinced of the chosenness and greatness of their ideal, as the followers of the man Jesus Christ were convinced of his divinity, and it is impossible to convince such people; admiration for them is stronger than logic and self-esteem.
Typically, the various kinds of “phenomena” that pseudoscience relies on are either illusions, either created or natural, or very distorted phenomena, exaggerated or misinterpreted, or these phenomena are simply fiction. Pseudosciences never study their phenomena, as happens in science; in pseudoscience, phenomena and laws are simply described, since they are the result of arbitrary thoughts of people outside of reality. Despite the fact that, for example, some specialized institutes officially confirm the presence of superpowers in people, nevertheless, these same institutes do not go beyond private “confirmation” and private conferences, and the topic of certain abilities does not turn into research, dissertations and articles, which in turn will prove human superpowers and make it part of science. This does not happen due to the falsification of the examination, which is limited to isolated cases and risks being immediately refuted by a full-fledged study. Such a synthesis of pseudoscience and scientific falsifications is most effective for the existence of pseudoscience, since it allows pseudoscience to be directly integrated into official science.
1.6 In former times and now, pseudoscience describes and uses real phenomena, dressing them in a kind of supernaturalism. The phenomenon of self-hypnosis, in which a person, with the help of the psyche, is able to unconsciously influence the functions of the body and stimulate internal reserves, has been well studied by official science. Based on the effect of self-hypnosis, there is a therapeutic agent - a placebo, which is an empty substance devoid of medicinal properties, but at the same time, has a therapeutic effect of the same strength as the disease is associated with the mental functions of the body. Pseudoscience uses the placebo effect, but under its guise they sell expensive substances and devices, receiving fraudulent income from “high-tech” placebos. In a similar way, pseudoscience uses hypnosis, subsuming under it certain properties of a certain soul or supersensible world, thereby achieving agreement with reality from its false teachings. The placebo effect also occurs during “fortune telling,” when a person sets up and unconsciously induces a prediction on himself, or during magical rituals, when “magic” acts on a person through self-hypnosis.
1.7 WAYS OF INFLUENCE OF Pseudosciences.
The most negative phenomenon for the state is the interaction between pseudoscience and circles of people with power or large sums of money, or managers of funds. Politicians and owners of large capital do not differ in intelligence from ordinary people, they are just as gullible, and are also unable to understand the difference between science and pseudoscience, therefore pseudosciences of various types, by manipulating the consciousness of such influential people, themselves receive part of this influence. Fooling influential and famous people (actors, astronauts) is even more profitable for pseudoscience in terms of income than influencing ordinary people. Pseudoscience successfully uses its influence on influential people to lobby for their interests, to disseminate and popularize pseudoscience, increase their authority, as well as to put pressure on science and counterattack criticism. Pseudosciences are especially eager to lobby their interests in power, since this will allow pseudosciences to be legalized “from above” and turn into science. The influence of pseudoscience on corrupt authorities is especially effective, since it becomes mutually beneficial. Only scientists can identify pseudoscience; ordinary people are fundamentally unable to do this; therefore, ordinary people, including politicians, can be fooled
for pseudoscientists it is worth nothing, and in turn, a duped politician is the best trophy for pseudoscience - for pseudoscience he becomes the key to gigantic state funds, he becomes protection from any attacks, including from the Academy of Sciences.
Pseudoscience also influences through science, by bribing specialists and editors of journals, patent offices, making its way into scientific journals, receiving fake reviews, diplomas and scientific titles, making its way to scientific conferences and buying expertise in institutes - that is, trying to purely mechanically take a place in science. Breaking into science for pseudoscience is the second most important task after obtaining funding, since it makes pseudoscience more scientific,
That’s why pseudoscientists especially spend money on gaining officiality and scientific character.
1.8 PROTECTIVE STRATEGIES OF Pseudosciences.
Pseudosciences show strong resistance to all kinds of attempts to eliminate them, connecting to this all possible resources into which they have penetrated, from politicians and courts (trials against the teaching of Darwin's theory), and ending with the involvement of the media and bribed scientists up to academicians. Pseudoscience exhibits such strong resistance for the reason that they bring high incomes to their creators, who, in turn, do not want to lose easy income and will take any action against critics. All scientific concepts are characterized by a “proof-refutation” dialogue, which constitutes the scientific process of searching for truth, in which criticism is of key importance, but pseudoscience cannot conduct such a dialogue, so they choose the tactics of aggressive and persistent opposition in the form of disagreement with criticism, and also attacks on the critics themselves, which are characterized by a derogatory tone. Trying to refute pseudoscience is as useless as justifying nonsense, if only because there is nothing to refute, it is difficult to find arguments for arbitrary ideas, this does not prevent official scientists from wasting time on refuting pseudoscience.
One of the defensive strategies of pseudoscience is its penetration into secret industries, primarily into the well-funded military sphere, for which entire military units have been created (military unit 10003). Protection by secrecy allows pseudoscientists to avoid publicity of their falsifications, which can cause a stream of reasonable criticism, and also to avoid any influence from the Russian Academy of Sciences and official science, which are limited by “military secrets” that protect a warm place for pseudoscientists - this is the most dangerous influence of pseudoscience, which undermines the country's defense capability. Pseudoscience has created a fundamentally new tactic of self-defense - it itself organizes the fight against pseudoscience, but at the same time is on the side of science and not only avoids purges, but also eliminates competitive trends; the Russian Orthodox Church resorted to similar tactics, which became one of the initiators of the creation of the Russian “Committee to combat pseudoscience,” which means that the minimum becomes protected in the process of persecution against pseudoscience, the maximum manages the process of eliminating pseudoscience, of course, this does not mean that the Committee to Combat Pseudoscience is not effective, it means that the Russian Orthodox Church has immunity from this committee .
1.9 Refutation of pseudoscience by scientists is undoubtedly the most reliable means of destroying pseudoscience, but scientific refutation is not always required to curb pseudoscience, since it is a waste of time and draws attention to pseudoscience, and the effectiveness of these methods is temporary, since arbitrary teachings in the form of pseudoscience are quite volatile, and capable overcome outdated rebuttals. The most effective criterion for pseudoscience is the internal and external inconsistency of these teachings: the internal one is associated with contradictions within the concept that inevitably arise from the arbitrary calculations of narrow-minded people; external contradictions are associated with incomparability with the achieved level of official science. Engaging in the refutation of pseudoscience is a rather thankless task, since you have to go down to the level of development of pseudoscientists, pay attention to them, and thereby indirectly raise their status by giving pseudosciences attention from science. Criticizing pseudoscience is also ineffective because human imagination is inexhaustible and pseudoscience, even with fully developed science, will find its place for existence - in the place of liquidated pseudosciences, new ones will arise, and this will continue indefinitely. It is the uselessness of criticism that leads modern science to a simple ban on any concept, for example, a ban on considering projects of perpetual motion machines, or on publishing criticism of the theory of relativity, since confronting the endless stream of pseudoscientific ideas that are obviously meaningless takes more time than, in fact, development of science.
1.10 Pseudosciences are actively taking root, using all kinds of funding, influence on the authorities, which create organized conglomerate centers - the so-called international academies and institutes (MAISU, International Academy of Trinitarianism, Academy of Bioenergy Informatics and the like). The organization greatly strengthens the influence of pseudoscience and makes it almost invulnerable to attacks from science, the public and the authorities. Suffice it to recall the massive support of the pseudoscientist Grabovoi, for which the Scientific and Practical Conference “Modern Problems of Science, Technology, Culture, Health, Society and Problems of Space Security of the Earth” was held, St. Petersburg, at which professors and candidates of science came to Grabovoi’s defense , hired by influential pseudoscientific organizations or who are simply imaginary scientists, ready to carry such nonsense for money, for which even a schoolchild would be given a bad grade, for example, at the same conference E.I. Borovkov, professor, director of the Research Institute of Astrobiological Problems and Space Security named after. S.I. Repyeva, the president of MAISU stated: “After all, until now, our modern meteorology knows nothing except the cyclone and anticyclone. She doesn’t even know where this very cyclone comes from. Where does an anticyclone form? And this is a projection of a circumsolar black hole. If even meteorologists don’t know where and what comes from, how can they correctly predict the weather? No way!” - there were a dime a dozen such anti-scientific pearls at that conference, and they were uttered by people with academic degrees and titles! For such reasoning, the scientist should simply be deprived or demoted of his scientific rank, and those persons (the Higher Attestation Commission, the Patent Bureau, the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences and others) who awarded him the title or patent should be subject to internal proceedings for incompetence.
1.11 Pseudosciences are developing in directions in which science has not developed,
and also in those knowledges that do not exist in nature. There are and can be imagined even more concepts and phenomena that are impossible according to the laws of nature, for example, “Perpetual motion machine”, antigravity, etc., which will always remain non-existent, and the impossibility of their existence is unprovable like the infinity of the universe, therefore pseudoscience especially strives to rehabilitate and describe them, and since it is impossible to prove their impossibility, they become stable concepts for the existence of pseudosciences.
2. CHARACTERISTIC SIGNS OF Pseudosciences.
2.1. Pseudosciences describe a certain unknowable, “hidden” world, possessing one or another spirituality, divinity, this allows you to use the faith of narrow-minded people in the supernatural and at the same time make your teaching more scientific - this allows you to integrate stupid trust and the “sphere of science”. Pseudosciences operate with abstractly comprehensive concepts and terminology, reminiscent of the reasoning of philosophers or people of the Middle Ages, which are formed from a limited set of words: god (creator, universal mind), soul, mind, thoughts, life, universe (space), space-time, waves ( resonance), energy (light, quantum), information, happiness, love, health, good and evil, freedom, new knowledge, from which the vast majority of reasoning and terms of false teachings are formed through combination.
2.2. Social and personal orientation. Pseudosciences describe personality, social life, human relationships, illnesses, business, wars and disasters, and other phenomena that are directly related to human life, while showing no interest in phenomena not related to humans (for example, stellar physics, volcanology, entomology ). This indicates that pseudoscience strives to develop in that area of human thinking that is of greatest importance to every person, and therefore most in demand by people, that is, pseudoscience is aimed at the greatest interest of people, receiving more attention. Regardless of the field of pseudoscience, be it physics, biology or religious teachings, they all ultimately converge on human properties.
2.3. A very characteristic feature of pseudoscience is its rapid introduction into practice. Pseudoscience not only rapidly reaches the level of application of its “ideas” in business, which sometimes outstrips the development of these ideas themselves, but also the desire to use the “idea” in the first place. A striking example is torsion technology, which developed before physicists developed the idea of torsion fields, which was later disproved.
2.4. Pseudoscience is implemented in trade and services. Pseudosciences primarily strive for the direct sale of their products, be they things in the form of amulets, horoscopes, healing remedies, etc., or services in the form of fortune telling or “cure.” This sign indicates the goal of pseudoscience - easy income, therefore pseudoscience develops where gullible people have large amounts of money and power, that is, politicians, businessmen, criminals and others, therefore, various kinds of pseudoscientists tend to strive in these circles in order to sell at a higher price their own inventions, for example, the court of kings and presidents always had their own astrologers, magicians, healers and other rabble.
2.5. Pseudoscience is highly universal. Usually, the basis of a holistic teaching is a certain single principle, reminiscent of arbitrary reasoning, like mythology, or a single phenomenon like bioinformatics (bioenergy and informatics), torsion fields, from which a certain doctrine develops, almost to a panacea or theory of everything. Pseudoscientific medicines, treatment methods and devices are characterized by a huge list of curable diseases, on the verge of a panacea for everything, and diseases that are in no way related to each other. The same pseudoscientific remedy treats both obesity and thinness at the same time.
2.6. Pseudosciences are created by borrowing concepts from disparate sciences that have minimal connection, in other words, pseudosciences are very interdisciplinary. In their interdisciplinary achievements, pseudoscience reaches high values, turning into a principled farce, for example, in medical and psychological areas, pseudoscientists actively use the concepts of quantum physics (torsion fields), in their physical areas they use religious and esoteric concepts (myology, bioenergy informatics). This quality of pseudoscience is also manifested in the fact that even scientists can create pseudoscience, only on the condition that the scientist is engaged in pseudoscience in a field of knowledge different from the one in which he is a specialist; for example, engineers, biologists, historians, philosophers and these arguments form pseudosciences.
2.7. In pseudoscience, all provisions are based on arbitrary fabrications, in the form of some kind of philosophizing or speculation, which are presented as conclusions, which must be experimentally confirmed. In other words, pseudoscientists replace experiments with reasoning in cases where this is unacceptable.
2.8. Pseudoscience develops in parallel with official science, adapting and borrowing knowledge from science in order to disguise itself as “scientific”; it develops after, that is, catching up, and not surpassing, since it cannot achieve new knowledge. Pseudoscience borrows terms from official science, such as quanta, black holes, space-time, waves, resonance and others, tying them to its teachings, doing it so stupidly and naively, like parrots that repeat words after a person and give the impression of conversation, although naturally they understand nothing about them. Science is developing, there are more terms, which means that the vocabulary of pseudoscientists is expanding and their speeches acquire a more scientific ring, while remaining
the meaningless babble of a parrot. Pseudoscience actively distorts the concepts of science, adapting them to its teachings, making complex interpretations of banal phenomena.
2.9. Pseudoscience is condoned and developed in directions that are more preferable to ordinary people with their archaic thinking. Pseudoscience does not try to convince, but on the contrary agrees that there is a certain divine world of the unknown, that man is a higher being, that there is a soul, that humanity and the Earth have chosenness, etc., precisely because such views are more preferable to ordinary people, pseudoscience penetrates especially easily into their consciousness. Pseudoscience “confirms” that there are certain human superpowers that an ordinary person wants to believe in, the same pseudoscience “refutes” Darwin’s theory, trying to prove to ordinary people who want to see something higher in themselves that they are really higher, similar encouragements to the archaic understanding of people there is a lot of pseudoscience on the part, since this is one of the incentives for their development.
2.10. Pseudoscience is characterized by rapid development, since it is based not on scientific research, but on arbitrary reasoning. This or that new pseudoscientific concept appears with ready-made basic knowledge, which was as if written by someone before them, and was studied by someone for a long time, although in reality it was invented in a short time by some rogue. Pseudoscience is characterized by a complete absence of any self-doubt; it asserts itself as the true truth, like religion “as it is written, so it is.” This is a sign that pseudoscience is borrowing
the method of self-education from the religious method, and therefore does not accept any refutations, and will never agree in a discussion with scientific examination, the result of which is predetermined, and not in favor of pseudoscientific teaching.
2.11. Pseudosciences do not oppose each other, coexisting quite tolerantly despite the fact that they constitute completely different ideas and competition. It would seem that religion should not recognize “reading the thoughts of God” in the form of astrology, and should not recognize teachings that do not coincide with religious teachings, but there is not even a hint of such opposition. Official science is presented by pseudoscience as a certain accurate and proven, but incomplete and limited knowledge, while pseudoscience is “deep and comprehensive knowledge”, which represents that part of “knowledge” to which official science cannot or does not want to develop. Pseudosciences do not pose a threat to each other, since they have the same goal - to influence people. Any attempts to refute pseudoscience are limited by the latter only to arguments that “science has not reached their level and therefore cannot prove it,” while it is unknown, let alone proven, how this knowledge related to pseudoscience was obtained.
2.12. It is characteristic of any pseudoscience that with “gigantic, limitless” possibilities there is a real zero effect. For example, if telepathy were real, then there would be no need for military intelligence, if telehypnosis was a reality, then there would be no need for diplomats, and so on. At the same time, telepathy and telehypnosis are not only more effective, but also much cheaper and safer - but there is nothing like it. Moreover, such technology could have been used since ancient times, when magic, prophecies, and spiritualism appeared. For example, if spiritualism were a reality, then it would be possible to convene the souls of great scientists (Newton, Einstein) and learn new ideas and theories from them. Torsion bar scientists promised a huge amount of energy from a physical vacuum, an absolute weapon, but neither one nor the other exists, and Europe still continues to purchase oil.
2.13 Pseudoscience is characterized by a complete lack of self-criticism. Most pseudoscientific concepts proclaim their conclusions to be final and correct, without a hint of doubt, although proper evidence is not attached to this, and the “truth” of this knowledge is only proclaimed. Healers and methods of alternative medicine have almost (or no) side effects, pseudo-historical concepts present themselves as “true history”, religious teachings proclaim themselves to be the absolute truth, and prohibit other truths, other religions.
3. INTERACTION between pseudoscience and science.
Science in its development steadily cognizes the world, and in this knowledge there are no facts that cannot be explained, there are no limits beyond which knowledge could not penetrate, in other words, in the world there is nothing divine and supernatural, but there is only what has already studied, and what remains to be studied. Physics has penetrated into the depths of the atom, studied it down to elementary particles and fields, and found the laws governing it. The atom did not turn out to be an indivisible “divine creation”; “God” decided to bother himself and complicated things to such an extent that they could exist without God. It would seem that pseudoscience should retreat and be destroyed under the influence of developing science, but this does not happen, this does not happen because the stupid ignoramuses who own money have not disappeared, which means that the soil for pseudoscience has been preserved.
Pseudoscience is even developing, it is developing in parallel with science, since it begins to use scientific concepts and laws to “explain” previously “unexplained things”, in fact, pseudoscience is trying to integrate into science, it stretches up the scientific tree, like a vine, reaching the top without its own strong trunk This mechanism for the formation of pseudosciences on the basis of achieved scientific knowledge is universal; what distinguishes pseudosciences is that they only adapt to science and do not develop knowledge, as science does. The explanation that pseudoscience makes on the basis of scientific knowledge is a rather primitive connection of analogies, a connection between what has been proven by science and what is similarly unproven. So, for example, astrologers are trying to explain the “influence of planets on people” by the gravitational field of these planets, even with all the absurdity of such conclusions that gravity can only cause mass displacement, for example, the gravitational field from the atmosphere and clouds exceeds the gravitational field of the planets, therefore It's better to predict fate by looking at the clouds.
Pseudoscience borrows phenomena from science, adapts them and even develops them in the wrong direction, while the more complex the phenomenon (quantum physics), the greater the effect obtained from its use, for example, certain “torsion fields” are subsumed under physical concepts, which are is no longer divinity and magic, but a kind of pseudoscientific concept formulated similar to scientific formulations. The Big Bang, which created the visible universe, was very successfully used by religious pseudoscientists as an act of divine creation, another important example of this borrowing of facts from science by pseudoscience is the introduction of newly discovered planets by astrology: Uranus, Neptune, Pluto, while the newly discovered planets were quite easily absorbed by astrology, also, for example, the well-known phenomenon “Kirlian effect”, which is only an electrical phenomenon similar to the discharges studied by Tesla, is presented by pseudoscience as the same mythical biofield that many pseudosciences talk about, but it remains unclear how the biofield appears in inanimate objects. A gift for pseudoscience are scientific hypotheses of fantastic content, for example, additional dimensions that we cannot detect due to
Latest publications on related topics
Comings per page: 1433
One cannot but agree that the spread and popularization of pseudoscience is one of the most serious problems of modern culture. The main difficulty in fighting it lies in the ability of its main adherents to combine scientism and messianism in their “works,” which for an unprepared person creates the illusion of a new word in science.
Origins of pseudoscience
Before defining the main features and varieties of this phenomenon, it is necessary to understand the question: how did the emergence of pseudoscience become possible? It is unlikely that, for example, 14th century alchemy or Babylonian astrology can be considered as such. Firstly, their development was not associated with the denial of existing knowledge about the properties of chemical substances in the first case and the laws of planetary movement in the second. Secondly, within the framework of these disciplines there was a real accumulation of scientific knowledge, although the goals set - the search for the philosopher's stone and the establishment of the influence of stars on the fate of man - do not inspire much confidence. Nowadays, we already boldly classify both alchemy and astrology as pseudosciences, since with the emergence of chemistry and astronomy, all that remained for these “sciences” was to convince people that with the help of a certain substance it is possible to turn any metal into gold and to look for signs of fate in solar eclipses .
Thus, the history of pseudoscience begins in the modern period (begins approximately from the middle of the 17th century). The religious picture of the world characteristic of the Middle Ages is consistently replaced by a rationalistic one, where evidence is assumed instead of faith. However, the volume of accumulation of scientific knowledge turned out to be so rapid, and the discoveries of scientists, especially in the field of natural sciences, sometimes contradicted established ideas. This led to the construction of numerous exotic theories. Over time, the flow of discoveries has not dried up. The theory of relativity and quantum mechanics have shown that even such an unconditionally scientific discipline as classical physics, created by Isaac Newton, does not work under certain conditions.
In addition, philosophy made a significant contribution to the possibility of developing pseudoscientific disciplines. In an effort to comprehend the world, many thinkers have put forward the idea that Being is an illusion. From this came the conclusion that scientific knowledge about the world is an illusion. Having escaped the boundaries of scientific reasoning, these ideas in the mass consciousness began to evoke thoughts that the world could be structured differently than what is assumed by the scientific community.
Thus, pseudoscience became a reaction to unexpected and sometimes contradictory data obtained by scientists. Since they themselves could not sometimes explain the discovered facts, pseudo-scientific speculation became common. The end of the 19th century was marked by a boom in spiritualistic séances, in which many prominent figures, in particular the writer Arthur Conan Doyle, saw one of the means of understanding the world. The development of the pseudosciences of that time was, in principle, closely connected with occult practices. Even then, their adherents took a rather aggressive position in relation to the scientific community. For example, H. P. Blavatsky, the founder of the Theosophical Society, in her “Secret Doctrine”, subtitled “Synthesis of Science, Religion and Philosophy,” openly ridiculed scientific achievements in the field of electromagnetism research.
Terminology problems
This excursion into history shows that the area of non-scientific “knowledge” is extremely wide. It can include both theories built in compliance with all the principles of science, but based on incorrect premises, and openly and aggressively opposing the established system of scientific knowledge. In view of this, it is necessary to introduce terms that would distinguish between non-scientific methods of “obtaining knowledge.” This is a rather difficult task, since the boundaries between them are quite blurred.
- Quasi-science is considered to be knowledge that contains both scientific and erroneous or deliberately falsified provisions in varying proportions.
- Parascience is understood as a system of theories, the main provisions of which significantly deviate from scientific dogmas with a significant preponderance towards erroneous ideas.
- Pseudoscience is a field of “knowledge” whose provisions either do not correspond to scientific data or contradict them, and the subject of research itself either does not exist or is falsified.
Separately, it should be said about the phenomenon of anti-science, which has been gaining momentum recently. As the term itself implies, its adherents see absolute evil in scientific knowledge. Anti-scientific statements, as a rule, are associated either with the activities of religious fanatics who believe that truth does not exist outside of some deity, or come from poorly educated segments of the population.
The boundaries between quasi-science and pseudoscience are very blurred. For two hundred years, homeopathy was considered a possible method of treating many diseases, and before the discoveries of Kepler and Halley, one could not speak of astrology as a pseudoscience. Therefore, when using these terms, it is necessary to take into account the historical stage and the conditions existing at it.
Factors in the emergence of pseudoscientific theories
One of the conditions for the emergence of extra-scientific “knowledge” has already been given: a change in pictures of the world and a corresponding worldview crisis. The second is associated with unacceptable errors during the research, such as the perception of some details as unimportant, the lack of experimental verification, or ignoring third-party factors. The logic of the study is thus straightened out and simplified. The result is the accumulation of erroneous facts and the construction of an incorrect theory.
The third condition also stems from errors in research work, but these did not arise due to the will of the researcher. In many areas of knowledge, some facts, due to insufficient development of the instrumental and theoretical base, turn out to be beyond his reach. Others cannot be tested experimentally. In this case, the researcher, following his intuition, may move to too strong generalizations, which also results in the construction of an erroneous theory.
If for quasi- and parascience it is possible to admit mistakes made, then pseudoscience does not at all seek to refute itself. On the contrary, there is a “scientific” substantiation of errors in which meaningless terms like “aura”, “torsion field” or “bioenergy” are used. Adherents of pseudoscience in their research sometimes use deliberately complicated language, citing a lot of formulas and diagrams, behind which the inexperienced reader loses sight of the very subject of the study and gains confidence in the “eruditeness” of its author.
Another factor in the emergence and successful spread of pseudoscientific theories is the crisis of official science. It should be recognized that the state or society is not always interested in fundamental research in any area. The vacuum created in this case is immediately occupied by all sorts of people seeking to profit from human trust. One of the most famous modern pseudosciences in this field is homeopathy.
Signs of a pseudoscientific theory
You don't have to be an expert in a particular field to determine whether a study is scientific or has no value. A scientific publication is always subject to a number of requirements, including those of a formal nature. Pseudoscientific publications rarely follow these rules.
An indispensable element of a truly scientific research is the presence of a list of sources and literature used in the work, which also includes publications previously made by the author in accredited publications. For obvious reasons, a pseudoscientific “research” cannot boast of such references.
A pseudoscientific publication does not have such an important structural element as an abstract or introduction, which would clearly formulate the goals and objectives of the study, as well as the methods used to solve them. Accordingly, there is no conclusion setting out the findings.
An adherent of pseudoscience almost always takes a pronounced aggressive position in relation to the data of official science. A considerable part of the text is spent on “debunking” the usual ideas that are supposedly imposed on society (it’s worth opening any volume of “New Chronology” by A. T. Fomenko and G. V. Nosovsky, and there will be accusations of professional historians falsifying data for unknown purposes). Instead, the author of such a work willingly talks about the unexpected discoveries he has made, leaving their subject aside. In the scientific community, such methods are considered unacceptable, and all the author’s merits consist only in listing the publications he has completed.
Science and pseudoscience also differ in that instead of the necessary overview information on the topic and its development by other researchers in the first case, the author of a pseudoscientific work gives his own reasoning of a philosophical nature, which, at best, has only an indirect relation to the problem being studied. In this regard, the exploitation of such topics as global catastrophes, life extension, decline of morals, and so on is especially popular. In addition to creating science, such reasoning is used as a publicity stunt.
Finally, one of the most recognizable moves of the authors of “research” from pseudoscience is the “claim to a miracle.” Such a work describes previously unknown facts, phenomena and theories, the verification of which cannot be carried out. At the same time, the author willingly uses scientific terminology, distorting its meaning at his own discretion. The inaccessibility of such information to the public is explained by various conspiracy theories.

Implementation of pseudoscience
The main disciplines in which various pseudosciences and pseudosciences have taken root and feel confident include medicine, physics, biology, areas of humanities (history, sociology, linguistics) and even such a seemingly protected sphere from speculation as mathematics. Distorting, simplifying or completely denying scientific knowledge, adherents of pseudoscience, primarily for the purpose of quick enrichment, created a number of theories and even “disciplines”. You can form the following list of pseudosciences:
- astrology;
- homeopathy;
- parapsychology;
- numerology;
- phrenology;
- ufology;
- alternative history (lately the term “folk history” has been increasingly used);
- graphology;
- cryptobiology;
- alchemy.
This list does not exhaust all the manifestations of pseudoscientific theories. Unlike official science, whose funding in most cases is not sufficient, adherents of pseudoscience earn substantial money from their theories and practices, so the emergence of new exclusive discoveries has become a mass phenomenon.
Astrology
Many serious scientists, citing examples of pseudosciences, consider astrology to be their standard representative. It should be borne in mind that we are talking specifically about modern astrological research. There is no doubt about the objective knowledge obtained by this science in the states of ancient Mesopotamia or Greece, just as it is impossible to deny their significance for the formation and development of astronomy.
But nowadays astrology has lost its positive side. The activities of its representatives boil down to drawing up horoscopes and vague predictions that can be interpreted in any way. At the same time, astrology uses outdated data. The zodiac circle used in this pseudoscience consists of 12 constellations, while it is known from astronomy that the trajectory of the Sun runs through the constellation Ophiuchus. Astrologers tried to correct the situation, but using fundamentally opposite methods. Some hastened to include Ophiuchus in the zodiac circle, while others said that the zodiac represents sectors of the ecliptic measuring 30 degrees, which are in no way tied to the constellations.

Already from such attempts we can conclude that modern astrology is a pseudoscience. However, many people continue to believe the predictions of astrologers, despite the fact that there are just over seven billion people living on earth, twelve constellations, which means that the same prediction is true for 580 million people at once.
Homeopathy
The emergence of this type of treatment can be attributed to historical oddities. Samuel Hahnemann, a physician who lived more than two hundred years ago, based on the fact that quinine, one of the then antimalarial drugs, like the disease, caused him a fever, decided that any disease can be fought by causing its symptoms. Thus, the essence of the homeopathic method is to take highly diluted medications.
Doubts about the effectiveness of this method existed from the very beginning of its existence. Realizing this, homeopaths persistently tried to bring it under their base, but to no avail. In 1998, a special and falsified scientific research was created at the Russian Academy of Sciences." Naturally, close attention was immediately paid to homeopathy. During the study, it was found that expensive homeopathic remedies pose a serious danger to health. It was indicated that by giving them preference, people they ignore medicines whose effectiveness has already been proven. In 2017, homeopathy was officially called pseudoscience. In addition, relevant recommendations were given to the Ministry of Health, the most important of which are to stop the use of homeopathic medicines in health care institutions, as well as to counteract their advertising.

Also, the Commission on Pseudoscience strongly recommended that pharmacies not place homeopathic medicines together with drugs with proven effectiveness and promote in print the idea of the equivalence of such concepts as “homeopathy”, “magic” and “extrasensory perception”.
Mathematical pseudosciences
One of the most popular objects for constructing pseudoscientific theories in the field of mathematics are numbers, and historically the most ancient such “discipline” is numerology. Its emergence is also connected with scientific needs: the Pythagorean school in Ancient Greece studied the fundamental properties of numbers, but this happened hand in hand with endowing the discoveries with some philosophical meaning. So, there were prime and composite, perfect, friendly and many other numbers. The study of their properties continues to this day and is of serious importance for mathematics, however, in isolation from purely scientific purposes, the ideas of the Pythagoreans became the basis for the search for signs of fate contained in numbers.
Like other esoteric practices, numerology exists in close connection with other pseudosciences: astrology, palmistry and even alchemy. Here, too, meaningless terminology is used: one is called a monad, instead of “eight” they say “oxoada”. Numbers are endowed with special properties. For example, 9 symbolizes the divine power of a certain Creator, and 8 symbolizes Providence and Fate.
Like others, this pseudoscience is rejected by scientists. In 1993, in the UK, and 19 years later in Israel, special experiments were conducted that were supposed to test whether numbers are really capable of influencing a person’s destiny in any way. Their result is expected: no connection was found, however, numerologists declared the findings false, without proving this in any way.
Frauds in the Humanities
History and linguistics are perhaps the most popular areas for the emergence of pseudoscientific theories. This is explained by the fact that these sciences do not provide the opportunity to test any concept. History very often, at the request of the ruling circles, was rewritten anew: some events were forbidden to be mentioned, the role of other statesmen was kept silent. This attitude and the loss of many sources for various reasons (for example, due to fires) led to the formation of numerous unexplored areas, which made it possible for people far from history to put forward absolutely fantastic theories, which they present as great discoveries that change all ideas.
Currently, the phenomenon of folk history or alternative history is gaining momentum. Arbitrarily using data from linguistics, astronomy and mathematics, “researchers”, to their own taste, either shorten the duration of history (“New Chronology”) or unlawfully make some events more ancient. As researchers note, professional historians for a long time preferred not to notice such publications, considering them too nonsensical to inspire confidence among the readership. However, the crisis in the scientific community and the lack of reaction from the scientific community have led to the fact that pseudoscientific theories of the origin of all languages of the world from Russian (at best Slavic) or the existence of a powerful Russian state back in the second millennium BC began to be perceived as true.
The already mentioned Commission on Pseudoscience is taking decisive steps to combat the dissemination of such “knowledge”. Round tables are being held on the problem, new publications are being published with a detailed and consistent debunking of the “advanced” methods of folk historians. Unfortunately, this has not yet produced tangible results: Fomenko’s publications and others like them are still published in large circulations, arousing interest among readers.
The fight against pseudoscience in the USSR
When listing the difficulties in defining the content of the term “pseudoscience,” one of them was deliberately omitted: under certain conditions and the presence of benefits (not necessarily material), truly scientific disciplines were classified as such.
Thus, during the period of Stalinism in the USSR, genetics turned out to be a pseudoscience. This event was entirely political in nature. The main opponent of the supporters of the new theory of heredity was agronomist and biologist T. D. Lysenko. Unable to oppose the principles of genetics with any convincing scientific counterarguments, Lysenko turned to political accusations and mockery. In particular, he stated that the doctrine of genes and heredity resulted in racism and fascism, and that the experiments carried out on Drosophila were a waste of people's money and direct sabotage. Conducted in the early 30s. discussions about genetics were soon abandoned. The Great Terror began in the country, the victims of which were many biologists: G. A. Nadson, N. I. Vavilov. They were accused of spying for hostile states and other types of anti-government activities.

In 1948, the fight against genetics ended in Lysenko's victory. In a report read at a session of the Lenin All-Union Academy of Agricultural Sciences, he repeated his previous argument: there is no “substance” of heredity. Proponents of genetics were allowed to issue rebuttals, but Lysenko then stated that his report had been personally approved by Stalin. Under these conditions, it was impossible to continue the discussion. As a bourgeois pseudoscience, genetics existed in the USSR until the mid-60s, when, after deciphering DNA, it became impossible to deny the existence of genes.
Another target of persecution in the USSR was cybernetics. It was first declared pseudoscience in the issue of Literary Gazette dated April 5, 1952. Again, the reasons for this were purely political: fearing that, having become acquainted with the Western way of life after the end of World War II, Soviet society would turn away from Marxist ideals, Stalin initiated and kowtowed to the West. Articles about the new science of information management and transmission that appeared in the foreign press were immediately declared bourgeois obscurantism.
Currently, articles are appearing that the persecution of cybernetics is a myth, since the USSR very soon began to conduct research in this direction, and the lag behind the United States in the field of computer technology was insignificant. However, we should not forget: Stalinism had almost twenty years to defeat genetics, and cybernetics took a year. Scientists who saw no reason to consider cybernetics a pseudoscience resisted the authorities. Soon the country's leadership made concessions, declaring that if society “does not object,” science will be rehabilitated. After the 20th Congress and criticism of the cult of personality, the opportunities for the development of cybernetics became much greater.

Pseudoscience and society
It must be admitted: a significant part of the population is not interested in pseudoscience and the fight against it. In the 90s, when Russian society was gripped by a systemic crisis, psychics, healers and other charlatans were actually the only ones who gave hope for a happy future. Naturally, not for free. It is not clear to the average person why ufology is a pseudoscience, but psychology is not. Publications on this topic exist, but they are clearly not enough, and sometimes they are inaccessible.
The most effective way to combat pseudoscience is to increase the educational level of the population. This, like many other things, comes down to the need to increase funding. Clearly insufficient funds are allocated for science and education. Failure to obtain the necessary knowledge is the reason for the spread in modern society of such seemingly unthinkable theories as the flat Earth theory. The geopolitical catastrophes that occurred in Russia at the beginning and end of the last century aroused in people the need for a heroic past: it seemed to be the only alternative to the hopeless present. “Historians” immediately appeared, happily fantasizing about the theme of the great all-Slavic state, which subjugated all its neighbors in the 9th (or 7th, or 2nd - it doesn’t matter) century. The high cost of healthcare, an indifferent attitude towards patients, and total bribery have led to an increase in distrust in medicine and increased requests for help from healers and homeopaths.
The psychology of pseudoscience is simple: if society has a demand for a miracle, then such a miracle will certainly appear for a certain price. However, from the rationalistic picture of the world, which all pseudosciences stubbornly fight, it follows that miracles do not exist. Numerology and phrenology could be considered only amusing curiosities from the history of scientific knowledge if interest in them were not fueled by people interested in it. Therefore, we must admit: the confrontation has only just begun. And what pseudosciences are yet to appear - time will tell.
Here you need to understand that pseudoscience implies a deliberate distortion of logic, misleading. Well, or this distortion may be a consequence of mental illness. It is quite natural for normal scientists to fantasize, invent hypotheses and make mistakes. But the system of the scientific world itself involves discussion, provision of evidence, publication in peer-reviewed journals, and conferences. The author of a scientific theory will be only too happy to discuss it, receive questions and make sure that he himself has really gotten to the bottom of the truth. And the pseudoscientist will reduce all attacks to conspiracy theories, a conspiracy of the scientific community controlled by reptilians, and, as has already been written here, avoid specialists and turn to the general public, gathering around him adherents who do not notice contradictions and inconsistencies.
A clear sign of pseudoscientific theories is that they are aimed at the average person. Their main task is not the development of science itself, but working for the public and creating an image (usually with the goal of making money). It is difficult for an ignorant person to distinguish truth from untruth, so even complete nonsense can be wrapped in “scientific terms” and presented as a scientific theory. Real scientists don’t care about such things; they do their work not for the sake of approval from the janitor Vasya Pupkin.
The main thing is not to confuse pseudoscience and the popularization of real science. Explaining a complex thing simply and clearly is popularization. Exposing stupidity to look abstruse and scientific is pseudoscience.
Sometimes it’s very simple, but there’s no luck at all. In any case, you need to look at how the theory is proven. At the moment, the main and only criterion of scientificity is the method of proof: all statements in science are proven by contradiction, and any theory lives exactly until the moment when it is refuted. More specifically, an alternative hypothesis/explanation (sometimes several) is formulated and evidence is provided why it is not valid.
Some sciences are more fortunate in this: they can conduct experiments and therefore there is no difference between rejecting an alternative hypothesis and proving the main one. For example, this is how things are in physics: if you threw an apple 1000 times, it fell 1000 times, which means there is a law of attraction; they threw an apple 1000 times at a speed of 8 km/s - it went into orbit 1000 times, which means 8 km/s is the first space one.
Things get more complicated when it becomes difficult or completely impossible to carry out experiments. For example, in medicine it is very difficult to conduct experiments, because, firstly, there are risks, and secondly, it is extremely difficult to mitigate the effects of other factors. In physics, you can throw a thousand identical balls or disperse a thousand “identical” particles in a collider, but in life you won’t find 1000 absolutely identical people, let alone them doing the same thing during an experiment (eating the same food, getting up in the same position). at the same time, did sports for the same time, etc.), and you don’t have to think about it. Sometimes experiments are not possible in medicine: you cannot force 1000 people to smoke half a pack a day if the task is to study the consequences of smoking. When experiments become difficult and/or impossible, it is necessary to constantly check whether there are other explanations for the observed phenomenon and test these alternatives. For example, could it be that smokers die earlier, not because of smoking, but because they eat fatty foods more often, drink alcohol, and generally lead a less healthy lifestyle than non-smokers? If the negative effect of smoking persists even if we compare people leading the same healthy lifestyle, then this alternative is rejected. Having gone through and rejected all alternative hypotheses, we can talk about the consistency of the original statement.
It gets really bad when it comes to social sciences such as economics and sociology. In such sciences, there can be a great many alternative hypotheses, and those who come up with new alternative hypotheses that no one has tested before are given respect and honor. The development of a methodology that allows us to immediately cut off many alternative explanations (including those that we are not aware of) occupies a very significant layer in the social sciences.
Non-sciences (in global terminology) or humanities (in Russian terminology) are both lucky and unlucky at the same time. Let's take a look at history. History does not ask the question common to all sciences: “what will happen if?” (for example, “Won’t I die faster if I smoke 10 more cigarettes a day?”), and therefore historians are lucky: historians don’t like to answer these questions and deliberately refuse (“history does not tolerate the subjunctive mood,” remember? ). History finds out whether certain events took place in the past (variations are possible: for example, what motives did people have for doing something). And here historians are out of luck, because this or that set of historical artifacts and documents could appear as a result of various events. Moreover, the number of different interpretations grows when there is less physical evidence. Therefore, in historical works (here, of course, historians would explain better) you can pay attention to the following couple of things. Are all historical evidence (artifacts, documents, eyewitness accounts) mentioned? If not, then there is a high risk that the author is trying to pull facts into his statement, deliberately ignoring some of the information. Are alternative explanations listed? And more specific is better. A phrase like “official science” is a very bad sign (excuse me, which alternative statement are you trying to reject?). Are alternative hypotheses truly rejected? For example, the phrase “if the statements of official science are true, then we cannot possibly observe phenomenon A” is not a refutation; a refutation is “if the statements of official science are true, then we should review phenomenon B, because BLABLABLAH, but in fact, we are reviewing phenomenon A.”
To begin with, if such a question is raised, let’s assume that you were unable to “catch” errors, logical contradictions, and inconsistencies (including with other theories).
The lion's share of friarism and all sorts of charlatans can usually be cut off by the criterion of falsifiability (or Popper's criterion), but explaining how to use it within the framework of this answer would be stressful and long, so if you are really interested, I suggest you google it. (Even though I myself understand how it’s not a good idea to go Google to answer a question)
Also, if we take into account the purposes for which any pseudoscientific dregs are spread, we can note a number of indirect signs with which it reveals itself and which are not at all characteristic of science. This allows you to make some decisions based on “how” the theory is presented, and not on its essence. (if you have enough knowledge to understand the essence, the following is not necessary)
1) As a rule, all sorts of freaks turn not to the scientific community, but to the “respectable public.” Whereas scientists always strive to convince only other scientists that they are right, and they do not need “support from fans.” In general, if there are doubts and you see that the text is addressed not to scientists, but to the people, this is a reason to doubt it even more.
2) Almost always, any anti-scientific graphomania and theories are presented using various polemical techniques, the so-called “demagogue’s rules,” involving oratory skills. Real scientific research is dry, written in clear scientific language, which is characterized not only by the use of terms, but by a unique way of presenting information.
For example, very often, after presenting various facts, among which there may be real facts, you are asked to form your own opinion. Such veiled flattery supposedly hints that you already have sufficient knowledge to reach the conclusion desired by the author.
3) it is often noticeable that the established terms are used too freely. Which, not infrequently, a “pseudo-scientist” cannot give a definition or the context of use of the term contradicts the definition.
4) Without a conspiracy theory, all sorts of global behind-the-scenes, it will not be possible to explain why all other scientists are mistaken. Also, the use of the phrases “conservative science”, “official science” and the like does not inspire confidence. In science there is simply no one to develop an “official” opinion, much less impose it. Scientists live in different states at war with each other, work for changing governments or commercial organizations, profess (in cases where they profess) all existing religions, including Jediism, and adhere to different political views. The scientific community is generally devoid of solidarity, but on the contrary, is imbued with the spirit of competition, both in personal and national competitions. This is a completely unsuitable environment for a “world conspiracy.” Only with a smile can one read about certain “forbidden” discoveries that pose a threat to established ideas and are therefore hidden from the public. (True, there was still one exception to this rule - the doctor who tried to convince his colleagues that they should wash their hands before childbirth, especially after they were picking around all sorts of insides in the morgue, turned out to be damn right, although he ended up in a mental hospital for it. But he is the only one, and the methods of science have changed significantly since then, and, again, he wanted to convince other doctors, not random people, society)
4) Substitution of evidence for a theory with criticism of another (so-called “official”) theory. If there is such a opposition, this is a bad sign. (although if you look at it, it tells you that you don’t need to read further).
5) selectivity to facts. Only those that cannot (or supposedly cannot) be explained by science/another theory and which can be explained by this theory in 2 counts are selected. In addition, in science, the inability of a theory to explain a fact may also indicate incompleteness or limitations of the conditions for applying the theory, in addition to possible error. In pseudoscience, everything is usually clear.
6) scientific theory explains the phenomena under study in already known concepts in such a way that these explanations have at least some “predictive power”, so that from this explanation we learn at least something new, and do not explain 1 unknown by 2 unknowns.
7) references to authority. True, this does not yet apply to some humanities, unfortunately. In real scientific works, as a rule, there is no reference to authority. It doesn’t matter what Einstein or academician Vasya said. What matters is that they proved it. At the same time, if he has proven it, it doesn’t matter whether he’s an academician at all. Of course, indicating the author of the quotation and links to sources are mandatory in scientific work, but these are measures against plagiarism, and a link to authority is “since Academician Vasya said it, it means it’s true”
Hmm, that’s a lot of “letters”, not concise, but still not enough.
Reasons for the popularity of pseudoscientific theories consist, on the one hand, in the general crisis of modern culture and the search for new values, and on the other, in man’s attraction to miracles. More diverse are the personal reasons that force a person to engage in pseudoscience: the desire for fame or money, sincere delusion or an order. Based on this, the following definition can be given.
Pseudoscience is the falsification of scientific data for political, religious, economic or personal purposes.
Pseudoscience uses scientific terminology in its constructions, acts on behalf of various organizations and “academies,” disguises its activities with academic degrees and titles, widely uses mass media and government agencies, and carries out extensive publishing activities. Therefore, it is often difficult for a person (even a specialist) to find criteria for distinguishing pseudoscience from real science. Nevertheless, some general indicators of pseudoscience can be identified.
Usually unscientific:
- concepts aimed at denying all previous science. As a rule, even the most "crazy" concept, if true, is consistent with a number of laws and previously confirmed fundamental principles. For example, Einstein's theory of relativity did not abolish Newtonian mechanics, but only limited it to certain conditions;
- universal and global theories- from a new theory of the structure of the Universe to the invention of a “cure for all diseases.” In an age of constantly increasing amounts of information, it is difficult to be an expert in all areas and take into account all the factors necessary for a global “theory of everything”; Such theories are contradicted by the increasingly realized complexity of the world. Such ideas are also usually characterized by excessive pathos and self-congratulation;
- theories characterized by vagueness and incomprehensibility of evidence. The most complex scientific theories can be explained in simple terms; if concepts are fundamentally undefinable, then most likely such vagueness masks the lack of evidence base;
- unsystematic and internally contradictory theories, which indicates the illiteracy of the author. The opposite is also true: illiterate work is usually meaningless;
- theories in which scientific terms and concepts from the sphere of mysticism are mixed (for example, “karma”, “grace”, “cosmic vibrations”, etc.) or ordinary concepts are given a “secret” meaning (Light, Origin, Mind, Nature, etc.) .d.);
- untestable theories, because they are based on irrational faith. For example, references to cosmic intelligence, the harmony of the universe, or revelation are not scientifically verifiable.
Proponents of pseudoscience often put forward new hypotheses not to gain new knowledge, but to provide additional support for their theories.
Creationists(supporters of the concept according to which the world was created by God) adjust their hypothesis every time science finds another refutation of the concept of the divine creation of the world. For example, the findings of paleontologists support the theory of evolution: the occurrence of fossils shows a sequence of species that succeeded each other over millions of years. Creationists have responded by theorizing that the fossils represent the remains of animals that died during the Flood, and that large, heavy bones (particularly dinosaur bones) are in lower layers because their weight sank deeper into the mud during the flood. .
In response to evidence that the Universe began more than 10 billion years ago (according to the creation hypothesis, the world is only 6-10 thousand years old), creationists respond that time is not something constant: it can slow down or speed up at divine command.
In general, if all the efforts of supporters of any ideas are aimed at defending theory rather than searching for new knowledge, this can serve as an indicator of the unscientific nature of the idea (often all subsequent activities of the “creators” of such an idea come down to constant justification of ideas or complaints about persecution by official science).
Real science has predictive power, i.e. capable of predicting new phenomena, and not just explaining long-known ones.
The presented indicators of pseudoscience are rather arbitrary and are not correct in all cases. A scientist can indeed come up with a new general theory, he can be unfairly persecuted, etc. But if his theory corresponds to several of the given indicators at once, then its scientific nature is more than doubtful.
Pseudoscience is usually is drawn up in the form esotericism, mysticism, sectarianism, falsifications and speculation, information and political orders, etc. She is rarely harmless: almost all of its forms have a negative impact on. Therefore, tolerance towards it should not extend to too wide limits: the mental health of society, undermined by faith in pseudoscience, is no less important for the future than physical health.
While the Svidomo dog krev nurtures everyday fascism and jumps into the abyss, let’s return to our sheep and continue to throw rotten tripe of pseudoscientific nonsense onto the fan.
Let's cleanse karma, Dear Comrades!
In parallel with science, many teachings developed, ostensibly based on scientific methodology, but in fact only imitating a professional approach. They often offer simple solutions to problems, the serious study of which requires special professional training, are uncritical of their own theories and place too much faith in random coincidences. “Theories and Practices” compiled a list of the most famous pseudosciences - from phrenology to socionics - and remembered why they never managed to earn the trust of scientists.
Astrology
Predicting the future, guided by the movements of planets and stars, began in ancient times - the first evidence of attempts to find out the future is found in Sumerian-Babylonian myths, where celestial bodies are identified with gods. Greek astrology adopted the idea of a "divine" star essence and developed it into the forms we are familiar with. The most significant phenomenon of astrology today is horoscopes, which are compiled based on the individual influence of the planets for the 12 zodiac signs.
The methodology of astronomy is incompatible with modern scientific methodology, which has been repeatedly proven by scientists. Textbook examples of evidence are the debunking of Michel Gauquelin’s statistical hypothesis, called the “Mars effect,” and Bertram Forer’s experiment called the “Barnum Effect.” Gauquelin discovered a relationship between the birth of champion athletes and the phases of Mars, and for a long time insisted on the veracity of the results of his research, until he was caught falsifying the original statistical data. In turn, Forer proved the inconsistency of astrology with the help of a social experiment: having given students a test to determine the specific traits of their personality, he promised to provide an individual psychological portrait of each on its basis, but instead gave everyone a uniform description drawn up on the principle of a horoscope. Most students appreciated their “personalized” description and were satisfied with the professor's efforts.
However, despite numerous arguments in favor of recognizing astrology as a pseudoscience, horoscopes continue to be updated daily, some people continue to believe in the existence of the mythical planet Nibiru, which is capable of destroying the Earth, and the “Flat Earth Society” (according to the postulates of which Antarctica is just an ice wall encircling the world , and photographs of the Earth from space are fakes) has not yet collapsed, so astrology, while remaining a pseudoscience in certain circles, is generally thriving.
Phrenology
Pseudoscience, which became widespread at the beginning of the 19th century thanks to the research of the Austrian physician and anatomist F.J. Gall, who established a connection between the mental portrait of a person and the physical characteristics of the skull. Gall believed that any internal changes in the brain, especially changes in the volume of its hemispheres, provoke visible changes in the corresponding parts of the skull, and therefore one can judge the development or underdevelopment of a person and the presence of certain skills, abilities and personal characteristics.
Phrenology is familiar to moviegoers thanks to Quentin Tarantino’s film “Django Unchained,” where the slave owner Candy is fond of comparing the skulls of representatives of different races. This detail is historically determined - many American slave owners really became interested in phrenology in the 19th century and carried out cruel experiments on their slaves. The debunking of phrenology occurred along with the development of neurophysiology, which scientifically proved that the characteristics of the psyche do not depend on the topography of the brain, and even more so on the structure of the skull.
Homeopathy
A pseudo-medical direction in science that calls for taking special homeopathic medicines to prevent the development of diseases in the future. The founder of the direction is the German doctor Christian Hahnemann, who at the end of the 18th century developed an entire system of treatment with homeopathy (he also put forward the so-called “coffee theory of diseases”, according to which almost all diseases known to people are provoked exclusively by drinking coffee). Homeopathy is based on the principle “like cures like”, which is contrary to modern rational pharmacotherapeutic medicine; therefore, a medicine in homeopathy, in fact, is a catalyst for the development of a milder form of the disease for which the patient is going to be treated. All supposedly effective drugs are diluted in at least twelvefold concentration and, according to the scientific community, are no different from a placebo - a substance that does not contain medicinal properties. At the very least, most studies have not confirmed the effectiveness of homeopathic medicines.
Parapsychology
Parapsychology studies supernatural phenomena such as telepathy, telekinesis, clairvoyance, teleportation and suggestion. This parascience is trying to convince the public that it is possible to move through time and space, and people endowed with special talents can predict the future, as well as control others with the power of thought. Calling for belief in astral duality, near-death experiences and reincarnation, parapsychologists conduct many experiments and experiments to prove that superhuman capabilities exist.
Telepathy, for example, was for some time explained by scientists using the “wave theory,” which reported the presence of special waves that, when captured by a person, could evoke in him a certain image similar to the image that arose in another person, but this theory did not was proven and found untenable. In the 1930s, a dice player was tested for superpowers by claiming that he could use his mind to arrange the dice to show the desired total, but more than 650,000 dice rolls disproved his claim, establishing that the matches were purely random. Uri Geller, known for his ability to change the physical form of material objects at a distance, also failed to establish the triumph of anomalous abilities. He was even caught in the fact that he had previously treated his fingers with a special chemical composition, which allowed him to bend spoons only by touching them.
Scientist Ian Stevenson tried to study reincarnation for 40 years, studying 3,000 cases of supposed rebirth, comparing moles and birth defects of children and deceased people who had moles and scars in the same places. He failed to scientifically prove the fact of reincarnation. In the same way, not a single extraordinary phenomenon has yet been scientifically proven, and the constant emergence of information about new phenomena of parapsychology occurs only because a certain percentage of the planet's population has not yet lost faith in paranormal phenomena.
Ufology
Parascience, mainly studying UFOs, as well as recorded facts and future possibilities of communication between the inhabitants of the Earth and aliens and extraterrestrials, poltergeists and ghosts. The main subject of study of ufology is paleocontacts - contacts of creatures of extraterrestrial origin with earthlings and even their visits to our planet in the past. As proof of the validity of the theory of paleocontact, ufologists cite signs left by aliens on the earth - crop circles, unidentified floating objects and other very dubious artifacts. As a science, ufology began only in the 1940s, when the first evidence of “flying saucers” moving at supersonic speeds began to arrive. Such statements were initially taken seriously even by the heads of many states, who immediately created special secret projects to study the phenomenon. In the USA - the "Sign" project and the "Blue Book" project, in Britain - "Room 801", in France - GEPAN. However, over the years of research, it was not possible to confirm the main fear of ufologists that the Earth is under the surveillance of other creatures.
Numerology
Parascientific teaching about the mystical meaning of numbers and their influence on people's lives. Numerology received its impetus many centuries ago thanks to the Hebrew alphabet, in which letters were also used to write numbers, which is why they had their own numerical values. The founder of the main principles of numerology is considered to be the philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras, who discovered the relationship between numbers and notes. After his discovery, he established the GDZ in 6th grade Mathematics, any subject and any phenomenon of reality can be expressed by numbers.
In numerology, any multi-digit number can be reduced to a single-digit number with its own characteristics by adding its components.
Letters also have an individual numerical equivalent, so numerology willingly reveals the “secrets of names” to everyone. The number makes it possible to unravel the weaknesses and strengths of a person under its influence, predict the future and describe the patterns of his life. The multiple number of numerological tables and the presence of various tactics for adding numbers does not allow us to come to a unified interpretation of numbers, which is always emphasized by opponents of the spread of numerology. Another compelling argument for those who doubt this parascience is related to women's surnames. If just yesterday a girl was, for example, “Anna Alekseevna Belousova” and her destiny number was considered to be “13,” and today she married a Spaniard and became, say, “Anna Alekseevna Mares,” then her destiny number is no longer “13.” ", and "1".
Cryptozoology and cryptobotany
Related disciplines involved in the search for animals and plants known to us only from legends, myths and eyewitness accounts, as well as the search for animals and plants that, according to scientists, are considered extinct. Cryptozoologists don't limit themselves to finding dinosaurs, dragons and unicorns; they also study creatures from more modern legends - Bigfoot and the Loch Ness Monster. Scientists themselves involved in cryptozoology or cryptobotany recognize it as pseudoscience, but still consider it a useful discipline and continue to search for lake demons (Ogopogo) and vampire goats (Chupacabra).
Palmistry
A non-scientific method of establishing the relationship between the lines on a person’s palm and his destiny. Palmistry examines the skin texture of the palms, especially the papillary lines - it is believed that each of the lines is responsible for some direction in a person’s life, and by studying its pattern, one can predict the success of a person’s fate in a particular area. The patterns on the palms, the shape of the palm and fingers allow you to understand the inner world: the thumb and the line extending from it is the line of life, the index finger corresponds to the line of the heart, the middle finger - the line of fate, the ring finger - the line of happiness. Additional lines, such as the marriage line and the line of descent, can be used to determine the success of the marriage and the number of children.
However, in numerous manuals on palmistry, the same signs on the palms are explained in different ways, and for predictions it is proposed to use either the left or the right palm, the patterns on which are most often contradictory. Palmistry is not recognized as a science in most countries, but in some it is still considered a serious activity: for example, the National Indian University still teaches palmistry today, and in Canada there is a “National Academy of Palmistry”. In contrast to palmistry, a science is actively developing that seriously studies the skin of the palms and makes it possible to determine the predisposition to hereditary diseases - dermatoglyphics.
Socionics
Pseudoscience, built on the basis of Jung’s teachings about typology and archetypes, offering the opportunity, based on a certain test methodology, to identify for each person his personal so-called type of “information metabolism” - the process of exchanging individual signals with the outside world - and classify it as one of 16 described in detail sociotypes. Socionics as a separate doctrine arose in the 1970s thanks to the efforts of the Lithuanian economist and psychologist Aushura Augustinaviciute. The key parameters for determining the type of information metabolism are “sensing”, “thinking”, “intuition”, “feeling” (in the physical sense of the word), “introversion” and “extroversion”: in different combinations they form different socionic personality types. Based on the results of the socionic test (it exists in several versions from different authors), each person is conditionally identified with one of 16 characters named after famous people and literary heroes (for example, Don Quixote, Dumas, Stirlitz or Napoleon) and gets the opportunity to find out about their compatibility with other sociotypes.
Socionics is known mainly in the post-Soviet space and is not considered an official science - it has neither a general scientific theory nor established uniform research methods. It has also been criticized for being too speculative and lacking empirical evidence. In addition, the concept was greatly discredited by crowds of enthusiasts who immediately began to determine the socionic types of strangers, already dead people and even entire countries - while the founders of socionics emphasized that they did not claim to create a universal psychological classification for all occasions.
Physiognomy
An alternative direction in science that tries to prove the connection between a person’s external appearance and his character and spiritual qualities. Physiognomy tries to “read” the face, structural features of the body, the meaning of gestures, postures and the general bodily impression that a person makes, as well as determine the level of a person’s intelligence solely by his appearance and demeanor. In eastern countries, physiognomy was not separated from medicine and began to develop even before our era, calling for the study of a person based on the principle of the “five peaks”: forehead, nose, chin, cheekbones. In European culture, science also found support, for example, GDZ Physics 7th grade, Charles Darwin supported the development of physiognomy, believing that by studying the work of an individual’s muscles, one can understand what his main personal inclinations are. Based on the shape of the face, hairline, location and shape of natural facial openings and other reliefs on the face, based on the basics of physiognomy, you can create a basic portrait of a person’s inner world.
The modern scientific community does not believe in the amazing possibilities of physiognomy, especially after studies have been conducted on twins, who, despite their external identity, often have diametrically opposed characters.
Folk history
Predominantly the Russian direction of pseudohistory, which is engaged in reshaping historical realities, most often with the aim of publishing books of mass appeal. Alternative history tends toward fiction and falsifications while apparently preserving the scientific form. The author of a work of folk history pretends that he is revealing a new story to the reader, but in reality he just juggles the facts and, breaking logical connections, creates a “new story” that runs counter to the events that have been established for certain.
Folk history began to actively develop in Russia in the years after the collapse of the USSR, when a single communist ideology ceased to dominate history. The predecessor of the movement is considered to be Lev Gumilyov, who, while offering readers his theory of passionary ethnogenesis, also put forward a very specific “author’s” version of history. .
 Lesson summary on the topic "Distinguish between optically similar letters and acoustically similar sounds M-N"
Lesson summary on the topic "Distinguish between optically similar letters and acoustically similar sounds M-N" Games and exercises for the development of speech breathing Exercises for the development of speech breathing in adults
Games and exercises for the development of speech breathing Exercises for the development of speech breathing in adults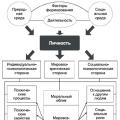 Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of interests
Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of interests