Geological eras and periods of the origin of life. Eras of earth development
The idea that our Earth is many millions of years old is officially taught in our schools and institutes. To confirm this point of view as scientific, a geochronological table is provided with long eras and periods that scientists allegedly calculated by layers sedimentary rocks and their fossils in them. Here's an example lesson:
"Teacher: For many years, geologists, studying rocks, tried to determine the age of the Earth. But until recently they were far from successful. At the beginning of the 17th century, the Archbishop of Armagh, James Ussher, calculated the date of creation of the world from the Bible, and determined it as 4004 BC AD
But he was more than a million times wrong. Today scientists believe that the age of the Earth is 4600 million years. The science that studies the age of the Earth by location rocks, is called geology."
(Geochronological table photo No. 1)
(geochronological table photo No. 2)

Students take this data on faith, trusting the teacher’s word and not checking how true this information is and whether it corresponds to reality. In fact, a lot of scientific evidence has long been known that shows the geochronological table to be invalid. There are scientists who have a different point of view on periods of the history of our Earth. For example, Walker's Geological Model modified by Klevberg:
(Geochronological table photo No. 3)

I think that every person, whether he is a student or a teacher, should thoroughly double-check the official data that he receives and form his own beliefs, based not on preconceived guesses, but on scientific research. To figure out which scientists' hypotheses are closer to the truth and which are not, read articles with a different point of view on the geochronological table than the official point of view taught in educational institutions.
Hello! In this article I want to tell you about the geochronological column. This is a column of periods of the Earth's development. And also in more detail about each era, thanks to which you can paint a picture of the formation of the Earth throughout its history. What types of life appeared first, how they changed, and how much it took.
The geological history of the Earth is divided into large intervals - eras, eras are divided into periods, periods are divided into epochs. This division was associated with events that took place on. Changes in the abiotic environment influenced the evolution of the organic world on Earth.
Geological eras of the Earth, or geochronological scale:

And now about everything in more detail:
Designations:
Eras;
Periods;
Epochs.
1. Catarchaean era (from the creation of the Earth, about 5 billion years ago, to the origin of life);
2. Archean era , the most ancient era(3.5 billion – 1.9 billion years ago);
3. Proterozoic era (1.9 billion – 570 million years ago);
The Archean and Proterozoic are still combined into the Precambrian. Precambrian covers the largest part geological time. Areas of land and sea were formed, and active volcanic activity occurred. Shields of all continents were formed from Precambrian rocks. Traces of life are usually rare.
4. Palaeozoic (570 million - 225 million years ago) with such periods :
Cambrian period (from the Latin name for Wales)(570 million – 480 million years ago);
The transition to the Cambrian was marked by the unexpected appearance of a huge number of fossils. This is a sign of the beginning of the Paleozoic era. Marine flora and fauna flourished in numerous shallow seas. Trilobites were especially widespread.
Ordovician period(from the British Ordovician tribe)(480 million – 420 million years ago);
Much of the Earth was soft, and most of the surface was still covered by seas. The accumulation of sedimentary rocks continued, and mountain building occurred. There were reef-formers. There is an abundance of corals, sponges and mollusks.
Silurian (from the British Silure tribe)(420 million – 400 million years ago);
Dramatic events in the history of the Earth began with the development of jawless fish-like fish (the first vertebrates), which appeared in the Ordovician. Another significant event was the appearance of the first land animals in the Late Silurian.
Devonian (from Devonshire in England)(400 million – 320 million years ago);
In the Early Devonian, mountain-building movements reached their peak, but basically it was a period of spasmodic development. The first seed plants settled on land. A large variety and number of fish-like species were noted, and the first terrestrial animals developed. animals- amphibians.
Carboniferous or Carboniferous period (from the abundance of coal in the seams) (320 million – 270 million years ago);
Mountain building, folding, and erosion continued. In North America, swampy forests and river deltas were flooded, and large coal deposits were formed. The southern continents were covered by glaciation. Insects spread rapidly, and the first reptiles appeared.
Permian period (from the Russian city of Perm)(270 million – 225 million years ago);
On a large part of Pangea - the supercontinent that united everything - conditions prevailed. Reptiles spread widely and modern insects evolved. New terrestrial flora developed, including conifers. Several disappeared marine species.
5. Mesozoic era (225 million - 70 million years ago) with such periods:
Triassic (from the tripartite division of the period proposed in Germany)(225 million – 185 million years ago);
With the onset of the Mesozoic era, Pangea began to disintegrate. On land, the dominance of conifers was established. Diversity among reptiles was noted, with the first dinosaurs and giant marine reptiles appearing. Primitive mammals evolved.
Jurassic period(from mountains in Europe)(185 million – 140 million years ago);
Significant volcanic activity was associated with the formation of the Atlantic Ocean. Dinosaurs dominated on land, flying reptiles and primitive birds conquered the air ocean. There are traces of the first flowering plants.
Cretaceous period (from the word "chalk")(140 million – 70 million years ago);
During maximum expansion Cretaceous deposits occurred in the seas, especially in Britain. The dominance of dinosaurs continued until the extinction of them and other species at the end of the period.
6. Cenozoic era (70 million years ago - up to our time) with such periods And epochs:
Paleogene period (70 million – 25 million years ago);
— Paleotse new era(“the oldest part of the new era”)(70 million – 54 million years ago);
— Eocene Epoch ("dawn of a new era")(54 million – 38 million years ago);
— Oligocene Epoch ("not very new")(38 million – 25 million years ago);
Neogene period (25 million - 1 million years ago);
— Miocene Epoch ("relatively new")(25 million – 8 million years ago);
— Pliocene Epoch ("very recent")(8 million – 1 million years ago);
The Paleocene and Neogene periods are still combined into the Tertiary period. With the onset of the Cenozoic era (new life), mammals began to spread spasmodically. Many have developed large species, although many became extinct. The number of flowering plants has increased sharply plants. As the climate cooled, herbaceous plants appeared. There was a significant uplift of the land.
Quaternary period (1 million – our time);
— Pleistocene epoch (“most recent”)(1 million – 20 thousand years ago);
— Holocene era(“a completely new era”) (20 thousand years ago – our time).
This is the last geological period that includes the present time. Four major glaciations alternated with warming periods. The number of mammals has increased; they have adapted to . The formation of man - the future ruler of the Earth - took place.
There are also other ways of dividing eras, epochs, periods, eons are added to them, and some epochs are still divided, like on this table, for example.
But this table is more complex, the confusing dating of some eras is purely chronological, not based on stratigraphy. Stratigraphy is the science of determining the relative geological age of sedimentary rocks, the division of rock strata, and the correlation of different geological formations.
This division, of course, is relative, since there was no sharp distinction from today to tomorrow in these divisions.
But still, at the turn of neighboring eras and periods, significant geological transformations predominantly took place: processes of mountain formation, redistribution of seas, changing of the climate etc.
Each subsection was, of course, characterized by its unique flora and fauna.
, And You can read it in the same section.
Thus, these are the main eras of the Earth on which all scientists rely 🙂
The history of our planet still holds many mysteries. Scientists from various fields of natural science have contributed to the study of the development of life on Earth.
Our planet is believed to be about 4.54 billion years old. This entire time period is usually divided into two main stages: Phanerozoic and Precambrian. These stages are called eons or eonothema. Eons, in turn, are divided into several periods, each of which is distinguished by a set of changes that occurred in the geological, biological, and atmospheric state of the planet.

- Precambrian, or cryptozoic is an eon (time period in the development of the Earth), covering about 3.8 billion years. That is, the Precambrian is the development of the planet from the moment of formation, the formation of the earth’s crust, the proto-ocean and the emergence of life on Earth. By the end of the Precambrian, highly organized organisms with a developed skeleton were already widespread on the planet.
The eon includes two more eonothems - catarchaean and archaean. The latter, in turn, includes 4 eras.

1. Katarhey- this is the time of the formation of the Earth, but there was no core or crust yet. The planet was still a cold cosmic body. Scientists suggest that during this period there was already water on Earth. The Catarchaean lasted about 600 million years.
2. Archaea covers a period of 1.5 billion years. During this period, there was no oxygen on Earth yet, and deposits of sulfur, iron, graphite, and nickel were being formed. The hydrosphere and atmosphere were a single vapor-gas shell that enveloped the globe in a dense cloud. The sun's rays practically did not penetrate through this curtain, so darkness reigned on the planet. 2.1 2.1. Eoarchaean- This is the first geological era, which lasted about 400 million years. The most important event of the Eoarchean was the formation of the hydrosphere. But there was still little water, the reservoirs existed separately from each other and did not yet merge into the world ocean. At the same time, the earth's crust becomes solid, although asteroids are still bombarding the earth. At the end of the Eoarchean, the first supercontinent in the history of the planet, Vaalbara, formed.
2.2 Paleoarchean- the next era, which also lasted approximately 400 million years. During this period, the Earth's core is formed, tension increases magnetic field. A day on the planet lasted only 15 hours. But the oxygen content in the atmosphere increases due to the activity of emerging bacteria. Remains of these first forms of Paleoarchean life have been found in Western Australia.
2.3 Mesoarchean also lasted about 400 million years. During the Mesoarchean era, our planet was covered by a shallow ocean. The land areas were small volcanic islands. But already during this period the formation of the lithosphere begins and the mechanism of plate tectonics starts. At the end of the Mesoarchean the first glacial period, during which snow and ice first form on Earth. Biological species are still represented by bacteria and microbial life forms.
2.4 Neoarchaean- the final era of the Archean eon, the duration of which is about 300 million years. Colonies of bacteria at this time form the first stromatolites (limestone deposits) on Earth. The most important event of the Neoarchean was the formation of oxygen photosynthesis.

II. Proterozoic- one of the longest time periods in the history of the Earth, which is usually divided into three eras. During the Proterozoic, the ozone layer appears for the first time, and the world ocean reaches almost its modern volume. And after the long Huronian glaciation, the first multicellular life forms appeared on Earth - mushrooms and sponges. The Proterozoic is usually divided into three eras, each of which contained several periods.
3.1 Paleo-Proterozoic- the first era of the Proterozoic, which began 2.5 billion years ago. At this time, the lithosphere is fully formed. But the previous forms of life practically died out due to an increase in oxygen content. This period was called the oxygen catastrophe. By the end of the era, the first eukaryotes appear on Earth.
3.2 Meso-Proterozoic lasted approximately 600 million years. The most important events of this era: the formation of continental masses, the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia and the evolution of sexual reproduction.
3.3 Neo-Proterozoic. During this era, Rodinia breaks up into approximately 8 parts, the superocean of Mirovia ceases to exist, and at the end of the era, the Earth is covered with ice almost to the equator. In the Neoproterozoic era, living organisms for the first time begin to acquire a hard shell, which will later serve as the basis of the skeleton.

III. Paleozoic- the first era of the Phanerozoic eon, which began approximately 541 million years ago and lasted about 289 million years. This is the era of emergence ancient life. The supercontinent Gondwana unites southern continents, a little later the rest of the land joins it and Pangea appears. Begin to form climatic zones, and the flora and fauna are represented mainly by marine species. Only towards the end of the Paleozoic did land development begin and the first vertebrates appeared.
The Paleozoic era is conventionally divided into 6 periods.
1. Cambrian period lasted 56 million years. During this period, the main rocks are formed, and a mineral skeleton appears in living organisms. And the most important event of the Cambrian is the emergence of the first arthropods.
2. Ordovician period- the second period of the Paleozoic, which lasted 42 million years. This is the era of the formation of sedimentary rocks, phosphorites and oil shale. Organic world The Ordovician is represented by marine invertebrates and blue-green algae.
3. Silurian period covers the next 24 million years. At this time, almost 60% of living organisms that existed before die out. But the first cartilaginous and bony fishes in the history of the planet appear. On land, the Silurian is marked by the appearance of vascular plants. Supercontinents are moving closer together and forming Laurasia. By the end of the period, ice melted, sea levels rose, and the climate became milder.

4. Devonian period characterized by the rapid development of various forms of life and the development of new ecological niches. The Devonian covers a time period of 60 million years. The first terrestrial vertebrates, spiders, and insects appear. Sushi animals develop lungs. Although, fish still predominate. The flora kingdom of this period is represented by propferns, horsetails, mosses and gosperms.
5. Carboniferous period often called carbon. At this time, Laurasia collides with Gondwana and a new supercontinent Pangea appears. A new ocean is also formed - Tethys. This is the time of the appearance of the first amphibians and reptiles.

6. Permian period- the last period of the Paleozoic, ending 252 million years ago. It is believed that at this time a large asteroid fell on Earth, which led to significant climate change and the extinction of almost 90% of all living organisms. Most of the land is covered with sand, the most extensive deserts appear that have ever existed in the entire history of the development of the Earth.

IV. Mesozoic- the second era of the Phanerozoic eon, which lasted almost 186 million years. At this time, the continents acquired almost modern outlines. A warm climate contributes to the rapid development of life on Earth. Giant ferns are disappearing and are being replaced by angiosperms. The Mesozoic is the era of dinosaurs and the appearance of the first mammals.
The Mesozoic era is divided into three periods: Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous.
1. Triassic period lasted just over 50 million years. At this time, Pangea begins to break apart, and the internal seas gradually become smaller and dry out. The climate is mild, the zones are not clearly defined. Almost half of the land's plants are disappearing as deserts spread. And in the kingdom of fauna the first warm-blooded and land reptiles appeared, which became the ancestors of dinosaurs and birds.

2. Jurassic covers a span of 56 million years. The Earth had a humid and warm climate. The land is covered with thickets of ferns, pines, palms, and cypresses. Dinosaurs reign on the planet, and numerous mammals were still distinguished by their small stature and thick hair.

3. Cretaceous period- the longest period of the Mesozoic, lasting almost 79 million years. The split of the continents is almost over, Atlantic Ocean significantly increases in volume, ice covers form at the poles. Increase water mass oceans leads to the formation of the greenhouse effect. At the end of the Cretaceous period, a catastrophe occurs, the causes of which are still not clear. As a result, all dinosaurs and most species of reptiles became extinct and gymnosperms.

V. Cenozoic- this is the era of animals and homo sapiens, which began 66 million years ago. At this time, the continents acquired their modern shape, Antarctica occupied the south pole of the Earth, and the oceans continued to expand. Plants and animals that survived the disaster of the Cretaceous period found themselves in a completely new world. Unique communities of life forms began to form on each continent.
The Cenozoic era is divided into three periods: Paleogene, Neogene and Quaternary.

1. Paleogene period ended approximately 23 million years ago. At this time, a tropical climate reigned on Earth, Europe was hidden under evergreen tropical forests, only deciduous trees grew in the north of the continents. It was during the Paleogene period that mammals developed rapidly.

2. Neogene period covers the next 20 million years of the planet's development. Whales and bats appear. And, although saber-toothed tigers and mastodons still roam the earth, the fauna is increasingly acquiring modern features.

3. Quaternary period began more than 2.5 million years ago and continues to this day. Two major events characterize this time period: the Ice Age and the emergence of man. The Ice Age completely completed the formation of the climate, flora and fauna of the continents. And the appearance of man marked the beginning of civilization.
According to modern ideas, has an age of 4.5 - 5 billion years. In the history of its occurrence, planetary and geological stages are distinguished.
Geological stage- sequence of events in the development of the Earth as planets since the formation of the earth's crust. During it, relief forms arose and were destroyed, the land submerged under water (the advance of the sea), the retreat of the sea, glaciations, the appearance and disappearance of various types animals and plants, etc.
Scientists, trying to reconstruct the history of the planet, study rock layers. They divide all deposits into 5 groups, distinguishing the following eras: Archean (ancient), Proterozoic (early), Paleozoic (ancient), Mesozoic (middle) and Cenozoic (new). The border between eras passes through the largest evolutionary events. The last three eras are divided into periods, since in these deposits the remains of animals and plant remains were better preserved and in greater quantity.
Each era is characterized by events that have had decisive influence to modern relief.
Archean era was distinguished by violent volcanic activity, as a result of which igneous granite-containing rocks appeared on the surface of the Earth - the basis of future continents. At that time, the Earth was inhabited only by microorganisms that could live without oxygen. It is believed that the deposits of that era are covered with an almost continuous shield separate areas sushi, they contain a lot of iron, gold, silver, platinum and ores of other metals.
IN Proterozoic era Volcanic activity was also high, and mountains of the so-called Baikal fold were formed. They have practically not been preserved and now represent only isolated small uplifts on the plains. During this period, the planet was inhabited by blue-green algae and protozoan microorganisms, and the first multicellular organisms arose. Proterozoic rock layers are rich in minerals: iron ores and ores of non-ferrous metals, mica.
At first Paleozoic era formed mountains Caledonian folding, which led to the reduction of sea basins and the emergence of large areas of land. Only isolated ridges of the Urals, Arabia, Southeast China and Central Europe. All these mountains are low, “worn out”. In the second half of the Paleozoic, the mountains of the Hercynian fold were formed. This era of mountain building was more powerful; vast mountain ranges arose in Western Siberia and the Urals, Mongolia and Manchuria, most of Central Europe, the eastern coast of North America and Australia. Now they are represented by low blocky mountains. In the Paleozoic era, the Earth was inhabited by fish, amphibians and reptiles, and algae predominated among the vegetation. The main deposits of oil and coal arose during this period.
Mesozoic era began with a period of relative calm internal forces Earth, the gradual destruction of previously created mountain systems and the immersion of flattened plain areas, for example, most of Western Siberia. Mountains formed in the second half of the era Mesozoic folding. At this time, vast mountainous countries appeared, which even now have the appearance of mountains. These are the Cordillera mountains Eastern Siberia, certain areas of Tibet and Indochina. The ground was covered with lush vegetation, which gradually died and rotted. In a hot and humid climate, swamps and peat bogs were actively formed. This was the age of the dinosaurs. Giant predatory and herbivorous animals have spread throughout almost the entire planet. The first mammals appeared at this time.
Cenozoic era continues to this day. Its beginning was marked by an increase in the activity of the Earth's internal forces, which led to a general rise of the surface. During the era of Alpine folding, young folded mountains arose within the Alpine-Himalayan belt and the continent of Eurasia acquired its modern shape. In addition, there was a rejuvenation of the ancient mountain ranges of the Urals, Appalachians, Tien Shan, and Altai. The climate on the planet changed sharply, and a period of powerful ice sheets began. The cover glaciers advancing from the north changed the relief of the continents of the Northern Hemisphere, forming rolling plains with a lot of lakes.
All geological history The Earth can be traced on a geochronological scale - a table of geological time, showing the sequence and subordination of the main stages of geology, the history of the Earth and the development of life on it (see Table 4 on pp. 46-49). The geochronological table should be read from bottom to top.
Questions and tasks to prepare for the exam
1. Explain why they are observed on Earth polar days and nights.
2. What would conditions be like on Earth if its axis of rotation were not inclined to the orbital plane?
3. The change of seasons on Earth is determined by two main reasons: the first is the rotation of the Earth around the Sun; name the second one.
4. How many times a year and when is the Sun at its zenith above the equator? Over the Northern Tropic? Over the South Tropic?
5. In what direction do constant winds and sea currents moving in the meridional direction deviate in the Northern Hemisphere?
6. When is the shortest night in the Northern Hemisphere?
7. What are the characteristics of the days of the spring and autumn equinoxes on Earth? When do they occur in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres?
8. When are the days of summer and winter solstice in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres?
9. In what light zones is the territory of our country located?
10. List geological periods Cenozoic era, starting from the most ancient.
Table 4
| Eras (duration - in million years) | Periods (duration in million years) | Major events history of the earth | Characteristic minerals formed in given time |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Cenozoic 70 million years | Quaternary 2 Ma (Q) | General rise of land. Repeated glaciations, especially in the Northern Hemisphere. The emergence of man | Peat, placer deposits of gold, diamonds, precious stones |
| Neogene 25 Ma (N) | The emergence of young mountains in areas of Alpine folding. Rejuvenation of mountains in areas of all ancient folds. Dominance of flowering plants | Brown coals, oil, amber | |
| Paleogene 41 Ma (P) | Destruction of the mountains of Mesozoic folding. Widespread development of flowering plants, birds and mammals | Phosphorites, brown coals, bauxites |
| Mesozoic 165 Ma | Cretaceous 70 Ma (K) | The emergence of young mountains in areas of Mesozoic folding. Extinction of giant reptiles (dinosaurs). Development of birds and mammals | Oil, oil shale, chalk, coal, phosphorites |
| Jurassic 50 Ma (J) | Formation of modern oceans. Hot and humid climate over most of the land. The rise of giant reptiles (dinosaurs). Dominance of gymnosperms | Hard coals, oil, phosphorites | |
| Triassic 40 Ma (T) | The greatest retreat of the sea and rise of land in the entire history of the Earth. Destruction of the mountains of the Caledonian and Hercynian folds. Vast deserts. First mammals | Rock salts | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Paleozoic 330 million years | Permian 45 Ma (P) | The emergence of young folded mountains in the areas of the Hercynian fold. Dry climate over most of the land. The emergence of gymnosperms | Rock and potassium salts, gypsum |
| Carboniferous 65 Ma (C) | Hot and humid climate over most of the land. Wide use marshy lowlands in coastal areas. Forests of tree ferns. The first reptiles, the rise of amphibians | Coal, oil | |
| Devonian 55 Ma (r) | Hot climate over most of the land. The first deserts. The appearance of amphibians. Numerous fish | Salts, oil | |
| Silurian 35 Ma (S) | The emergence of young folded mountains in the areas of the Caledonian folding. First land plants(moss mosses and ferns) | |
| | Ordovician 60 Ma (O) | Reducing the area of sea basins. Appearance of the first terrestrial invertebrates | |
| Cambrian 70 Ma | The emergence of young mountains in the areas of the Baikal fold. Flooding of vast areas by seas. The flourishing of marine invertebrates | Rock salt, gypsum, phosphorites | |
| Proterozoic era 600 million years | The beginning of the Baikal folding. Powerful volcanism. Development of bacteria and blue-green algae | Iron ores, mica, graphite | |
| Archean era 900 million years | Formation of the continental crust. Intense volcanic activity. The time of primitive single-celled bacteria | Ore | |
Maksakovsky V.P., Petrova N.N., Physical and economic geography of the world. - M.: Iris-press, 2010. - 368 pp.: ill.
Lesson content lesson notes supporting frame lesson presentation acceleration methods interactive technologies Practice tasks and exercises self-test workshops, trainings, cases, quests homework discussion questions rhetorical questions from students Illustrations audio, video clips and multimedia photographs, pictures, graphics, tables, diagrams, humor, anecdotes, jokes, comics, parables, sayings, crosswords, quotes Add-ons abstracts articles tricks for the curious cribs textbooks basic and additional dictionary of terms other Improving textbooks and lessonscorrecting errors in the textbook updating a fragment in a textbook, elements of innovation in the lesson, replacing outdated knowledge with new ones Only for teachers perfect lessons calendar plan for a year guidelines discussion programs Integrated LessonsWe present to your attention an article about the classical understanding of the development of our planet Earth, written in a fun, understandable and not too long way..... If any of the people mature age I forgot - it will be interesting to read, well, for those who are younger, and generally excellent material for an essay.
In the beginning there was nothing. In the endless space there was only a giant cloud of dust and gases. It can be assumed that from time to time through this substance enormous speed rushed by spaceships with representatives of the universal mind. The humanoids looked boredly out the windows and did not even remotely realize that in a few billion years intelligence and life would arise in these places.
The gas and dust cloud transformed over time into solar system. And after the star appeared, the planets appeared. One of them was ours motherland. This happened 4.5 billion years ago. It is from those distant times that the age of the blue planet is counted, thanks to which we exist in this world.
The entire history of the Earth is divided into two huge stages.
- The first stage is characterized by the absence of complex living organisms. There were only single-celled bacteria that settled on our planet about 3.5 billion years ago.
- The second stage began approximately 540 million years ago. This is the time when living multicellular organisms spread across the Earth. This refers to both plants and animals. Moreover, both seas and land became their habitat. The second period continues to this day, and its crown is man.
Such huge time stages are called eons. Each eon has its own eonothema. The latter represents a certain stage of the geological development of the planet, which is radically different from other stages in the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. That is, each eonoteme is strictly specific and not similar to others.
There are 4 eons in total. Each of them, in turn, is divided into eras of the Earth’s development, and those are divided into periods. From this it is clear that there is a strict gradation of large time intervals, and the basis is taken geological development planets.
Katarhey
The oldest eon is called Katarchean. It began 4.6 billion years ago and ended 4 billion years ago. Thus, its duration was 600 million years. Time is very ancient, so it was not divided into eras or periods. At the time of the Katarchaean there was neither the earth's crust nor the core. The planet was a cold cosmic body. The temperature in its depths corresponded to the melting point of the substance. From above, the surface was covered with regolith, like the lunar surface in our time. The relief was almost flat due to constant powerful earthquakes. Naturally, there was no atmosphere or oxygen.
Archaea
The second eon is called Archean. It began 4 billion years ago and ended 2.5 billion years ago. Thus, it lasted 1.5 billion years. It is divided into 4 eras:
- Eoarchaean
- paleoarchean
- mesoarchaean
- neoarchaean
Eoarchaean(4–3.6 billion years) lasted 400 million years. This is the period of formation of the earth's crust. A huge number of meteorites fell on the planet. This is the so-called Late Heavy Bombardment. It was at that time that the formation of the hydrosphere began. Water appeared on Earth. IN large quantities it could have been carried by comets. But the oceans were still far away. There were separate reservoirs, and the temperature in them reached 90° Celsius. The atmosphere was characterized by a high content of carbon dioxide and a low content of nitrogen. There was no oxygen. At the end of this era of Earth's development, the first supercontinent of Vaalbara began to form.
Paleoarchaean(3.6–3.2 billion years) lasted 400 million years. During this era, the formation of the solid core of the Earth was completed. A strong magnetic field appeared. His tension was half the current one. Consequently, the surface of the planet received protection from solar wind. This period also saw primitive forms of life in the form of bacteria. Their remains, which are 3.46 billion years old, were discovered in Australia. Accordingly, the oxygen content in the atmosphere began to increase, due to the activity of living organisms. The formation of Vaalbar continued.
Mesoarchean(3.2–2.8 billion years) lasted 400 million years. The most remarkable thing about it was the existence of cyanobacteria. They are capable of photosynthesis and produce oxygen. The formation of the supercontinent has completed. By the end of the era it had split. There was also a fall huge asteroid. The crater from it still exists in Greenland.
Neoarchaean(2.8–2.5 billion years) lasted 300 million years. This is the time of formation of the present earth's crust - tectogenesis. Bacteria continued to develop. Traces of their life were found in stromatolites, whose age is estimated at 2.7 billion years. These lime deposits were formed by huge colonies of bacteria. They were found in Australia and South Africa. Photosynthesis continued to improve.
With the end of the Archean era, the Earth's era continued in the Proterozoic eon. This is a period of 2.5 billion years - 540 million years ago. It is the longest of all the eons on the planet.
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic is divided into 3 eras. The first one is called Paleoproterozoic(2.5–1.6 billion years). It lasted 900 million years. This huge time interval is divided into 4 periods:
- siderian (2.5–2.3 billion years)
- Rhyasian (2.3–2.05 billion years)
- orosirium (2.05–1.8 billion years)
- statherians (1.8–1.6 billion years)
Siderius notable in the first place oxygen catastrophe. It happened 2.4 billion years ago. Characterized by a dramatic change in the Earth's atmosphere. In it in a huge number free oxygen appeared. Before that, the atmosphere was dominated carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, methane and ammonia. But as a result of photosynthesis and extinction volcanic activity at the bottom of the oceans, oxygen filled the entire atmosphere.
Oxygen photosynthesis is characteristic of cyanobacteria, which proliferated on Earth 2.7 billion years ago. Before this, archaebacteria dominated. They did not produce oxygen during photosynthesis. In addition, oxygen was initially consumed in the oxidation of rocks. It accumulated in large quantities only in biocenoses or bacterial mats.
Eventually, a moment came when the surface of the planet became oxidized. And the cyanobacteria continued to release oxygen. And it began to accumulate in the atmosphere. The process accelerated due to the fact that the oceans also stopped absorbing this gas.
As a result, anaerobic organisms died, and they were replaced by aerobic ones, that is, those in which energy synthesis was carried out through free molecular oxygen. The planet was shrouded in the ozone layer and decreased Greenhouse effect. Accordingly, the boundaries of the biosphere expanded, and sedimentary and metamorphic rocks turned out to be completely oxidized.
All these metamorphoses led to Huronian glaciation, which lasted 300 million years. It began in Sideria, and ended at the end of Rhiasia 2 billion years ago. The next period of orosiria is notable for its intense mountain building processes. At this time, 2 huge asteroids fell on the planet. The crater from one is called Vredefort and is located in South Africa. Its diameter reaches 300 km. Second crater Sudbury located in Canada. Its diameter is 250 km.
Last staterian period notable for the formation of the supercontinent Columbia. It includes almost all the continental blocks of the planet. There was a supercontinent 1.8-1.5 billion years ago. At the same time, cells were formed that contained nuclei. That is, eukaryotic cells. This was a very important stage of evolution.
The second era of the Proterozoic is called Mesoproterozoic(1.6–1 billion years). Its duration was 600 million years. It is divided into 3 periods:
- potassium (1.6–1.4 billion years)
- exatium (1.4–1.2 billion years)
- sthenia (1.2–1 billion years).
During such an era of the Earth's development as potassium, the supercontinent Columbia broke up. And during the Exatian era, red multicellular algae appeared. This is indicated by a fossil find on the Canadian island of Somerset. Its age is 1.2 billion years. A new supercontinent, Rodinia, formed in Stenium. It arose 1.1 billion years ago and disintegrated 750 million years ago. Thus, by the end of the Mesoproterozoic there was 1 supercontinent and 1 ocean on Earth, called Mirovia.
The last era of the Proterozoic is called Neoproterozoic(1 billion–540 million years). It includes 3 periods:
- Thonium (1 billion–850 million years)
- Cryogenian (850–635 million years)
- Ediacaran (635–540 million years)
During the Thonian era, the supercontinent Rodinia began to disintegrate. This process ended in cryogeny, and the supercontinent Pannotia began to form from 8 separate pieces of land formed. Cryogeny is also characterized by complete glaciation of the planet (Snowball Earth). The ice reached the equator, and after it retreated, the process of evolution of multicellular organisms sharply accelerated. Last period The Neoproterozoic Ediacaran is notable for the appearance of soft-bodied creatures. These multicellular animals are called Vendobionts. They were branching tubular structures. This ecosystem is considered the oldest.
Life on Earth originated in the ocean
Phanerozoic
Approximately 540 million years ago, the time of the 4th and last eon began - the Phanerozoic. There are 3 very important eras of the Earth. The first one is called Paleozoic(540–252 million years). It lasted 288 million years. Divided into 6 periods:
- Cambrian (540–480 million years)
- Ordovician (485–443 million years)
- Silurian (443–419 million years)
- Devonian (419–350 million years)
- Carboniferous (359–299 million years)
- Permian (299–252 million years)
Cambrian considered to be the lifespan of trilobites. These are marine animals similar to crustaceans. Along with them, jellyfish, sponges and worms lived in the seas. Such an abundance of living beings is called Cambrian explosion. That is, there was nothing like this before and suddenly it suddenly appeared. Most likely, it was in the Cambrian that mineral skeletons began to emerge. Previously, the living world had soft bodies. Naturally, they were not preserved. Therefore, complex multicellular organisms of more ancient eras cannot be detected.
The Paleozoic is notable for the rapid expansion of organisms with hard skeletons. From vertebrates, fish, reptiles and amphibians appeared. IN flora At first algae predominated. During Silurian plants began to colonize the land. At first Devonian The swampy shores are overgrown with primitive flora. These were psilophytes and pteridophytes. Plants reproduced by spores carried by the wind. Plant shoots developed on tuberous or creeping rhizomes.

Plants began to colonize land during the Silurian period
Scorpions and spiders appeared. The dragonfly Meganeura was a real giant. Its wingspan reached 75 cm. Acanthodes are considered the oldest bony fish. They lived during the Silurian period. Their bodies were covered with dense diamond-shaped scales. IN carbon, which is also called the Carboniferous period, a wide variety of vegetation rapidly developed on the shores of lagoons and in countless swamps. It was its remains that served as the basis for the formation of coal.
This time is also characterized by the beginning of the formation of the supercontinent Pangea. It was fully formed during the Permian period. And it broke up 200 million years ago into 2 continents. These are the northern continent of Laurasia and the southern continent of Gondwana. Subsequently, Laurasia split, and Eurasia and North America. And from Gondwana arose South America, Africa, Australia and Antarctica.
On Permian there were frequent climate changes. Dry times alternated with wet ones. At this time, lush vegetation appeared on the banks. Typical plants were cordaites, calamites, tree and seed ferns. Mesosaur lizards appeared in the water. Their length reached 70 cm. But by the end of the Permian period, early reptiles died out and gave way to more developed vertebrates. Thus, in the Paleozoic, life firmly and densely settled on the blue planet.
The following eras of the Earth's development are of particular interest to scientists. 252 million years ago came Mesozoic. It lasted 186 million years and ended 66 million years ago. Consisted of 3 periods:
- Triassic (252–201 million years)
- Jurassic (201–145 million years)
- Cretaceous (145–66 million years)
The boundary between the Permian and Triassic periods is characterized by mass extinction of animals. 96% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrates died. The biosphere was dealt a very strong blow, and it took a very long time to recover. And it all ended with the appearance of dinosaurs, pterosaurs and ichthyosaurs. These sea and land animals were of enormous size.
But the main tectonic event of those years was the collapse of Pangea. A single supercontinent, as already mentioned, was divided into 2 continents, and then broke up into the continents that we know now. The Indian subcontinent also broke away. It subsequently connected with the Asian plate, but the collision was so violent that the Himalayas emerged.

This is what nature was like in the early Cretaceous period
The Mesozoic is notable for being considered the warmest period of the Phanerozoic eon.. This time global warming. It began in the Triassic and ended at the end of the Cretaceous. For 180 million years, even in the Arctic there were no stable pack glaciers. Heat spread evenly across the planet. At the equator average annual temperature corresponded to 25-30° Celsius. For circumpolar regions The climate was temperate and cool. In the first half of the Mesozoic, the climate was dry, while the second half was characterized by humid climate. It was at this time that the equatorial climate zone was formed.
In the animal world, mammals arose from the subclass of reptiles. This was related to improvement nervous system and brain. The limbs moved from the sides under the body, and the reproductive organs became more advanced. They ensured the development of the embryo in the mother's body, followed by feeding it with milk. Hair appeared, blood circulation and metabolism improved. The first mammals appeared in the Triassic, but they could not compete with dinosaurs. Therefore, for more than 100 million years they occupied a dominant position in the ecosystem.
The last era is considered Cenozoic(beginning 66 million years ago). This is the current geological period. That is, we all live in the Cenozoic. It is divided into 3 periods:
- Paleogene (66–23 million years)
- Neogene (23–2.6 million years)
- modern Anthropocene or Quaternary period, which began 2.6 million years ago.
There are 2 main events observed in the Cenozoic. The mass extinction of dinosaurs 65 million years ago and the general cooling of the planet. The death of the animals is associated with the fall of a huge asteroid with a high content of iridium. Diameter cosmic body reached 10 km. As a result, a crater was formed Chicxulub with a diameter of 180 km. It is located on the Yucatan Peninsula in Central America.

Surface of the Earth 65 million years ago
After the fall, there was an explosion of enormous force. Dust rose into the atmosphere and blocked the planet from the sun's rays. average temperature fell by 15°. Dust hung in the air for a whole year, which led to a sharp cooling. And since the Earth was inhabited by large heat-loving animals, they became extinct. Only small representatives of the fauna remained. It was they who became the ancestors of the modern animal world. This theory is based on iridium. The age of its layer in geological deposits corresponds exactly to 65 million years.
During the Cenozoic, the continents diverged. Each of them formed its own unique flora and fauna. The diversity of marine, flying and terrestrial animals has increased significantly compared to the Paleozoic. They became much more advanced, and mammals took a dominant position on the planet. Higher angiosperms appeared in the plant world. This is the presence of a flower and an ovule. Cereal crops also appeared.
The most important thing in the last era is anthropogen or quaternary period, which began 2.6 million years ago. It consists of 2 eras: the Pleistocene (2.6 million years – 11.7 thousand years) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years – our time). During the Pleistocene era Mammoths, cave lions and bears, marsupial lions, saber-toothed cats and many other species of animals that became extinct at the end of the era lived on Earth. 300 thousand years ago, man appeared on the blue planet. It is believed that the first Cro-Magnons chose the eastern regions of Africa. At the same time, Neanderthals lived on the Iberian Peninsula.
Notable for the Pleistocene and Ice Ages. For as long as 2 million years, very cold and warm periods of time alternated on Earth. Over the past 800 thousand years, there have been 8 ice ages with average duration 40 thousand years. During cold times, glaciers advanced on the continents, and retreated during interglacial periods. At the same time, the level of the World Ocean rose. About 12 thousand years ago, already in the Holocene, the next ice age ended. The climate became warm and humid. Thanks to this, humanity spread throughout the planet.
The Holocene is an interglacial. It has been going on for 12 thousand years. Over the past 7 thousand years, human civilization has developed. The world has changed in many ways. Flora and fauna have undergone significant transformations thanks to human activity. Nowadays, many animal species are on the verge of extinction. Man has long considered himself the ruler of the world, but the era of the Earth has not gone away. Time continues its steady course, and the blue planet conscientiously revolves around the Sun. In a word, life goes on, but what will happen next - the future will show.
 See what “Legion (number)” is in other dictionaries
See what “Legion (number)” is in other dictionaries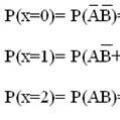 Examples of solving problems on the topic “Random variables”
Examples of solving problems on the topic “Random variables” I’m reading the poem “Frost, Red Nose” by Nekrasov
I’m reading the poem “Frost, Red Nose” by Nekrasov