Formed universal educational actions uud. What is UUD? Version for parents
In today's society, saturated with the latest technology, the qualities and ability to learn require special efforts from both parents and teachers. In view of this situation, a new concept has been introduced into the learning process. What is UUD? How can you help your child learn to develop his own personality from an early age? How important are universal learning activities in modern society? We will try to give answers to these questions.
Definition of UUD
It may not be difficult for teachers to answer the question of what UUD is, but parents often do not understand the abbreviation, and the concept of “universal learning activities” is unfamiliar to them. Many still studied according to the standard scheme created in the USSR. Teachers imparted knowledge in lessons, and the process took place at home. But today the world has changed, which means that the methods of teaching children in educational institutions must also change.
This is the ability to learn, independently develop one’s abilities, as well as absorb new knowledge and apply it in practice. Essentially, this is a child’s ability for self-development and self-improvement. It is necessary to teach the student to independently set tasks, see ways to solve them, analyze the information received and draw the right conclusions.
Today, children are well versed in technology, but do not think about the basic rules of behavior. What caused this unbalanced development? Will the new standards introduced in the Russian Federation be able to cope with such a difficult task as raising young children as individuals?
Reasons for changing teaching methods
The 20th century was industrial, and the 21st is informative. Children today are well versed with mobile phones, tablets and computers. The flow of information flows like a river onto the still unformed child’s psyche. As a result, they are unable to process all the information they receive. As a result, children do not know how to study, conduct independent research and solve assigned problems.
In addition, most parents focus their attention on the intellectual development of their children and completely ignore moral and spiritual education. As a result, smart children are not able to develop communication skills and at the same time the desire to learn disappears. Pride, selfishness, and an inability to cooperate with others lead to detrimental consequences both in school and in adult life.
Today it is not fashionable to read books, especially classics. Children are more occupied with movies and video games, which do not contribute to the development of mental abilities. This results in learning difficulties, poor imagination, and inability to analyze the material read and think logically.
These are just some of the reasons why a review of the entire educational system is brewing. That is why the introduction of universal learning activities into secondary general education is required. Consideration of the four types of UUD will help to better understand what actions will be required from the student.
Personal UUD
Let's consider the types of UUD that relate to the development of personal qualities. They provide students with value-semantic orientation, that is, the ability to compare events and actions with existing moral principles and moral standards. Children must learn not to get lost in relationships with others and in social roles. What types of activities are included in this?

- Self-determination. There are personal, life and professional. The child must grow up to be an individual and learn to express his own opinions.
- Sensemaking. Essentially, students must ask themselves this question: “How does learning matter to me?” They must see the connection between learning and the motive that motivates action.
- Moral and ethical orientation. Evaluation of the material being studied based on social and personal values. Personal choice based on moral principles is provided.
Cognitive UUD
They include logical actions, general educational and symbolic ones. These types of UUD promote the development of logical thinking in schoolchildren. What exactly do cognitive activities involve?
Logical actions cover the analysis of objects in order to detect certain characteristics, as well as the selection of criteria for comparing and classifying objects. It requires finding a cause-and-effect relationship and building a consistent chain of reasoning. Students can provide their own evidence and put forward hypotheses with personal justifications.
General educational activities include: independent determination of a cognitive goal, finding useful information, structuring the acquired knowledge. Students should be able to express their thoughts meaningfully and freely, both in writing and orally. It is necessary to solve the assigned problems by finding your own algorithm and solving the issues that arise creatively and searching for the necessary information.
It is necessary to develop cognitive abilities in schoolchildren with the help of UUD. Mathematics in the primary grades helps develop logic when solving problems, while drawing up diagrams. A brief description of the problem conditions gives students a specific algorithm, which they can subsequently use when solving more complex options.
Regulatory UUD
Regulatory qualities ensure that students organize their activities. Essentially, they need to be able to organize themselves. To do this, you need to learn how to set goals and achieve them. You will need to apply some principles to your learning activities.
Goal setting teaches children to set learning goals and relate already known material to unfamiliar material. Next, planning is required - this means that the student must determine the sequence of actions in solving the given problem, develop a specific plan and follow it. Forecasting will help you see the preliminary result and degree of assimilation, as well as the timeline for obtaining the result.
Monitoring, correction and evaluation of actions will help develop self-control abilities. By monitoring and checking his work with the proposed model, correcting his actions in accordance with the correct decision, the child learns to make decisions correctly and develop a specific plan of action. Self-regulation is also required - the ability to mobilize one’s own strength and overcome obstacles that arise.
Communication skills
Communicative UUDs provide social awareness and consideration of other people's views on the same issue. Children need to learn to listen and hear others, enter into dialogue and learn to discuss problems peacefully, conduct discussions and build mutual relationships with peers and adults.

To develop such qualities, the teacher will need to create situations in which cooperation between students is provided. For example, you can use technology-based learning activities: invite schoolchildren to work together on a project, dividing the class into groups. For junior grades, the following tasks are given: “find differences in identical objects made using different techniques” or “what tools are needed or not needed when performing a certain task.” You can come up with a lot of tasks, the main thing is that they develop the communication abilities of each child in the class.
Federal state standard
To develop children's learning skills and personal qualities, new standards have been introduced. Federal State Educational Standard “School of Russia” is introduced on September 1, 2011 throughout the Russian Federation. It makes a number of demands on the teaching process in schools.
First of all, the requirements are imposed on the formation of the student’s personality, and not only on his acquisition of the necessary knowledge and skills. Thus, the system completely abandons the old training program. Secondary general education should shape the student’s personality. The consequence of learning is personal, meta-subject and subject results.
An integral part of the new standard is the introduction of universal learning activities. To introduce new methods, a UUD program was developed. A separate textbook has been compiled for each subject to help teachers develop the required skills.
Along with the acquisition of standard learning skills and the development of the student’s personality, a methodology is being introduced to orient younger schoolchildren in information and communication technologies, as well as to develop the ability to use them knowledgeably. What does this look like in practice?
Introduction of UUD into educational subjects
Thematic planning with UUD will allow you to see students as individuals with their own abilities from the very first lessons. Since the peculiarity of the new standards is not only the formation of the student’s personality, but also the introduction of modern technologies, the teacher will need good preparation. The requirements include, in addition to normal traditional writing skills, the introduction of keyboard typing on a computer. This will help the child quickly master new technologies and develop memory, logic and the ability to communicate with peers.

Today, a whole system of textbooks has appeared for the new standards of the Federal State Educational Standard “School of Russia”. They passed the federal examination and received positive reviews from the Russian Academy of Sciences. All textbooks are included in the recommended federal list. They have revised the approach to education. The materials explain what UUD is and how to apply it in practice. According to the new standards, textbooks are aimed at developing universal learning activities in students. They also contain methods for involving children in the educational process when studying all school subjects.
Innovations
The school’s UUD program helps teachers, with the help of modern teaching aids, develop given skills in children. The textbooks included special assignments that develop students’ ability to independently formulate an educational task for a given topic or a specific lesson.
The number of tasks and questions of an educational and exciting nature has been increased, as well as for working in groups or in pairs. They help the student focus on his own point of view and connect existing knowledge with real events.
The textbooks contain new sections that help you reflect on the material you have learned: “What you have learned. What have we learned”, “Let’s test ourselves and evaluate our achievements.” The sections “Our Projects”, “Pages for the Curious” and “Express Your Opinion” will help teachers develop the necessary skills in younger schoolchildren.
UUD by technology
What new things can be introduced and how can the requirements of modern standards be included in the learning process? The work of experienced teachers will help with this. What is the most important thing to develop in younger schoolchildren? UUD technology requires the teacher to be attentive to his students.

He will need to develop in children the ability to evaluate their own work; for this, an algorithm for evaluating their work should be developed. In this case, it is important not to compare students with each other, but to show the child’s success in comparison with his past work.
The teacher must involve children in the discovery of new knowledge. To do this, you will need to discuss together why the task is needed and how it can be applied in life.
One more point: it is the technology teacher who is responsible for helping children learn cooperation in a group. This basic communication skill only develops when working together. Here it is necessary to teach children to discuss the task together, find a collective solution to issues and analyze the result.
To develop all kinds of skills, high-quality educational planning will be required, especially with younger students. While children have not yet learned anything, you can use various methods and tasks. For example, the favorite children's game “find the differences”. You can indicate the number of differences, or you can let the kids find them themselves and share with their classmates.
There are different types of tasks that are aimed at developing universal learning activities. For example, participation in projects, summarizing the lesson, creative tasks, visual, motor and verbal perception of music.
3rd grade (FSES) with advanced learning skills can already cope with more complex tasks, including organizing, drawing up support diagrams, working with different types of tables, correcting “intentional” errors, searching for necessary information in the proposed sources, and mutual control.
To test knowledge, you can use CONOP (a test on a specific problem), interactive listening, tasks “prepare a story...”, “describe orally...”, “explain...”.
Technology can become a stronghold in the development of universal learning activities.
UUD in physical education
It may seem that a lesson such as physical education cannot teach moral skills in children. But this is far from true. New methods of education and development of the right attitude towards one’s own health help to use the UUD in physical education.

It is the trainer who can encourage you to lead a healthy lifestyle. How to develop children's skills through physical education? Let's start with what universal abilities can be developed.
- Firstly, the child must be able to organize his activities and selectively use means to achieve his goal.
- Secondly, be able to actively collaborate with the team, join forces with peers to achieve collective goals.
- Thirdly, only in physical education can you learn to present information simply, in an expressive and vivid form, in the process of communication and cooperation with classmates and adults.
What personal qualities will students acquire? You can learn to communicate and cooperate with peers, based on the principles of respect and goodwill, mutual assistance and empathy. It is equally important to be able to express positive personality traits and manage your feelings in a variety of unusual circumstances and conditions. These results will help raise a balanced person. Physical education will promote discipline, hard work and perseverance in achieving your goals.
ISO
Each fine arts lesson should be focused on solving subject problems and forming certain qualities of the child. UUD according to the Federal State Educational Standard for Fine Arts helps to develop the necessary skills in younger schoolchildren.
The example of a teacher can inspire students to be more willing to explain their impressions of the picture they saw, to choose words to express emotions, and to tell their elders and friends about what they saw.
The joint creativity of children, divided into pairs or groups of several people, allows them to quickly gain positive experience in solving communicative and regulatory problems: here children learn to conduct a conversation, and even defend their opinion, respect the opinion of their partner, focus on the end result, and not personal , but general. All this allows you to quickly join the team and acquire positive qualities.

For clarity, here is an example of joint creativity. The children were given the task of drawing mittens for their hands in a group. How can their teamwork be assessed by the actions they produced? Assessment levels are different.
- Low: The patterns are drawn with obvious differences or no similarities at all. What happened? Children do not try to negotiate with each other; everyone insists on their preferences.
- Medium: partial similarity - individual drawings are the same, but there are also noticeable differences. The result of an inept agreement, everyone wanted to stand out in some way.
- Tall: The mittens are decorated in the same way or with a very similar pattern. Children work with pleasure, animatedly discuss existing variations, compare methods of action and coordinate them, make joint plans and monitor the implementation of their ideas. This option is the best way to show what UUD is, or rather its application in practice.
In view of the requirements of new standards for teaching children new technologies, not only traditional fine arts are possible, but also the use of computer technologies in teaching children. For example, draw a picture not only on a landscape sheet, but also do it in a certain program. You can also teach children to take photographs, photo reports, and teach them how to use graphics programs correctly.
Science and education now go hand in hand and teaching methods must also change according to the needs of the new generation.
In order to improve the educational process, the Ministry of Education constantly introduces some innovations into it, filling it with new terms and concepts. An ordinary person, studying methodological literature or reading news about education, very often comes across the incomprehensible phrase UUD according to the Federal State Educational Standard. How does this abbreviation stand for and what does it mean in simple words?
Content:
The concept of "UUD"
UUD is a universal educational activity. It includes:
- Ability to learn and acquire new knowledge, ability to learn;
- A person’s desire for self-improvement through acquiring new experience;
- Understanding the need to acquire knowledge and a conscious approach to the educational process;
- Understanding the essence of education itself and its constituent parts;
- Purposeful human actions to search for opportunities for broad orientation both in different subject areas and in the structure of the educational activity itself;
- Understanding the target orientation of the educational process, its value-semantic and operational properties.
The development of UUD was carried out back in the twentieth century in the Soviet Union. At that time, pedagogical science was undergoing active development and the foundation of its new trends was being laid. The concept of “universal educational activities” has become very popular nowadays; the scope of its application is quite wide and covers almost all possible levels and types of education. The development of UUD is based on the activity approach, which was developed by L.S. Vygotsky, A.N. Leontyev, D.B. Elkonin, P.Ya.Galperin, V.V. Davydov and other scientific schools.
Elkonin and Davydov are the founders of the theory of developmental learning, the key concept of which is UDT.
What is GEF?

This is the Federal State Educational Standard. It includes:
- List of requirements for state educational institutions;
- The Law “On Education” is the basis of the Federal State Educational Standard;
- The updated standard has been in effect in all schools since September 1, 2011 - Federal State Educational Standard for Primary General Education (GES).
Federal State Educational Standards requirements relate to:
- Structures of the educational process. Every year it is necessary to draw up and approve a work plan aimed at optimally promoting students towards acquiring new knowledge; guided by this plan, periodically improve the educational and methodological complex (EMC) of disciplines.
- Implementation of the educational program. If the structure of the educational process lies in the area of responsibility of the administration and methodological departments, then the teaching staff of schools is directly responsible for the implementation of the plan;
- Educational results. Student performance is a clear demonstration and evidence of the success of the developed educational structure and program and compliance with all requirements. The average performance assessment for the entire school is taken into account.
Basic groups of UUD?

Requirements for UUD depend on what level of classes - primary, middle or high school - the students are studying in. The requirements put forward must be consistent with the age of the children. For all of them, the requirements for the use of computer equipment and information technology in educational activities have recently increased.
There are the following basic groups of universal educational actions:
- Personal – aimed at finding opportunities to know oneself and understand one’s own personality. Their goal is to form in students a correct, adequate moral and ethical assessment of themselves;
- Cognitive - refers to the possibilities of developing basic skills and abilities in the perception of information, its processing and analysis, on the basis of which certain conclusions and conclusions are drawn. The group of cognitive actions includes a system of general and logical educational actions, the process of posing and solving a problem;
- Communicative - contribute to the socialization of students, the formation of skills for effective interaction with others - classmates, teachers, friends and other people. At school, every child goes through the most important stage of social development. If problems that arise in the process of communication are not resolved in time, then they can move into adulthood and will remind of themselves for many years, even after graduation;
- Regulatory – aimed at developing the ability to draw up a plan of one’s actions and change it under the influence of various environmental factors. This useful skill acquired at school will be useful in later life.
Students master UDL in the process of studying various academic subjects. The result of successful mastery is the formation of initiative, the desire of students to independently acquire knowledge and gain competence. Students should be able to independently organize the learning process without the help of adults.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Homeschooling

Homeschooling is an alternative option for school education. When the reason for this choice of parents is medical conditions (physical or mental illnesses), homeschooling is the best option. But if parents are driven by other motives - fears about the child’s socialization, reluctance to send their children to school because they will not be able to solve school problems on their own without mom or dad - all this leads to the most unpredictable negative consequences.
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of homeschooling.
|
pros |
Minuses |
|
Attacks and ridicule from classmates are excluded, the child will not become an object of bullying |
Students lack motivation; in the classroom, students watch each other, compete, follow each other, strive for a better result, and have richer material for analysis |
|
Greater flexibility of the study schedule compared to school education, the ability to independently plan the number of lessons per day |
There is no opportunity to learn to interact with each other within a team; the world of building social relationships remains closed |
|
Learn material in less time because student and teacher collaborate one-on-one |
They don’t learn to make new acquaintances, defend their point of view, and don’t contact anyone except family and close friends |
|
More free time appears, which can be spent on visiting clubs and sports sections |
When learning at home, the child is in a comfort zone, but as soon as he is left alone with himself, he becomes completely defenseless and does not know how to behave in a given situation. |
|
The opportunity to individually work with the child on all the difficulties and weak points that arise during the development of the curriculum |
Homeschooling excludes the possibility of a child developing effective ways to counter the infringement of his rights |
The impact of UUD according to the Federal State Educational Standard on schoolchildren is contradictory, since each child is a unique personality, individuality, each has different abilities and talents. UUD promotes the assimilation of moral norms and principles developed by society, which leads to the formation of a holistic personality. At the same time, the Federal State Educational Standard limits the child to rigid boundaries and does not allow him to show initiative and love of freedom.

Important! UUD according to the Federal State Educational Standard is a set of requirements for the educational process. The development of standards is based on the desire to provide every child with the opportunity to obtain and assimilate all the knowledge that will be useful to him in the future. The task of the school is to develop skills that will not only be useful in further education, but will also ensure the normal functioning of every person in society.
Today the request is made not just for a person, but for a Personality, which must have a whole set of qualities:
Independence in decision making and choice;
The ability to be responsible for your decisions;
The ability to bear responsibility for oneself and for loved ones;
Willingness to act in non-standard situations;
Possession of teaching techniques and readiness for constant retraining;
Possession of a set of competencies, both key and in various areas of knowledge, etc.
It is clear that the task of raising a person with such qualities over the years of schooling is extremely difficult.
Achieving this goal becomes possible thanks to the formation of a learning learning system, mastery of which gives students the opportunity to independently successfully acquire new knowledge, skills and competencies based on the formation of the ability to learn.
So, what do universal learning activities provide?
The main types of UUD include:
Personal
Cognitive
Regulatory
Communication
Personal UUDs include:
Self-determination
Sensemaking
Moral and ethical standards
Regulatory UUDs include:
Goal setting
Planning
Forecasting
Control
Correction
Communicative UUDs include:
Interaction
Cooperation
Communication
Cognitive UUDs include:
General education UUD:
Searching for the necessary information to complete educational tasks using educational literature;
Use of symbolic means (graphs, models, diagrams, tables);
Conscious and voluntary construction of speech utterances in oral and written form;
Focus on a variety of ways to solve problems;
Structured knowledge
Logical learning activities:
Basics of semantic reading (the ability to isolate essential information from texts of various types)
Ability to analyze objects (identify essential features)
Ability to compare, seriate and classify according to specified criteria
Ability to establish cause and effect relationships
The ability to build reasoning, evidence, put forward hypotheses and their justification
Statement and solution of the problem:
Formulation of the problem
Creating ways to solve a problem
Solution
In modern conditions, the teacher’s task is to show the student the path to knowledge, to teach him to learn. Therefore, the priority direction of new educational standards for both primary and basic education is the task of forming not only subject theoretical knowledge, but also the formation of universal educational activities as one of the ways to improve the quality of education.
Modern educational technologies in the aspect of implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard, ensuring the formation of cognitive universal actions
|
Technologies |
Methods |
Formed UUD |
|
Problem-based learning |
Creating a problem situation |
Cognitive: general educational cognitive actions, problem formulation and solution |
|
Pedagogy of cooperation |
Joint activity, heuristic conversation, collective conclusion, comparison |
Cognitive: logical universal actions |
|
Individual - differentiated approach |
Multi-level tasks |
|
|
Competence-oriented training |
Research work, project activities |
Cognitive: general educational cognitive actions, formulation and solution of problems, logical universal actions |
|
Information and communication technologies |
Introduction to new material on a PC, testing, presentation, interactive whiteboard |
Cognitive: logical universal actions, general educational cognitive actions. |
The formation and development of cognitive learning skills in the classroom occurs through various types of tasks. :
. "Find the Differences"
. "Search for the odd one out"
. "Labyrinths"
. "Chains"
Drawing up support diagrams
Working with different types of tables
Diagram creation and recognition
Working with dictionaries
The result of the formation of cognitive learning tools will be the student’s ability to:
Identify the type of problems and ways to solve them;
Search for the necessary information needed to solve problems;
Distinguish between reasonable and unfounded judgments;
Justify the stages of solving an educational problem;
Analyze and transform information;
Conduct basic mental operations (analysis, synthesis, classification, comparison, analogy, etc.);
Establish cause-and-effect relationships;
Possess a general technique for solving problems;
Create and transform diagrams necessary to solve problems;
Select the most effective way to solve a problem based on specific conditions.
In elementary school, while studying various subjects, a student, at the level of capabilities of his age, must master methods of cognitive, creative activity, master communication and information skills, and be ready to continue his education. Successful education in primary school is impossible without the formation of educational skills in younger schoolchildren, which make a significant contribution to the development of the student’s cognitive activity, since they are general educational, that is, they do not depend on the specific content of the subject. Moreover, each academic subject, in accordance with the specific content, takes its place in this process.
Measuring the level of UUD formation:
Performing specially designed diagnostic tasks (assessing the formation of a specific type of UUD)
Successful completion of educational and practical tasks using educational subjects
Successful completion of complex tasks on an interdisciplinary basis.
Universal learning activities
Explanatory note
The changes taking place in modern society require accelerated improvement of the educational space, determination of educational goals that take into account state, social and personal needs and interests. In this regard, ensuring the developmental potential of new educational standards becomes a priority. Personal development in the education system is ensured primarily through the formation of universal learning activities (ULAs), which act as the invariant basis of the educational and upbringing process. Students' mastery of universal learning activities acts as the ability for self-development and self-improvement through the conscious and active appropriation of new social experience. UUDs create the opportunity for independent successful assimilation of new knowledge, skills and competencies, including the organization of assimilation, that is, the ability to learn. This possibility is ensured by the fact that universal learning actions are generalized methods of action that open up a broad orientation for students in various subject areas.
In a broad sense, the term “universal educational actions” means the ability to learn, i.e., the subject’s ability to self-development and self-improvement through the conscious and active appropriation of new social experience.
In a narrower (actually psychological) meaning, the term “universal learning actions” can be defined as a set of methods of action of a student (as well as associated learning skills) that ensure his ability to independently acquire new knowledge and skills, including the organization of this process.
Functions of universal learning activities include :
Ensuring the student’s ability to independently carry out learning activities, set educational goals, seek and use the necessary means and methods to achieve them, monitor and evaluate the process and results of the activity;
Creating conditions for the harmonious development of the individual and his self-realization based on readiness for lifelong education, the need for which is due to the multiculturalism of society and high professional mobility;
Ensuring the successful acquisition of knowledge, the formation of skills, abilities and competencies in any subject area.
Universal educational activities should be the basis for the selection and structuring of educational content, techniques, methods, forms of teaching, as well as the construction of a holistic educational process.
Students' mastery of universal learning activities occurs in the context of different academic subjects and ultimately leads to the formation of the ability to independently successfully assimilate new knowledge, skills and competencies, including independent organization of the assimilation process, i.e. the ability to learn.
This ability is ensured by the fact that universal learning activities are generalized actions that open up students the opportunity for broad orientation both in various subject areas and in the structure of the learning activity itself, including students’ awareness of its target orientation, value-semantic and operational characteristics. Thus, achieving the ability to learn presupposes the full mastery of all components of educational activity, which include:
1) educational motives,
2) educational purpose,
3) educational task,
4) educational activities and operations (orientation, transformation of material, control and evaluation).
So-called meta-subject learning activities should also occupy a significant place in the teaching of school disciplines. Meta-subject (i.e., “supra-subject” or “metacognitive”) actions are understood as students’ mental actions aimed at analyzing and managing their cognitive activity, be it determining a strategy for solving a mathematical problem, memorizing factual material on history, or planning a joint activity (with others). students) laboratory experiment in physics or chemistry.
Types of universal learning activities
As part of the main types of universal educational activities, dictated by the key goals of general education, four blocks can be distinguished:
1) personal;
2) regulatory (also including self-regulation actions);
3) educational;
4) communicative.
It is assumed that a clear identification of these types of educational activities will allow them to be given priority within the framework of the study of specific academic subjects.
Let us present these UUD blocks in a little more detail.
To block personal universal educational activities include the value-semantic orientation of students (the ability to correlate actions and events with accepted ethical principles, knowledge of moral standards and the ability to highlight the moral aspect of behavior), as well as orientation in social roles and interpersonal relationships. In relation to learning activities, two types of actions necessary in personally oriented learning should be highlighted. This is, firstly, the action of meaning formation, i.e., the establishment by students of a connection between the goal of educational activity and its motive, in other words, between the result - the product of learning that motivates the activity, and the reason for which it is carried out. The student should ask the question: what meaning and significance does the teaching have for me? - and be able to answer it. Secondly, this is the action of moral and ethical assessment of the acquired content based on social and personal values.
To block regulatory actions include actions that ensure that students organize their learning activities: goal setting as setting a learning task based on the correlation of what is already known and learned by the student and what is not yet known; planning - determining the sequence of intermediate goals taking into account the final result; drawing up a plan and sequence of actions; forecasting - anticipation of the result and level of assimilation, its time characteristics; control in the form of comparison of the method of action and its result with a given standard in order to detect deviations and differences from the standard; correction - making the necessary additions and adjustments to the plan and method of action in the event of a discrepancy between the standard, the actual action and its product; assessment - the student’s identification and awareness of what has already been learned and what still needs to be learned, awareness of the quality and level of assimilation. Finally, elements of volitional self-regulation as the ability to mobilize strength and energy, to volitional effort (to make a choice in a situation of motivational conflict) to overcome obstacles.
In the block of universal actions cognitive orientation, it is advisable to distinguish between general educational and logical actions. General educational ones include: independent identification and formulation of a cognitive goal, structuring knowledge, reflection on methods of action, control and evaluation of the process and results of activities, orientation not only to the rules, but also to the conditions of their applicability, selection of the most effective ways to solve problems depending on specific conditions, extracting the necessary information from listened texts of various genres, determining basic and secondary information; the ability to adequately, in detail, concisely, selectively convey the content of the text, comprehend the purpose of reading, choosing the type of reading depending on the purpose; freely navigate and perceive texts of artistic, scientific, journalistic and official & business styles; understand and adequately evaluate
media language; write texts of various genres, observing the norms of text construction (compliance with the topic, genre, style of speech, etc.); pose and formulate a problem, independently create activity algorithms for solving a wide range of problems, including creative and search ones, act with sign-symbolic means (replace, encode, decode, model), apply information retrieval methods, including using computer funds.
Along with general educational ones, universal logical actions are also distinguished: choosing grounds, criteria for comparing, juxtaposing, evaluating and classifying objects; synthesize: to compose a whole from parts, including independently completing, replenishing the missing components; summarize concepts, recognize objects; establish cause-and-effect relationships, build a logical chain of reasoning, prove; identify generic and situationally significant features.
Communication abilities are based on the conscious orientation of students to the position of other people (primarily a partner in communication or activity), the ability to listen and engage in dialogue, participate in a collective discussion of problems, the ability to integrate into a peer group and build productive interaction with peers and adults, the ability to express your thoughts completely and accurately. Accordingly, communicative actions include: planning educational cooperation with the teacher and peers - determining the goals, functions of participants, methods of interaction; asking questions - proactive cooperation in searching and collecting information; conflict resolution - identification, identification of problems, search and evaluation of alternative ways to resolve conflicts, decision-making and its implementation; managing the partner’s behavior - monitoring, correction, evaluation of the partner’s actions.
The concept of “universal learning activities”
In a broad sense, the term “universal educational actions” means the ability to learn, i.e. the subject’s ability to self-development and self-improvement through the conscious and active appropriation of new social experience.
The ability of a student to independently successfully assimilate new knowledge, to form skills and competencies, including the independent organization of this process, i.e. the ability to learn, is ensured by the fact that universal learning actions as generalized actions open up students the opportunity for broad orientation both in various subject areas and in the structure of the educational activity itself, including awareness of its target orientation, value-semantic and operational characteristics. Thus, achieving the ability to learn requires students to fully master all components of educational activity, which include: cognitive and educational motives, educational goal, educational task, educational actions and operations (orientation, transformation of material, control and evaluation). The ability to learn is a significant factor in increasing the efficiency of students’ mastery of subject knowledge, the formation of skills and competencies, the image of the world and the value-semantic foundations of personal moral choice.
Functions of universal educational actions:
- ensuring the student’s ability to independently carry out learning activities, set educational goals, seek and use the necessary means and methods to achieve them, monitor and evaluate the process and results of the activity;
- creating conditions for the harmonious development of the individual and his self-realization based on readiness for lifelong education; ensuring the successful acquisition of knowledge, the formation of skills, abilities and competencies in any subject area.
Personal UUD provide students with value and semantic orientation (the ability to relate actions and events with accepted ethical principles, knowledge of moral standards and the ability to highlight the moral aspect of behavior), as well as orientation in social roles and interpersonal relationships. In relation to educational activities, three types of actions should be distinguished:
- self-determination - personal, professional, life self-determination;
- meaning formation is the establishment by students of a connection between the purpose of educational activity and its motive, in other words, between the result of learning and what motivates the activity, for the sake of which it is carried out. The student must ask the question “what meaning does the teaching have for me,” and be able to find an answer to it;
- moral and ethical orientation is the action of moral and ethical assessment of the acquired content, ensuring personal moral choice based on social and personal values.
Regulatory UUD provide students with organization of their educational activities. These include the following:
- goal setting - as setting an educational task based on the correlation of what is already known and learned by the student and what is still unknown;
- planning - determining the sequence of intermediate goals taking into account the final result; drawing up a plan and sequence of actions;
- forecasting – anticipation of the result and level of assimilation; its temporal characteristics;
- control in the form of comparing the method of action and its result with a given standard in order to detect deviations from it;
- correction - making the necessary additions and adjustments to the plan and method of action in the event of a discrepancy between the expected result of the action and its actual product;
- assessment – the student’s identification and awareness of what has already been learned and what still needs to be learned, assessing the quality and level of learning;
- self-regulation as the ability to mobilize strength and energy; the ability to exert volition – to make a choice in a situation of motivational conflict and to overcome obstacles.
Cognitive UUD include general educational, logical actions, as well as actions of posing and solving problems.
General educational universal actions:
- independent identification and formulation of a cognitive goal;
- search and selection of necessary information; application of information retrieval methods, including using computer tools;
- structuring knowledge;
- conscious and voluntary construction of a speech utterance in oral and written form;
- choosing the most effective ways to solve problems depending on specific conditions;
- reflection on methods and conditions of action, control and evaluation of the process and results of activity;
- semantic reading; understanding and adequate assessment of the language of the media;
- formulation and formulation of problems, independent creation of activity algorithms when solving problems of a creative and exploratory nature.
A special group of general educational universal actions consists of sign-symbolic actions:
- modeling;
- transformation of the model in order to identify general laws that define a given subject area.
Logical universal actions:
- analysis;
- synthesis;
- comparison, classification of objects according to selected characteristics;
- summing up the concept, deriving consequences;
- establishing cause-and-effect relationships;
- building a logical chain of reasoning;
- proof;
- putting forward hypotheses and their substantiation.
Statement and solution of the problem:
- problem formulation;
- independent creation of ways to solve problems of a creative and exploratory nature.
Communicative UUD provide social competence and consideration of the position of other people, communication or activity partners, the ability to listen and engage in dialogue; participate in collective discussion of problems; integrate into a peer group and build productive interaction and cooperation with peers and adults. Types of communicative actions are:
- planning educational cooperation with the teacher and peers - defining goals, functions of participants, methods of interaction;
- asking questions – proactive cooperation in searching and collecting information;
- conflict resolution - identification, identification of problems, search and evaluation of alternative ways to resolve conflicts, decision-making and its implementation;
- managing the partner’s behavior – monitoring, correction, evaluation of the partner’s actions;
- the ability to express one’s thoughts with sufficient completeness and accuracy in accordance with the tasks and conditions of communication, mastery of monologue and dialogic forms of speech in accordance with the grammatical and syntactic norms of the native language.
Development of the UUD system as part of personal, regulatory, cognitive and communicative actions that determine the formation of the psychological abilities of the individual, it is carried out within the framework of the normative age development of the personal and cognitive spheres of the child. The learning process determines the content and characteristics of the child’s educational activity and thereby determines the zone of proximal development of the indicated learning activities - the level of their formation, corresponding to the normative stage of development and relevant to the “high norm” of development, and properties.
The criteria for assessing the development of students’ learning skills are:
- compliance with age-psychological regulatory requirements;
- compliance of UUD properties with predetermined requirements.
Conditions ensuring the development of UUD
The formation of UUD in the educational process is determined by the following three complementary provisions:
- The formation of UUD as the goal of the educational process determines its content and organization.
- The formation of UUD occurs in the context of mastering various subject disciplines.
- UUD, their properties and qualities determine the effectiveness of the educational process, in particular the acquisition of knowledge and skills, the formation of an image of the world and the main types of student competence, including social and personal.
 Partial derivatives of a function of three variables
Partial derivatives of a function of three variables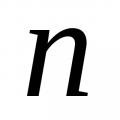 Empirical distribution function Using this sample, construct an empirical distribution function
Empirical distribution function Using this sample, construct an empirical distribution function No money, but you hold on
No money, but you hold on