Crossword puzzle representatives of the Russian direction. Slavophiles
Municipal educational institution
Secondary school No. 35
Additional history materials
Crosswords
A history teacher,
honorary worker of general education
Russian Federation
Art. Novotitarovskaya
Crossword No. 1. Currents of social life in Russia second
halfXIXcentury.
https://pandia.ru/text/77/496/images/image002_319.gif" width="2 height=42" height="42">they will not change that a revolution is needed and there is no need to prepare for it. 10. The main feature of the populists is the defense of the interests of the people.
Vertically: 1. What is the name of the movement whose followers believed that one must remember one’s duty to the people, there must be faith in socialism, that the peasants must be prepared through propaganda. 2. A current that required change. 6. What is the name of the movement whose representatives believed that an organization with strict discipline was needed so that no one knew about it. 8. Who created the “Union of Struggle for the Liberation of the Working Class”? 9. Who led the propaganda movement?
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Conservative. 4. Populism. 5. “Hell” 7. Rebellious. 10. Democracy.
Vertical: 1. Propaganda.
2. Liberal. 6. Conspiratorial. 8. Lenin. 9. Lavrov.
Crossword No. 2.
https://pandia.ru/text/77/496/images/image004_155.jpg" width="498" height="270 src=">
QUESTIONS: 1. Fortress. 2. A town in the foothills of the Alps. 3. Honorary title. 4. Fortress on a spit near the Dnieper -
Sko-Bug estuary. 5. Famous naval commander. 6. Central mountain range of the Alps. 7. Famous Russian commander, comrade-in-arms and. 8. Fortress. 9. Name of the bridge.
Keyword: A. V. SUVOROV.
Crossword No. 4. Find the word!
https://pandia.ru/text/77/496/images/image006_123.jpg" width="484" height="296 src=">
QUESTIONS:
1. A means of human transportation on water from ancient times to the present day. 2. A group of primitive people who are related and lead a common household. 3. One of the first activities of ancient man. 4. Tools made of copper (6-5 thousand years ago). 5. Tools for cultivating the land (13-7 thousand years ago). 6. A farmer’s labor tool, which appeared as a result of the improvement of the hoe (605 thousand years ago). 7. First pet. 8. Material for making dishes on a pottery wheel. 9. Human tools and weapons (200 thousand years ago). 10. Association of several clans living in one area.
Crossword No. 6.
https://pandia.ru/text/77/496/images/image008_89.jpg" width="519" height="212 src=">
QUESTIONS:
1. Provincial division unit. 2. Temporary cessation of hostilities. 3. The closest friend of Peter I. 4. Nobles under Peter I. 5. The city founded by Peter the Great. 6. “Great, wise mother of the Fatherland.”
ANSWERS: 1. District. 2. Truce. 3. Menshikov. 4. Boyars. 5. Petersburg. 6. Ekaterina P.
Keyword: RECRUIT.
Crossword No. 8.
Governing bodies" href="/text/category/organi_upravleniya/" rel="bookmark">governing body under Peter I. 3. Written appeal of the supreme power to the people. 4. Central body for managing church affairs. 5. Central institution for managing cities 6. Modern central government body 7. One of the achievements of science during the reign of Peter I.
ANSWERS:
1. Peter. 2. Senate. 3. Manifesto. 4. Synod. 5. Magistrate. 6. Duma. 7. Printing house.
Keyword: REFORM.
Crossword No. 9.
 |
QUESTIONS:
Horizontal: 3. The name of the legendary king of England, the hero of chivalric novels. 4. Leader of the uprising in Azerbaijan, directed against Arab domination. 6. Clergyman. 9. The name of the Arab religion. 10. Holy city of Muslims.
Vertical: 1. What was the mid-century name for a person who opposed the teachings of the Catholic Church? 2. Representative of the ruling class in the Middle Ages. 5. City in Palestine. 7. Capital of the Arab Caliphate. 8. The name of one of the Germanic tribes.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Arthur. 4. Babek. 6. Bishop. 9. Islam. 10. Mecca.
Vertical: 1. Heretic. 2. Feudal lord. 5. Jerusalem. 7. Damascus. 8. Franks.
Crossword No. 10.
https://pandia.ru/text/77/496/images/image012_68.jpg" width="550" height="378 src=">
QUESTIONS:
Horizontally: 1. An ordinary member of the monastery community. 4. Small-scale production in a medieval city, based on manual labor. 5. Pseudoscience about combining various substances to obtain gold. 6. Abbot of the monastery. 8. Fortified place, settlement of artisans and merchants.
Vertical: 1. A picture made of colored pebbles or pieces of glass. 2. Part of communal land owned by an individual family. 3. State of the Arabs. 7. Vassal of a duke or count and lord of knights.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 1. Monk. 4. Craft. 5. Alchemy. 6. Abbot. 8. City.
Vertical: 1. Mosaic. 2. Allotment. 3. Caliphate. 7. Baron.
Crossword No. 12.

QUESTIONS:
Horizontal: 3. Pseudoscience of predicting the future by the location of the stars. 5. Military servant of the feudal lord. 7. City Council building in Western Europe.
Vertically: 1. Military competition of knights in strength and dexterity. 2. Owner of land and serfs in the Middle Ages. 3. Pseudoscience about combining various substances to obtain gold. 4. Annual auctions in which merchants from different cities and countries took part. 6. The main church in the medieval city. 8. A collection of rules binding on all members of a guild in a medieval city.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Astrology. 5. Vassal. 7. Town Hall.
Vertically: 1. Tournament. 2. Feudal lord. 3. Alchemy. 4. Fairs. 6. Cathedral. 8. Charter.
Crossword No. 13.For the period of 1 year.
Orthodoxy (from the Greek." href="/text/category/ortodoksalmznostmz__ot_grech_/" rel="bookmark">orthodox communists in the early 90s. 17.. Well-known human rights activist, plenipotentiary of the President of the Russian Federation for human rights. 22. Subject of the Russian Federation , capital of Kazan 23. Chechen terrorist, “hero” of Budyonovsk 25. Name of the Popular Front of Lithuania, leader V. Landsbergis 28. Subject of the Russian Federation, capital of Vladikavkaz 29. Minister of Finance of the Russian Federation since 1996 30. One of the leaders of the State Emergency Committee 32. Resort village in Crimea, where during the 1991 coup he was located.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 6. Ryzhakov. 7. Ilyushin. 10. Tax. 11. Kazakh. 12. Yavlinsky. 15. Shahray. 18. "Youth". 19. Zyuganov. 20. Camarilla. 21. Parliament. 24. Ligachev. 26. Voucher. 27. Sobchak. 31. Acceleration. 33. Chechnya. 34. Shokhin. 35. Berlin. 36. Niyazov.
Vertical: 1. Market. 2. Moscow. 3. Leningrad. 4. Yeltsin. 5. China. 8. Gaidar. 9. Memory. 13. Nazarbayev. 14. Unitary. 16. Tyulkin. 17. Kovalev. 22. Tatarstan. 23. Basayev. 25. Sąjūdis. 28. Ossetia. 29. Livshits. 30. Yanaev. 32. Foros.
Crossword No. 14. For the period of 1 year.
December 8" href="/text/category/8_dekabrya/" rel="bookmark">December 8, 1991, the Agreement on the creation of the CIS was signed. 23. The first president of the Russian Federation. 25. One of Stalin’s closest associates. 28. Mayor St. Petersburg in the early 90s. 29. Founder of the People's Republic of China, a great friend of the USSR. 30. A city in the North-West of Russia, which has become a border town since 1991. 32. A resort village in Crimea, where during the 1991 coup .was ev.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 5. Shahray. 6. Mozhaev. 10. Larin. 11. "Cobra". 12. "Rail". 15. Voucher. 18. Grachev. 19. Gagarin. 20. Gosplan. 21. Moldova. 24. Khariton. 26. Glushko. 27. Swan. 31. Communism. 33. Minsk. 34. Popov. 35. Tor-gau. 36. Rutskoy.
Vertical: 1. Mafia. 2. Fadeev. 3. Kovpak. 4. Belov. 7. Gaidar. 8. Oistrakh. 9. Khrushchev. 13. Helsinki. 14. Prokofiev. 16. Karabakh. 17. Simonov. 22. “Visculi.” 23. Yeltsin. 25. Zhdanov. 28. Sobchak. 29. Zedong. 30. Pskov. 32. Foros.
Crossword No. 15.For the period of 1 year.
Military leader" href="/text/category/voenachalmznik/" rel="bookmark">military leader, commanded a tank army during the Great Patriotic War. 19. General Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee from 1982 to 1984, former head of the KGB. 20. Soviet writer a front-line soldier, whom Stalin loved, lived in Paris in the 70s 23. Secretary of the Writers' Union, author of the novel “The Young Guard” 25. A city in the Smolensk region, in the area of which in the fall of 1941 the co-battle of Smolensk in 1941 28. "Forge of Victory", an economic region in the deep rear, the main supplier of weapons for the front 29. Brand of heavy fascist tank.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 8. Sorge. 9. Charter. 10. Nazarbayev. 11. Pact. 13. Yalta. 15. Chernenko. 16. Mongolia. 17. Chubais. 18. Grishin. 21. Bukovina. 22. Germany. 24. Reich. 26. Kohl. 30. Repression. 31. Anapa. 32. Galich.
Vertical: 1. Volga. 2. Vienna. 3. Discharge. 4. Goering. 5. Abakumov. 6. Tuva. 7. Garst. 12. Caribbean. 14. Le-lyushenko. 19. Andropov. 20. Nekrasov. 23. Fadeev. 25. Yelnya. 27. Lukin. 28. Ural. 29. "Tiger".
Crossword No. 16.

QUESTIONS:
By horizontal: 8. Indian humanist writer and public figure of the first half of the 20th century. 9. Russian writer, author of “Cursed Days.” 10. One of the political groups in the Convention, led by Danton. 11. The river on which Rome was founded. 13. Leader of the anti-Soviet rebellion in the Tambov region in the years. 14. In Greek mythology: the king of Attica, from whose name the name of the sea comes. 18. A city in the USA where peace was concluded in 1905, ending the Russo-Japanese War. 19. Another name for the Eastern Roman Empire. 20. One of the leaders of the Tula and Ryazan nobles during the Bolotnikov uprising (Soviet scientist, agricultural economist, writer, popular in the 20s of the XX century. 24. The ninth month (May - June) of the French revolutionary calendar, translated as meadow. 25 . Appeal of a political party containing a program of activity or a special act of the head of state 27. “General Jewish Labor Union” founded in Vilna in 1897 29. One of the leaders of Slavophilism, son of a Russian writer of the 19th century 30. River, left tributary of the Oka, near which in 1480 a “stand” took place, putting an end to the Mongol-Tatar yoke 34. An elected head of state with a republican form of government 35. A part of the city allocated for the isolated residence of Jews 36. Payments from peasants to the feudal landowner for the use of land.
Vertical: 1. An island in the Greater Antilles group, discovered by X. Columbus in 1492 and named Hispaniola. 2. One of Caesar’s military leaders, a participant in the conspiracy against him in 44 BC. e. 3. English battleship (built 1906), which gave its name to powerful battleships. 4. The mayor of St. Petersburg, on whom V. Zasulich made an attempt. 5. The state where in 1921, under the leadership of Sukhbaatar, the people's revolution won. 6. One of the leaders of the extreme Jacobins. 7. German philosopher of the 19th century, created the myth of the “superman”, the cult of a strong personality, author of the work “Thus Spoke Zarathustra” and others. 12. One of the leaders of German Social Democracy and the Second International, and a geologist of revisionism. 15. German inventor of printing in the 15th century. 16. The main work of Herodotus. 17. An island off the coast of Greece, near which in 480 BC. e. The Greek fleet defeated the Persian fleet. 22. Russian general. After 1917, he led the White Guard Volunteer Army. 23. French Emperor, native of Corsica. 26. Nickname of Moscow Prince Ivan I. 28. Khan of the Golden Horde. He introduced Islam as the state religion and suppressed an uprising in Tver in 1327. 31. Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars after death. 32. ancient historical and heroic songs (for example, epics). 33. The smallest particle, from the multitude of which, according to Democritus, the world consists.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 8. Tagore. 9. Bunin. 10. Moderate. 11. Tiber. 13. Antonov. 14. Aegean. 18. Portsmouth. 19. Byzantium. 20. Pashkov. 21. Chayanov. 24. Prairial. 25. Manifesto. 27. Bund. 29. Aksakov. 30. Ugra. 34. President. 35. Ghetto. 36. Quit.
Vertical: 1. Haiti. 2. Brutus. 3. "Dreadnought". 4. Trepov. 5. Mongolia. 6. Eber. 7. Nietzsche. 12. Bernstein. 15. Gutenberg. 16. "History". 17. Salamis. 22. Alekseev. 23. Napoleon. 26. Kalita. 28. Uzbek. 31. Rykov. 32. Epic. 33. Atom.
Crossword No. 17.
“Do you know the story?” based on the results of the entire course
stories for high school.
Dagestan" href="/text/category/dagestan/" rel="bookmark">Dagestan, where in 1859 the leader of the highlanders surrendered to the Tsarist troops. 22. Marshal of France, commander of the corps in the campaign against Russia in 1812 23 . English inventor of the steam engine 26. “Rotten Sea”, a system of small bays in the western Sea of Azov, the most important link in the White Guard defense of Perekop 30. The name of the disinformation operation that was successfully carried out by Hitler’s intelligence in early 1942 31. Frankish Margrave, nephew of Charlemagne. Killed in a battle with the Basques in the Roncesval gorge. 34. One of the organizers of the Socialist Revolutionary Party, the leader of a number of terrorist acts. Turned out to be a provocateur. 35. A figure of the Reformation, the founder of one of the movements in Protestantism. “The Pope of Geneva.” 36. The Princely Throne Ancient Russia 39. Leader of a secret revolutionary society in Moscow in the 40s, Hitler's policy of forced annexation of Austria to Germany 41. Prime Minister of Louis
XIII, cardinal who contributed to the strengthening of absolutism in France. 42. A state in Europe where the government has been headed by socialists since 1982.
Vertically: 2. City of Russian gunsmiths. 3. The highest commander of the Cossack army. 5. The name of the sailing sloop of war, on which in the years. Russian expedition discovered Antarctica. 6. In Roman mythology: deity of love. 7. Sailor of the Baltic Fleet, in 1917 chairman of Tsentrobalt, then Soviet military leader. 8. One of the islands of the Kuril chain, disputed by Japan from Russia. 9. The English physicist, who substantiated the law of conservation of energy, determined the equivalent of heat. 11. Abbot of an Orthodox monastery. 12. Russian count, statesman, one of the organizers of the assassination of Paul I. 16. Great Italian painter of the Renaissance, author of the Sistine Madonna. 17. In Ancient Rome: “Temple of all gods.” 20. National hero of the Czech people, ideologist of the Czech reformation. 21. US President 24. The name of one of the two German Reichskommissariat on temporarily occupied Soviet territory. 25. The great Hungarian poet and democrat who led the uprising in Pest in 1849. 27. The leader of the peasant movement in northern Mexico during the revolution. 28. Russian sculptor, author of the monument to Minin and Pozharsky in Moscow. 29. National hero of Mexico, leader of a popular uprising that grew into a war of independence. 32. Leader of the liberation war of the Caucasian highlanders, imam of Dagestan and Chechnya (Greek mythology: god of viticulture and winemaking. 37. Minister of police in France at the beginning of the 19th century, created a system of political investigation and intelligence. 38. City in
Crimea, where a conference of the heads of government of the USSR, USA and Great Britain took place in 1945.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 1. Oistrakh. 4. Habakkuk. 9. Dallas. 10. Ussuri. 13. Yezhov. 14. Marathon. 15. Fleece. 18. Kolchak. 19. Mazepa. 20. Gunib. 22. Davout. 23. Watt. 26. Sivash. 30. "Kremlin". 31. Roland. 34. Azef. 35. Calvin. 36. Table. 39. Ishutin. 40. Anschluss. 41. Richelieu. 42. Spain.
Vertical: 2. Tula. 3. Ataman. 5. "East". 6. Cupid. 7. Dybenko. 8. Shikotan. 9. Joule. 11. Hegumen. 12. Palen. 16. Raphael. 17. Pantheon. 20. Gus. 21. Bush. 24. "Ukraine". 25. Petofi. 27. Villa. 28. Martos. 29. Hidalgo. 32. Shamil. 33. Dionysus. 37. Fouche. 38. Yalta.
Test No. 1.
Russian culture in the XII - XVI centuries.
Specify construction time:
Assumption Cathedral in the Moscow Kremlin. B) Brick walls of the Moscow Kremlin.
The first stone Kremlin in Moscow. G) .
D) Annunciation Cathedral in the Moscow Kremlin. E) Faceted Chamber in the Moscow Kremlin. G) Archangel Cathedral in the Moscow Kremlin.
Possible answers:
1) 1367
3) 1y09
Answers: A-2;B-5;C-1;D-7;D-3;E-4;G-6.
Test No. 2.
Indicate which of the figures of Russian culture:
published the book “Apostle”; B) cast the Tsar Cannon;
painted the Trinity icon;
D) wrote the poem “Zadonshchina”; D) compiled the “Great Menaions”; E) wrote “Walking across the Three Seas”; G) built the “Assumption Cathedral in the Moscow Kremlin”; 3) painted churches in Novgorod and Moscow with frescoes and icons;
I) created the “slave doctrine”;
K) built the Intercession Cathedral on Red Square in Moscow.
Possible answers:
1) Andrey Chokhov. 6. Theodosius Kosoy.
2) Sophony of Ryazan. 7. Afanasy Nikitin.
3) Ivan Fedorov. 8. Theophanes the Greek.
4) Andrey Rublev. 9. Barma and Postnik.
5) Macarius. 10. Aristotle Fioravanti.
Answers: A - 3; B - 1; AT 4; G - 2; D - 5; E - 7; F - 10; 3 - 8; I - 6; K-9.
Test No. 3. Economic and socio-political development of Russia in the second halfXVIIcentury.
A) Issuance of a decree on the right of landowners to exile serfs
peasants to Siberia.
B) The reign of Catherine II Alekseevna.
B) Activities of the “Commission for drafting a new
th Code".
D) An uprising led by D) Publication of the Charter of the nobility - “Charter of the rights, liberties and advantages of the noble Russian nobility.”
E) Cancellation of internal customs duties. G) “Plague riot” in Moscow.
3) Publication of the Manifesto “On the granting of liberty and freedom to the entire Russian nobility.”
I) Publication of a Decree prohibiting peasants from complaining about landowners.
K) Publication of the Letter of Complaint to the cities. K) Publication of a Decree ordering landowners to exile serfs to hard labor. M) The reign of Paul I Petrovich.
H) Carrying out provincial reform.
O) The reign of Peter III Fedorovich.
P) Publication of the Manifesto on freedom of enterprise.
Possible answers:
1.1754 9.1771
2.1760 6.1765
3. years 7.1767
4. 1762 8.1 12.1785
Answers: A - 2; B - 5; AT 8; G - 10; D - 12; E - 1; F - 9; 3 - 4; I - 7; K-12;L-6;M-13;N-11;0-3;P-11.
Test No. 4. Russian culture in the second halfXIXcentury.
Indicate which of the Russian scientists of the second half of the 19th century. made a great contribution to the development of:
mathematics; B) physicists;
D) biology and medicine;
D) geography and ethnography;
E) history, philosophy, sociology and political economy.
Possible answers:
1) . 12. SV. Kovalevskaya.
4) A. S. Popov. 15. A. M. Lyapunov.
6) SM. Nightingale. 17. .
7) -Tian-Shansky. 18. .
8) A. M. Butlerov. 19. .
11) -Maclay. 22. .
Answers: A-3, 12.15; B-4, 9, 14, 19; V-8, 17; G - 1, 5, 10, 16; D - 2, 7, 11; E - 6, 13, 18,20,21,22.
Test No. 5. Indicate the names of Russian cultural figures who contributed to the second halfXIXcentury of development:
A) literature;
B) painting;
B) architecture;
D) sculptures;
D) drama theater;
E) music, opera and ballet.
Possible answers:
5) . 18. I. L.. Ropet.
9) A. M. Opekushin. 22. .
11) -Korsakov. 24. .
12) . 25. -Shchedrin.
Answers:, A-3, 6, 7, 12, 13, 17,<22>, 25; B - 1, 8, 14, 20; B-4, 18.23; G-2, 9, 26; D-<7>, 15, 16, 21, 22; E-5, 10, 11, 19,24.
Test No. 6.
Indicate the dates characterizing the labor movement:
A) “Obukhov Defense” - clash of workers Peter
burg with troops.
B) General strike of Baku workers.
B) General strike Ivanovo-Voznesenskaya.
D) “Industrial war” of the workers of St. Petersburg. D) General strike of workers in different cities of Russia. E) Political strikes of workers after the Lena execution. G) A strike by workers in St. Petersburg, after which a law was passed limiting the working day to 11.5 hours.
3) Strikes and political demonstrations of workers of Rostov-on-Don, accompanied by active clashes with the police.
I) General All-Russian October political strike.
K) General strike of workers in the south of Russia.
Possible answers:
Answers: A - 3; B - 7; AT 5; G - 1; D 2; E - 9; F - 2; 3-4; I -5; K-5.
Test No. 7. Russian foreign policy at the beginningXXcentury.
Arrange the events of the Russo-Japanese War in chronological order.
Signing of the Portsmouth Peace Treaty.
An attack by a Japanese squadron in the port of Chemulpo on two Russian ships: the cruiser Varyag and the gunboat Koreets.
Surrender of the Port Arthur fortress by General A. M. Stessel.
Death of Vice Admiral SR. Makarov and his staff on the ship "Petropavlovsk"
Attack of Japanese ships on the Russian squadron in the roadstead of the Port Arthur fortress.
Counter-offensive of Russian troops on the Shahe River.
The first assault on the Port Arthur fortress by Japanese troops.
Defeat of the Russian army near the city of Mukden.
Japanese landings in Korea and on Liaodong Island.
The death of the Russian squadron near the island of Tsushima.
The battle of Liaoyang - the Russian army's disruption of the Japanese offensive.
Answers: 5,2,4,9,7, P,6,3,8, 10, 1.
Test No. 8,
Indicate which of the socio-political figures of Russia at the end of the 19th - beginning of the 20th centuries. was:
A) the leader of the Cadet Party, a famous historian and publicist;
B) the leader of the Progressive Party and the Progressive Bloc. ka":
C) Minister of Internal Affairs in 1. and the boss
"gendarmes; D) Minister of Internal Affairs and Chairman of the Council of Ministers in 1st year;
D) Minister of Railways, Minister of Finance in 1, Chairman of the Committee of Ministers, in October 1905 - April 1906. Chairman of the Council of Ministers;
E) populist, Marxist, organizer of the “Emancipation of Labor” group, leader of the Menshevik wing of the RSDLP.;
"G) a “legal” Marxist, then the leader of the Union of Liberation, from 1905 a member of the Central Committee of the Cadet Party; 3) the main theorist and leader of the Socialist Revolutionary Party; I) leader of the Union of October 17, chairman of the III State
| Vienna Duma;
K) leader of the Octobrists, chairman of the IV State Duma;
K) organizer of the RSDLP, leader and theoretician of Bolshevism; M) Chairman of the First State Duma, cadet.
Possible answers:
SY. Witte. 7. .
11. (Lenin).
Answers: A - 4; B - 9; AT 3; G - 2; D - 1; E - 6; F - 8; 3 - 7; AND -
5; K-10; L-11; M - 12.
shortcodes">
1
Secondary school No. 35
Additional history materials
Crosswords
A history teacher,
Honorary Worker of General Education
Russian Federation
Vorobyova Natella Rafikovna
Art. Novotitarovskaya
Crossword No. 1. Currents of social life in Russia second
half of the 19th century.
QUESTIONS:
Horizontally: 3. What is the name of the movement that is “fearful” of change? 4. This direction appeared when
Nihilism, that is, the denial of noble values, began to spread among young people, and the idea that a return to the old was needed took over the minds. 5, What is the name of the group that went over to terror, organized by Ishchuchintsev? 7. A movement whose followers believed that reforms would not change anything, that a revolution was needed and there was no need to prepare for it. 10. The main feature of the populists; protecting the interests of the people.
Byverticals: 1. What is the name of the movement whose followers believed that one must remember one’s duty to the people, there must be faith in socialism, that the peasants must be prepared through propaganda. 2. A current that required change. 6. What is the name of the movement whose representatives believed that an organization with strict discipline was needed so that no one knew about it. 8. Who created the “Union of Struggle for the Liberation of the Working Class”? 9. Who led the propaganda movement?
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Conservative. 4. Populism. 5. “Hell” 7. Rebellious. 10. Democracy.
Vertical: 1. Propaganda.
2.
Liberal. 6. Conspiratorial. 8. Lenin. 9. Lavrov.
Crossword No. 2.

QUESTIONS:
1. City. 2. A town in the foothills of the Alps. 3. Commander-in-Chief of Russian troops in the war with Turkey of 1787-1791. 4. The village where peace was signed. 5. The commander who commanded the Russian troops in the Seven Years' War of 1756-1763. 6. Fortress. 7. Commander. 8. Snow ridge in the Alps. 9. Fortress. 10. Inaccessible mountain range in the Alps. 11. The name of the famous campaign of A.V. Suvorov.
Keyword: SWISS.
Crossword No. 3.
QUESTIONS: 1. Fortress. 2. A town in the foothills of the Alps. 3. Honorary title A.V. Suvorov. 4. Fortress on a spit near the Dnieper -
Sko-Bug estuary. 5. Famous naval commander. 6. Central mountain range of the Alps. 7. Famous Russian commander, ally of A.V. Suvorov and M.I. Kutuzova. 8. Fortress. 9. Name of the bridge.
Keyword: A.V. SUVOROV.
Crossword No. 4. Find the word!

QUESTIONS:
1.
An activity in which ancient man used a harpoon. 2. One of the first activities of ancient man. 3. Human tools (30-20 thousand years ago). 4. The first stone human tool (200 thousand years ago). 5. A tool made of bone or horn. 6. A huge animal that was hunted by people. 7. One of the stone tools (13-7 thousand years ago). 8. Man's first home. 9. One of the first means of transportation of ancient people on water. 10. Leader of a military squad, ruler of a feudal state. 11. First pet. 12. Farmer’s tool (13-7 thousand years ago). 13. The occupation of ancient man, which arose from hunting. 14. The most ancient and simplest tool (200 thousand years ago).
Crossword No. 5. Dare to read!

QUESTIONS:
1. A means of human transportation on water from ancient times to the present day. 2. A group of primitive people who are related and lead a common household. 3. One of the first activities of ancient man. 4. Tools made of copper (6-5 thousand years ago). 5. Tools for cultivating the land (13-7 thousand years ago). 6. A farmer’s labor tool, which appeared as a result of the improvement of the hoe (605 thousand years ago). 7. First pet. 8. Material for making dishes on a pottery wheel. 9. Human tools and weapons (200 thousand years ago). 10. Association of several clans living in one area.
Crossword No. 6.
QUESTIONS:
1. The name of forced duties performed by serfs. 2. What improvements in metallurgy marked the 16th century? 3. What were the names of the Bulgarian and Serbian partisans? 4. What are people who profess Islam called? 5. What did the emperor collect from merchants for transporting and selling goods? 6. What did the vassals call their master? 7. Traveling actors who performed in cities and villages. 8. The name of the Muslim temple.
9. What were the records of events by year called? 10. Protective
armor that replaced chain mail. 11. Decoration at the top of the columns
us. 12. People who exchanged money from different countries.
ANSWERS: 1. Duties. 2. Blast furnace. 3. Haiduki. 4. Muslims. 5. Duty. 6. Senor. 7. Jugglers. 8. Mosque. 9. Chronicles.
10. Shell. 11. Capital. 12. Money changers.
Key word: INDULGENCE.
Crossword No. 7"

QUESTIONS:
1. Provincial division unit. 2. Temporary cessation of hostilities. 3. The closest friend of Peter I. 4. Nobles under Peter I. 5. The city founded by Peter the Great. 6. “Great, wise mother of the Fatherland.”
ANSWERS: 1. District. 2. Truce. 3. Menshikov. 4. Boyars. 5. Petersburg. 6. Ekaterina P.
Keyword: RECRUIT.
Crossword No. 8.

QUESTIONS:
1. The first Russian emperor. 2. The central state governing body under Peter I. 3. A written appeal from the supreme power to the people. 4. The central body for managing church affairs. 5. Central institution for the management of cities. 6. Modern central government authority. 7. One of the achievements of science during the reign of Peter I.
ANSWERS:
1. Peter. 2. Senate. 3. Manifesto. 4. Synod. 5. Magistrate. 6. Duma. 7. Printing house.
Keyword: REFORM.
Crossword No. 9.

QUESTIONS:
Horizontal: 3. The name of the legendary king of England, the hero of chivalric novels. 4. Leader of the uprising in Azerbaijan, directed against Arab domination. 6. Clergyman. 9. The name of the Arab religion. 10. Holy city of Muslims.
Vertical: 1. What was the mid-century name for a person who opposed the teachings of the Catholic Church? 2. Representative of the ruling class in the Middle Ages. 5. City in Palestine. 7. Capital of the Arab Caliphate. 8. The name of one of the Germanic tribes.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Arthur. 4. Babek. 6. Bishop. 9. Islam. 10. Mecca.
Vertical: 1. Heretic. 2. Feudal lord. 5. Jerusalem. 7. Damascus. 8. Franks.
Crossword No. 10.

QUESTIONS: Horizontal: 8. The order of arrangement of lands in a feudal estate.
Vertical: 1. Large land owner in the Middle Ages. 2. The people against whom Charlemagne waged numerous wars. 3. The home of a large feudal lord in the Middle Ages. 4. Weapons used in ancient times and the Middle Ages. 5. The name of the most powerful ruler of the Frankish Empire. 6. The river on the banks of which the Franks originally lived. 7. The river on the banks of which one of the tribes of the Eastern Slavs settled.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 8. Striped.
Vertical: 1. Senor. 2. Saxons. 3. Castle. 4. Sword. 5. Karl. 6. Rhine. 7. Oka.
Crossword No. 11.

QUESTIONS:
Horizontally: 1. An ordinary member of the monastery community. 4. Small-scale production in a medieval city, based on manual labor. 5. Pseudoscience about combining various substances to obtain gold. 6. Abbot of the monastery. 8. Fortified place, settlement of artisans and merchants.
Vertical: 1. A picture made of colored pebbles or pieces of glass. 2. Part of communal land owned by an individual family. 3. State of the Arabs. 7. Vassal of a duke or count and lord of knights.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 1. Monk. 4. Craft. 5. Alchemy. 6. Abbot. 8. City.
Vertical: 1. Mosaic. 2. Allotment. 3. Caliphate. 7. Baron.
Crossword No. 12.

QUESTIONS:
Horizontal: 3. Pseudoscience of predicting the future by the location of the stars. 5. Military servant of the feudal lord. 7. City Council building in Western Europe.
Byverticals: 1. Military competition of knights in strength and dexterity. 2. Owner of land and serfs in the Middle Ages. 3. Pseudoscience about combining various substances to obtain gold. 4. Annual auctions in which merchants from different cities and countries took part. 6. The main church in the medieval city. 8. A collection of rules binding on all members of a guild in a medieval city.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 3. Astrology. 5. Vassal. 7. Town Hall.
Vertically: 1. Tournament. 2. Feudal lord. 3. Alchemy. 4. Fairs. 6. Cathedral. 8. Charter.
Crossword No. 13. For the period 1985 - 1996.

QUESTIONS: Horizontal: 6. Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the USSR during the reign of M.S. Gorbachev. 7. Senior assistant to the President of the Russian Federation since 1991. 10. State tax from the population and enterprises. 11. Nationality of Aman Tuleyev, Minister for CIS Affairs in the government of B.C. Chernomyrdin. 12. Leader of the Yabloko movement. 15. Leader of the PRES, former Deputy Prime Minister, representative of the President of the Russian Federation in the Constitutional Court since 1996. 18. Literary and artistic magazine popular in the late 80s. 19. Leader of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation. 20. The court clique, running state affairs in their own personal interests, the president’s entourage. 21. Supreme Legislative Representative Assembly. 24. Leader of anti-reform forces in the late 80s, member of the Politburo of the PC CPSU. 26. Privatization check. 27. Mayor of St. Petersburg in the early 90s. 31. One of Gorbachev’s slogans in 1985 - 1986. 33. “Hot spot” of Russia in 1994 - 1996. 34. First Deputy Prime Minister in the government of reformers, Deputy Chairman of the State Duma in 1996. 35. City where, thanks to the support of M.S. Gorbachev, in 1989 the wall dividing it into West and East was destroyed. 36. Head of independent Turkmenistan since 1991
Vertical: 1. The sphere of commodity circulation, the goal of transformation of Russian reformers in the early 90s. 2. The city, the site of the main events of the coup attempt in August 1991. 3. The former name of the city of St. Petersburg. 4. First President of the Russian Federation. 5. A state in the East that is successfully implementing market reforms. 8. Chairman of the Russian government in 1991-1992, leader of the “Choice of Russia” movement. 9. The name of the far-right national-patriotic front. 13. President of Kazakhstan since 1991. 14. State, in form opposite to the federation. 16. One of the leaders of the orthodox communists in the early 90s. 17.. Well-known human rights activist, plenipotentiary of the President of the Russian Federation for human rights. 22. Subject of the Russian Federation, capital Kazan. 23. Chechen terrorist, “hero” of the city of Budyonovsk. 25. Name of the Popular Front of Lithuania, leader V. Landsbergis. 28. Subject of the Russian Federation, capital city of Vladikavkaz. 29. Minister of Finance of the Russian Federation since 1996. 30. One of the leaders of the State Emergency Committee. 32. Resort village in Crimea, where M.S. was staying during the 1991 coup. Gorbachev.
ANSWERS:
Horizontal: 6. Ryzhakov. 7. Ilyushin. 10. Tax. 11. Kazakh. 12. Yavlinsky. 15. Shahray. 18. "Youth". 19. Zyuganov. 20. Camarilla. 21. Parliament. 24. Ligachev. 26. Voucher. 27. Sobchak. 31. Acceleration. 33. Chechnya. 34. Shokhin. 35. Berlin. 36. Niyazov.
Vertical: 1. Market. 2. Moscow. 3. Leningrad. 4. Yeltsin. 5. China. 8. Gaidar. 9. Memory. 13. Nazarbayev. 14. Unitary. 16. Tyulkin. 17. Kovalev. 22. Tatarstan. 23. Basayev. 25. Sąjūdis. 28. Ossetia. 29. Livshits. 30. Yanaev. 32. Foros.
Crossword No. 14. For the period 1939 - 1996.
QUESTIONS:
Horizontally: 5. Leader of the PRES, former Deputy Prime Minister, representative of the President of the Russian Federation in the Constitutional Court since 1996. 6. Soviet writer, author of the story “Alive”. 10. Soviet academician, physiological scientist, falsely accused in 1949 of having connections with US intelligence. 11. Brand of an American fighter supplied under Lend-Lease to the Soviet Union during the war. 12. Partisan warfare during the war, aimed at destroying communication lines, roads, bridges. 15. Privatization check. 18. Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation, who started the war in Chechnya. 19. The first cosmonaut of the world. 20. Union-republican body that carried out long-term and current planning of the national economy. 21. Former Soviet republic, capital Chisinau. 24. Soviet scientist, academician, one of the creators of the thermonuclear bomb. 26. Soviet scientist, academician, founder of liquid rocket propulsion. 27. Paratrooper general, one of the presidential candidates in the 1996 elections. 31. Marxist-Leninist theory, which for a long time was the state ideology in the USSR. 33. Capital of the Republic of Belarus. 34. Mayor of Moscow in the early 90s. 35. City on the river. Elbe, where the Soviet and American wars met in 1945. 36. Vice-President of the Russian Federation until 1993. Former Afghan pilot.
Vertical: 1. Organized crime, secret terrorist organization. 2. Secretary of the Writers' Union in the 40-50s, author of the novel “Young Guard” 3. Commander of the Sumy partisan unit, conducted several raids behind the Nazis’ rear lines. 4. Soviet writer-villager, author of “Carpenter's Stories”. 7. Chairman of the Russian Government in 1991-1992, leader of the “Choice of Russia” movement. 8. Soviet violinist, founder of the Soviet violin school, participant in front-line concerts during the war. 9. First Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee, author of the famous report at the 20th Congress “On the Cult of Personality.” 13. The capital of Finland, where in 1975 Brezhnev signed the Final Act of the Conference (CSCE). 14. Soviet composer, pianist and conductor, author of the ballet “Romeo and Juliet” and many other works. 16. Territory in the Caucasus, which became the subject of a military conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan. 17. Famous Soviet writer, poet. Author of the poem “Wait for Me”, the novel “The Living and the Dead” 22. The name of the Belarusian residence in Belovezhskaya Pushcha, where the Agreement on the creation of the CIS was signed on December 8, 1991. 23. First President of the Russian Federation. 25. One of Stalin's closest associates. 28. Mayor of St. Petersburg in the early 90s. 29. Founder of the People's Republic of China, great friend of the USSR. 30. A city in the North-West of Russia, which has become a border city since 1991. 32. Resort village in Crimea, where M.S. was staying during the 1991 coup. Gorbachev.
Representative of one of the directions of Russian social thought of the 19th century
First letter "s"
Second letter "l"
Third letter "a"
The last letter of the letter is "l"
Answer to the question "Representative of one of the directions of Russian social thought of the 19th century", 10 letters:
Slavophile
Alternative questions in crossword puzzles for the word Slavophile
A word whose invention is attributed to the Russian poet K.
A word whose invention is attributed to the Russian poet K. Batyushkov
Supporter of Slavophilism
Supporter of Russian thought
Definition of the word Slavophile in dictionaries
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. D.N. Ushakov
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. D.N. Ushakov
Slavophile, Moscow (book, history). Supporter of Slavophilism; opposite Westerner. Supporter of cultural and political rapprochement with Slavic peoples and states, friend of the Slavs; opposite Slavophobe. See (phil).
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova.
-a, m. Supporter of Slavophilism. and. Slavophile -i. adj. Slavophile, -aya, -oe.
New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova.
m. Supporter of Slavophilism (1*). Representative of Slavophilism (1*). m. One who treats favorably, with interest and respect everything Slavic, the Slavs themselves (opposite: Slavophobe).
Examples of the use of the word Slavophile in literature.
Sergei Sergeevich Averintsev once very correctly noted that in the past Slavophiles and the Westerners were people who opposed each other, but knew how to respect their opponent.
Here everyone works for him - as before, Vasilievka, Moscow and St. Petersburg, Westerners and Slavophiles.
Vadim Passek, Vitberg, Polezhaev, from an emphatically impartial story about Slavophiles to touchingly tender commemorations of friends, from the majestic portraits of Garibaldi, Owen, Mazzini to the subtle irony in the characteristics of such figures of the 1848 revolution as Ledru-Rollin and others.
All these laws of social development were in effect in the Nicholas era, and due to their action, the youth of the Nicholas era became carried away by second-rate, false ideas, the ancestor of which was Voltairianism and Freemasonry, and did not become the ideological heir to the treasures left by Pushkin, Gogol and Slavophiles.
The most diverse strata of society, Westerners and Slavophiles, liberals and conservatives - all unitedly opposed the Polish rebels.
According to Speransky, political rights, which consist “of participation in state forces: legislative, judicial and executive,” should be enjoyed
(*answer*) Owners only
All adult male citizens
All citizens of Russian nationality
All citizens without exception
According to C. Fourier, at the head of the phalanx is
(*answer*) Areopagus
Sanhedrin
Prime Minister
Senate
According to Speransky’s proposal, the
(*answer*) State Council
Imperial Council
The Supreme Council
Secret committee
The political thinker of the mid-19th century, who in his book “On Freedom” paid close attention to the possible negative consequences of democracy, namely, the despotism of public opinion, was
(*answer*) J.S.Mill
O.Comte
A.Hamilton
R.Owen
Colonel, participant in the Patriotic War of 1812, founder and leader of the Southern Society of Decembrists, author of the constitutional and legal treatise “Russian Truth” - this
(*answer*) P.I. Pestel
N.M. Karamzin
K.D.Kavelin
N.M. Muravyov
After 1821, two organizations arose almost simultaneously in Russia on the basis of the “Union of Welfare”
(*answer*) Southern and Northern societies
"Land and Freedom" and "Liberation of Labor"
"Union of Salvation" and "Narodnaya Volya"
Western and Eastern societies
He proposed a two-stage scheme for the abolition of serfdom: first, peasant duties are limited, the personal liberation of peasants from the landowners is carried out, and then the right of transition is returned to the peasants (Yuriev Day)
(*answer*) M.M. Speransky
K.S. Aksakov
N.M. Karamzin
P.I. Pestel
Proposed a plan for the reorganization of Russia on the principles of a constitutional monarchy, in which the Emperor would henceforth be considered as the highest official ("the supreme official of the Russian government"), taking an oath of allegiance to the constitution
(*answer*) N.M. Muravyov
N.M. Karamzin
P.Ya.Chaadaev
P.I. Pestel
He assumed that Russia went through three stages in its historical development: in the Middle Ages - appanage; in modern times - absolute monarchy; and in the present period - the industrial state
(*answer*) M.M. Speransky
P.Ya.Chaadaev
N.M. Karamzin
Alexander I
Representatives of the direction of Russian social thought of the mid-19th century, who advocated the development of Russia along the Western European path, were called
(*answer*) Westerners
Socialists
Populists
Slavophiles
Representatives of one of the directions of Russian social and philosophical thought of the 40s - 50s of the 19th century, who spoke with the justification of a special, different from Western European, path of historical development of Russia, were called
(*answer*) Slavophiles
Populists
Soil scientists
Westerners
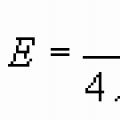 Ostrogradsky–Gauss theorem
Ostrogradsky–Gauss theorem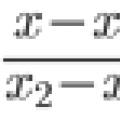 How to learn to solve problems in analytical geometry?
How to learn to solve problems in analytical geometry? The meaning of the word mercantile The meaning of the word mercantile
The meaning of the word mercantile The meaning of the word mercantile