The origin of man theory and hypothesis briefly. Abstract: Theories of the origin of man
This question interests almost everyone. At least, I do not know a single person who would not like to know the answer to it. And so it has always been. I thought about this problem for ten or eleven years.
About how specific living beings appear - individuals, people have known for a very long time. Adult individuals of animals give birth to their own kind. For this, females and males are needed, their copulation is necessary, the female must become pregnant from this copulation and after some time, having carried the fetus, give birth to a cub. A new individual appears small and weak, it needs the care of parents, grows and after a certain time turns into an adult individual - male or female. And everything repeats. Children are born who are like their parents. At a certain stage of their ontogenesis, they produce offspring.
And so it was, so it is, and so it will be. Our distant ancestors always knew about this. It seems to me that even the higher animals know this. The child asks the adult: “Daddy, where do babies come from?”. The answer to it may sound like this: "Of course, in cabbage." Other adults disagree with this theory: "Of course the stork brings." The most theoretically advanced parents answer: “The doctor cuts the mother’s tummy and takes the children out of there.” A child at the age of 10-12 learns from his older friends in the yard that one mother is not enough to have a baby in her stomach. Finally, at the age of 13-14 at school in a biology lesson, he learns the real answer to the question posed at 3-4 years old.
And where did the very first dad and the very first mother come from? And who took the very first birth of the very first woman? This is the question of the origin of Homo sapiens as a species of living beings on Earth. Religion answers it simply: “The first man (of course, a man!) was created by God in his own image and likeness. Seeing that the man was uncomfortable alone, the same god took a rib from him and created the first woman from this rib. But God did not teach them to multiply, because he considered that he had created immortal creatures, like himself. But God was wrong. The first people were mortal. Then the devil came to the rescue in the form of a snake and taught the first people to multiply. God realized that people would multiply quickly and there would not be enough space for them in paradise, they would embarrass the Lord God. He took and drove his creatures from paradise to earth. It seems to me that this explanation of the origin of Man is of the same level of plausibility as the explanation of the appearance of a sister to an older brother by the fact that she was found in cabbage.
The problem of the origin of man
Another concept of the appearance of the first people on Earth boils down to the fact that their ancestors flew from space, could not return back, gradually their descendants gradually settled down on Earth. Perhaps, in order to adapt to the conditions of the new world for them, these aliens “conjured” a little with the local monkeys and, with the help of genetic engineering, created the first man and the first woman. I believe that this answer is consistent with the explanation that the stork brings children.
Charles Darwin proposed a third answer, the essence of which is simple: "Man appeared on Earth in the process of natural evolution of the animal world, and the great apes were the distant ancestors of Man." He brought natural scientific proof of his theory from the field of comparative anatomy. I equate this answer in truthfulness and closeness to the truth with explaining the appearance of children by getting them out of their mother's tummy. It is clear that this is closer to the truth than the stork hypothesis, and even more so than the cabbage hypothesis.
Friedrich Engels decided that the ape turned into a Man through work. A bold idea, right in the spirit of Lamarck. The role of labor in humanizing the monkey reminds me of the role of a doctor, without whose help the baby cannot get out of the mother's tummy. Only for some reason, chimpanzees and gorillas, despite the hard work of obtaining food, for hundreds of thousands of years have not turned into people.
I want to offer on the pages of this site an explanation of the origin of Man on Earth, other than F. Engels. Its essence is that no labor has produced a human from a monkey. But what then made the ape Man? So, let's look for the factor due to which the mother monkey, having become pregnant from the father's monkey, gave birth to the first person.
What is evolution, and why could a person on Earth have arisen naturally, like many other types of living beings?
I do not believe that the evolution of living beings on our planet is a random process, and I do not believe that the emergence of a new species is a simple game of chance. What seems to us random from the “test tube and flask point of view” is not accidental “from the point of view of the biosphere as a whole”. We still have a very poor understanding of the laws of large numbers, large spaces, large times, and superdiversity. The lady's slipper orchid flower arose not as a whim of Nature, not as a game of chance, but at least as part of the "plant - insect pollinator" system. But all the living beings that make up the biocenosis have evolved not separately, but together. Evolution is the co-evolution (joint interconnected evolution) of hundreds and thousands of species of plants, microorganisms, animals and fungi. The mode (direction or vector) of co-evolution can change, and in some epochs this change can be abrupt. In such epochs of change, fundamentally new habitats arise on our planet, accordingly, new biocenoses are formed and, of course, new species and even new genera and families of living beings appear. But species populations evolve in conjugation with each other, and not separately.
Human origin concepts
In relatively calm geological epochs, the biosphere and its constituent genetic systems - species - change little. We live in a relatively stable era, so it seems to us that species changes are rare and accidental. In addition to rapidly and dramatically mutating influenza viruses, hepatitis and other pathogens, little changes in our biosphere.
Although ... In the last 2-3 hundreds of years, many species of living beings have disappeared from the face of the Earth. Have new species emerged? I think there must be something.
Humanity has caused the extinction of many species of living beings, but it can also cause the emergence of new species as a result of genetic engineering and increased levels of radiation and chemical pollution. In general, evolution in the biosphere leads to an increase in the stability of its main parameters, allows it to survive in sharply changing conditions of climate, orography, background radiation, etc. Evolution in the biosphere is an anti-entropic process.
That's what scientists say. The life of the biosphere is a constant opposition to the growth of chaos, the thermal depreciation of energy. Everything that resists chaos is evolution. By creating thermodynamics, scientists have created a science that can be compared to a bird with one wing. Such a bird cannot fly, and even then it walks with difficulty, constantly making zigzags.
Today, the second wing of scientific knowledge is being created - the theory of self-organization. Here in it lies the key to understanding the process of evolution, which led to the appearance of Man on Earth. The self-organization of matter is just as natural a process as its degradation. Moreover, these two processes are inextricably linked with each other, generate and support (nourish) each other. Good and evil, entropy and negentropy, god and devil are all different expressions of two sides of the same coin.
This medal is the Universe, at least that part of it that is given to us in sensations and in ideas. Remember M.V. Lomonosov: "If where a few of the matter is combined, then exactly the same amount of it will be combined in another place." Today we take the next step and say: "If some chaos is added somewhere, then exactly the same amount of order will be added elsewhere." It is the entropy processes on our planet, leading to the destruction of mountains and the peneplanation of continents, to the dissipation of the internal energy of the planet and the energy of the Sun, leading to the alignment of thermodynamic gradients in the geosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere, that caused the opposite processes - the processes of evolution of the biosphere, its constituent ecosystems and genetic systems - species.
Hypotheses of the origin of man
I am a supporter of the pulsating Earth hypothesis. The main provisions of which are set out on this site. Here I will try to link the theory of the origin of Man on Earth (of course, in a natural way!) With the hypothesis of a pulsating Earth. And then it will become clear to everyone that "We are the children of the Galaxy."
Why did an amphibious monkey have to arise on Earth at the beginning of the Paleogene?
Mammals appeared at the end of the Mesozoic era, about 70-80 million years ago. But then reptiles - dinosaurs - dominated the ecosystems of land, water and air. The first mammals that arose in the second half of the Mesozoic era occupied third-rate ecological niches and were small, most similar to modern mice. Of course, they could not compete directly with dinosaurs and did not try to do so. They were the new, which, compared with the massive old, seems pathetic and miserable.
But then a global catastrophe happened. The conditions of life on the planet changed dramatically, and dinosaur monsters began to die out. Not from competition with miserable mammals, but primarily from climate change, as a result of which their habitat was destroyed. When dying out, reptiles liberated various ecological niches: on land, in water and in the air. It was in these niches that the modus of evolution of different taxa of animals turned out to be, representatives of which were able to survive in this planetary catastrophe. Mammals survived, and in the absence of competition from the Mesozoic monsters, they began to multiply intensively and fill the vacant niches, first of all on land, then in water. They're out of luck with air. Some small reptiles were able to survive the disaster and turned out to be the main contenders for capturing the air. They transformed into birds, occupied the air environment and kept it, not letting mammals into it. Mammals simply did not have time to evolve and capture the air. What happened can be formulated as follows: "Who did not have time, he was late," - so says the wisdom of the people. Thus, birds are the same age as mammals in geological time.
The Alpine orogeny cycle at the beginning of the Cenozoic Era is a geological epoch during which the globe contracted. First of all, the thin basalt crust at the bottom of the oceans and deep seas was crumpled into folds, caved in in some places and piled up with huge blocks crawling on top of each other in others, the continental crust of human origin. In the center of the oceans, mid-ocean ridges rose from the bottom of the sea, and on the continents blocky mountains and vaulted weakly dissected uplifts of the Tibet and Pamir type formed. At the same time, the volume of the bath of the world ocean was reduced, and the water flooded the lowlands and plains. The land area has decreased, and the area of shallow water has increased dramatically. Due to the predominance of the area covered by water over the land area, the climate on Earth as a whole then became more humid and less continental.
At that time, in almost all large taxa (families and orders) of mammals (and not only mammals!) the vectors of evolution changed towards humid tropical and subtropical forests, swamps and aquatic ecosystems. There were migrations of species adapted to living in the humid regions of the Earth, deep into the continents, where the climate became wetter and milder. Phylogenetic adaptations towards feeding shallow waters led to the emergence of new genera of amphibious mammals (seals, fur seals, walruses, sea lions), some taxa of mammals almost completely lost contact with land over time (cetaceans).
Proof of human origin
We see phylogenetic adaptations to the aquatic environment among rodents (beavers, water voles), ungulates (hippos) and other orders. Surely, in the order of primates (or maybe their direct ancestors) in this era, a branch also arose in the direction of the development of the aquatic environment. Most likely, they were tailless monkeys related to the long-extinct dryopithecus and australopithecines, as well as modern chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. In the beginning, shallow waters were feeding places for them, mollusks, frogs were found in abundance here, it was possible to feast on small fish and caviar. In order to get all this, one had to go into the water, dive headlong into it (dive), swim in order to cover the distance from one shallow to another without going to land. A new ecological niche, which appeared as a result of the compression of the Earth in the form of shallow, well-heated sea bays, estuaries, was a new mode of evolution for many species of plants and animals, which, adapting to it, transformed into new species and genera and formed new communities and ecosystems. Shallow waters not only fed, but also saved these monkeys from predators that attacked both from the ground and from the air. Here you could save yourself in a forest fire. The mild warm climate contributed to the development of shallow water by monkeys.
The process of adaptation of monkeys to the aquatic environment lasted several million years, it ended with the emergence of a new genus, which we call Homo (Man). This happened (the appearance of the genus Homo) no less than 10-15 million years ago. In all likelihood, then this genus was represented by many species that lived on different continents, in fresh, salty and brackish waters. Some of them were more adapted to life in water, others less, some were more thermophilic, others less. Almost all the main anatomical, physiological and morphological features of modern Man, which distinguish him from monkeys, then arose 10-15 million years ago as adaptations to living in two elements at once - in water and on land. These are: the loss of hair to a large extent, bipedalism, the ability to dive and see under water, the subcutaneous layer of fat as a device to protect against hypothermia, the use of various objects to extract mollusks from shells, dexterous fingers capable of subtle manipulation, degradation of the toes , wide palms and feet, which arose not as adaptations for movement on land, but as adaptations for swimming, and much more. 3.8 million year old fossil human footprints found on fossilized volcanic ash in Africa suggest that by this time walking on two legs was the norm for Man.
The ancient Homo, however, never completely lost touch with the land. On land in the coastal strip, they built nests and shelters, slept, mated, spent their free time, collected bird eggs, fruits and rhizomes of coastal plants. That is why they did not turn into seals, beavers or mermaids. Living in two elements at once contributed to the development and complication of the nervous system, including its central part - the brain. Fangs and powerful jaws were not needed for creatures that eat shellfish. They escaped from enemies on land by jumping into the water, and from enemies from the air - by diving or hiding in dense coastal thickets of bushes, as well as in holes along the banks of water bodies.
The ancient females of Homo gave birth to cubs in the water, so the cubs first learned to swim, and then crawl on all fours and only then walk on their hind limbs, first in the water, and then on land. Short forelimbs made it impossible to move on all fours. In general, moving on land on only two hind limbs is a biomechanical nonsense that cannot be explained if we assume that the ancestors of man were monkeys that lived in trees. Adapting to life in the savannah, such monkeys had to keep moving on all four limbs. By the way, they did just that (chimpanzees, gorillas). When walking upright, the load on the spine increases sharply. Diseases of modern people associated with the spine are a consequence of the fact that we were created to live in water, where gravity is greatly reduced by the Archimedean buoyancy force, we are forced to live on land.
The origin of man from animals
Probably, each person, according to his nature, should spend at least 2-3 hours daily immersed in water and thereby giving rest to his skeleton and muscles, which ensure upright walking on land. Swimming pools should be made not only in apartments and sports complexes, they should be in offices, factories and factories. And how wonderful we feel when plunging into a pool of water or into a bath! Why? Yes, because it is our native, it is deeply rooted in our genetic memory of the origin of man. And the inexplicable passion of many for fishing ... For the sake of a dozen fish the size of a finger, many modern men spend many hours on ice, in the cold, sometimes risking their lives. This, too, is nothing but the atavistic call of genetic memory. The vast majority of people wash their faces in the morning, rinsing their hands and face with water. Have you ever wondered why we do this? Cats, for example, perfectly “wash themselves” without water. I have never seen cows, horses, dogs, monkeys washing themselves with water. Why do we need to moisten the skin with water at least once a day?
In the last 1-2 decades, an original “fashion” has appeared for women to give birth in water. They say it is not so painful and less dangerous for both the woman in labor and the child. Discovered a new way to give birth? No. Genetic memory suggested that our distant foremothers did this many millions of years ago. Truly: "Everything new is well forgotten old." It turns out that a child who left the womb in the water does not drown, does not choke. He has innate instincts to keep him afloat. Maybe babies scream during birth because they are out of their element? I think that obstetricians and women themselves can tell more about this, so I’m finishing my discussion on this topic.
Science does not know the inert remains of the most ancient amphibian Homo. Why? Firstly, because in shallow water conditions they were very poorly preserved. Secondly, the number of populations of the first people was small. Thirdly, we are not looking there. Fourthly, there is something, but we interpret it incorrectly. But more on that in the next sections.
When did primates appear and who could be their ancestors?
 Man belongs to the Hominid family of the order Primates of the class Mammals.
Man belongs to the Hominid family of the order Primates of the class Mammals.
Of all mammals, the insectivores are the most likely ancestors of primates. Representatives of this vast detachment of primitive mammals, which include shrews and hedgehogs, have a low braincase, a long stigma and unspecialized limbs. And of all the insectivores, the most likely contender for the role of our ancestor is the tupaya animal, at one time the tupaya itself was attributed to primates. But these nimble little Southeast Asian forest dwellers look more like squirrels with long pointed snouts than monkeys. However, like primates, the tupaya has a large, relative to body size, brain, large eyes, primitive molars, and thumbs that tend to oppose the rest of human origin.
 A close examination of these features suggests that tupai and primates have fewer similarities than previously thought, although the hemoglobin molecules of both are surprisingly similar.
A close examination of these features suggests that tupai and primates have fewer similarities than previously thought, although the hemoglobin molecules of both are surprisingly similar.
Some experts tend to look for the ancestors of primates among long-extinct insectivores, which are called microsyopids. It is possible that early microsyopids lived even before the first primates and were their ancestors.
But most zoologists do not accept this hypothesis either. The order of ancient primates generally lacked features that would make it possible to establish their undoubted relationship with any other group of animals that were their ancestors.
Therefore, primates are a very ancient branch of mammals!
Plesiadapis was more like a squirrel with a long muzzle, lateral eyes, protruding chisel-like incisors, a bushy tail, and claws on paws not adapted for grasping.
It fed on leaves, jumped well, and may have lived in herds, often not in trees, but on the ground. Time - Middle Paleocene - Early Eocene. Location - Colorado (USA) and France. Family Plesiadapidae.
a - long tail
b - Movable limbs
c - Claws, not nails
d - Jaws and teeth characteristic of rodents
e - Eyes on the sides of the head.
Evidence for the origin of man from animals
In the middle of the Cenozoic, more than 25 million years ago, the first primates probably appeared. It is believed that one of them - driopithecus - appeared 17 - 18 million years ago, at the end of the Neogene, and died out about 8 million years ago. Driopithecus lived in tropical forests. At the same time, or a little later, Australopithecus lived, leading a terrestrial lifestyle. It seems very likely that at this time another branch of primates arose - hydropithecus, which ultimately led to the emergence of Man.
 Hydropithecus lived in the Neogene along the shores of shallow lagoons, rivers, lakes and other freshwater and brackish water bodies.
Hydropithecus lived in the Neogene along the shores of shallow lagoons, rivers, lakes and other freshwater and brackish water bodies.
They were engaged in catching and collecting mollusks, crayfish, frogs, turtles, rodents, bird eggs, coastal berries, fruits and other fruits, roots and insects, and used split pebbles, sticks and bones to catch and open shells and shells. Their former arboreal existence, which had developed in them flexible and prehensile five-fingered paws, colored binocular vision, exceptional spatial coordination of movements, an enlarged occipital visual and parietal kinesthetic cortex of the brain, and therefore quick wit, prepared them well for this way of coastal life, which is not no other animal origin of man.
The Oligocene was a period of ray adaptive divergence of anthropoids.
At the beginning or middle of the Paleogene, when the Earth was undergoing a cycle of strong compression, large expanses of land turned out to be shallow bays due to powerful marine transgression. The land area has drastically decreased, while the area occupied by shallow water has increased.
New ecological niches dramatically changed the vector of macro and microevolution in all groups of animals. Then the so-called "return" of animals to the aquatic environment began. For some lines of "return" evolution, the process, which lasted several tens of millions of years, ended with the transformation into typically aquatic creatures (whales, dolphins), for others, partly terrestrial, but mostly aquatic ( walruses, seals). Still others were able to balance on the “fifty-fifty” principle.
The primate order, like many other orders of mammals, also branched off in the direction of an amphibious way of life. In addition to woodpithecus, australopithecines, hydropithecus lived on our planet.
Homo erectus was formed as a species in the water the origin of man
In 1987 I came to the conclusion that the theory of the origin of man in the spirit of F. Engels does not withstand any criticism. The idea of the amphibious origin of our distant ancestors haunted me, but only in May 2000 I posted my thoughts on this topic on the Internet as a comment on some message about the finds of the bones of the ancient ancestors of Man. Here is that note:
The essence of the hypothesis about the amphibious origin of our ancestors is that about 25 million years ago (and possibly earlier), one of the branches of the evolution of primates mastered the shallow waters of the seas - estuaries, shallow bays - as a habitat. It was in this environment of shallow water-land that the human appearance was formed in one of the phylogenetic branches in the order of primates: upright walking, the ability to swim and dive, holding the breath for up to 8-10 minutes, omnivorous, hair loss. Living in two environments at the same time required the development of the brain. Males probably went out on land more often than females. Climate change on Earth, a reduction in the area of shallow water, and some other reasons have forced amphibious people to spend more and more time on land. This is where a developed brain comes in handy. Fleeing from the cold (and a cooling took place on Earth in the Pleistocene), our ancestors learned how to build dwellings, make clothes, were able to unite in groups and established communication using gestures and sounds. Most likely, the amphibious stage of human evolution took place in Gondwana (Southern Continent), from there, having gone to land, our ancestors began to spread throughout the globe. One thing is clear, that 6-7 million years ago, ancient people already lived on many continents, but still strongly gravitated towards shallow seas, lakes and rivers - to the aquatic environment. Hypotheses about the origin of man from arboreal and terrestrial monkeys over a period of 700-800 thousand years look very ridiculous. The anatomy, physiology and biology of man as a species are more conservative than F. Engels imagined.
Several practical conclusions can be drawn from this hypothesis:
1. Women should give birth in water.
2. Every day a person should spend at least 2-3 hours in the water.
3. The most ancient human bones should be looked for in Antarctica, South Africa, Australia and South America.
4. The theory of human settlement of America should be revised.
Origin of modern man
The main provisions of the theory of the amphibious origin of Man, as opposed to the traditional ones, I will formulate as follows:
1. Homo sapiens is indeed a distant relative of the great apes, but very distant. The phylogenetic lines that led to Man, Australopithecus, chimpanzee, gorilla and orangutan diverged at least 25-30 million years ago at the end of the Neogene.
2. The ancestor of Man were amphibious monkeys, which already lived in shallow rivers, lakes and shallow sea lagoons in the middle of the Paleogene - about 30-35 million years ago.
3. The appearance of Man, which distinguishes him from modern anthropoid apes, was formed not under the influence of labor, as F. Engels argued, but due to living in two environments at the same time - in water and on land.
Homo habilis (“handy man”) is the most ancient species of the genus Homo known today.
Homo habilis (“handy man”) was the first known species of our genus Homo. Height 1.2-1.5 m. Weight - about 50 kg. Height no higher than 1.5 m. Foot and hand (above). This species existed about 2-1.5 million years ago. (Most likely, a skilled man is much older! A.G.)
The face had an archaic shape with supraorbital ridges, a flat nose, and protruding jaws. The brain was half ours and the face was smaller and less protruding; the molars were also comparatively smaller, but the incisors were larger, and the dentition had an open shape similar to the Latin letter U. The arms were shorter, and the shape of the pelvic bones made it possible to walk on two legs and give birth to children with large heads.
The bulge inside the thin-walled skull indicates that they have a speech center, but the larynx was not yet capable of producing as many sounds as our larynx. The jaws were less massive than those of Australopithecus; the bones of the arms and thighs seem more modern, and the legs already had a completely modern form of human origin.
A skilled man lived in East and South Africa, as well as in Southeast Asia (“Meganthropus”). In all likelihood, at that time Homo habilis was not the only species of this genus. There were species and subspecies, both more advanced and more primitive (in the sense of proximity to monkey ancestors).
The remains of material culture, found near the bones of a skilled man, allow us to think that these creatures were engaged in the manufacture of primitive stone tools, built simple shelters, collected plant food, hunted small, and perhaps quite large game. Homo erectus probably evolved from Homo habilis. Or maybe these two species existed simultaneously, occupying slightly different habitats.
Judging by the found bones of the foot and hand, the skilled man walked on two legs, and the fingers of his hands had a strong and precise grip.
In favor of the amphibious way of life of the habilis, they say: a significant volume of the brain, an average of 650 cm3, a greater length of the legs than the arms; arching of the foot and short toes, the structure of the ankle and pelvis, free balancing of the head on the neck and other signs of bipedalism; the absence of a bone (sagittal) ridge on the crown and, therefore, weakness of the masticatory muscles; smaller than even in Pithecanthropes, the size of the face, lower jaw and teeth; unusually wide phalanges of the fingers, therefore, strong and tenacious hands, capable of powerfully clamping pebble tools. Placers of chipped pebbles, mountains of shells and remains of turtles, fish, flamingos, water rabbits, frogs and other aquatic animals, the presence of habilis in clay layers formed in the coastal zone, petrified papyrus rhizomes - all this clearly shows that the Lower Olduvai creatures were coastal amphibians life. One of the subspecies or species of hydropithecus, as a result of further evolution, probably became the ancestor of modern people.
Water and occupation of the front paws prevented the hydropithecus from getting down on all fours and led to the development of bipedal locomotion. The bottom of shallow waters, often soft, required large, flat feet. Semi-aquatic existence led to the loss of hairline by hydropithecus. On the head, the hairline was preserved, as it often remained on the surface. Head hair prevented sunstroke. The eyebrows protected the eyes from the water flowing down the face. Diving has developed the ability to reflex, although not as strong as in cetaceans, slowing down the heartbeat when immersed in water, voluntary control of breathing, and even to some extent anoxic (anaerobic) oxidation of carbohydrates with the release of lactic acid into the blood. The need to split shells and shells and the presence, as they say, of stones (pebbles) rolled in water at hand naturally led coastal monkeys to use these stones as tools for obtaining food. Hence the flexible, dexterous fingers and the eye of human ancestors, far superior in this to other monkeys (even chimpanzees are not capable of either breaking or throwing a stone far and accurately). At first, simply picked up stones, sticks and bones served as tools, then the hydropithecus moved to the selection of more convenient, pointed objects, and, finally, they began to make tools themselves.
Exposure of the skin in hydropithecus was accompanied by the development of a layer of subcutaneous fat, although not as thick as in pigs, hippos, rhinos and other semi-aquatic mammals living in hot climates. In addition, the number of sweat glands increased (up to two to five million), which also saved them from overheating. Under the influence of sunlight, a darkening of the skin occurred - a tan, caused by increased formation of a special pigment - melanin. This kept the blood vessels deeper under the skin from overheating. The need to protect the nostrils from solar radiation and the oncoming flow of water when diving led to the protrusion and convexity of the nose down. Human lips are distinguished by great mobility, rootedness, thickness and the ability to close tightly, not letting water into the mouth when swimming and diving. Other land mammals, in order not to choke while swimming, are forced to keep their heads high above the water.
Diving can explain the innate predisposition of people to myopia, although this, of course, differs from the constant myopia of fish and other inhabitants of the aquatic environment. Of course, hydropithecus did not spend as much time under water as seals, and the adaptive change in their eyes could not be significant; but why, after all, are people the only, it would seem, purely terrestrial and in need of distant vision, a creature who has such a frequent predisposition to myopia, moreover, not only due to unfavorable conditions of vision, which would be natural, but also innate, inherited? In all human newborns, the refractive power of the eye is nearly one and a half times greater than in adults with normal vision; and if, nevertheless, newborns are distinguished by some hypermetropia, it is due to an even greater shortness of the eye along the optical axis. Regulation inside the eye pressure (ophthalmology) by means of the release of special moisture and its outflow through the sclerous sinus is supplemented in humans by a certain (of course, less than in pinnipeds and dolphins) pronounced ability to compensate for changes in external hydrostatic pressure on the eyes by filling the arterial vessels of their posterior chamber with blood, leading to the redness of the eyes from diving the origin of man.
The need to scrape and chew the slippery springy body of a mollusk, hold it and move freely in the mouth led to the most important odontological differences between humanoids and monkeys (which have long served as signs for determining the type and classification of fossils, but have not yet received an explanation): the loss of protruding fangs; the development of the spatulate front teeth, which are necessary for scraping the contents of the shell, biting off and holding the bitten off; an increase in the number of tubercles on molars from four to five; replacement of the cutting first lower premolars with two tuberculate ones; addition of jaw movements up and down with rotational movements; the location of the teeth is not on the sides of the quadrangle, but along the arc; arching of the palatine vault; dense closure of the lips and tightness of the oral cavity with the cheeks. As a result, the jaws of coastal monkeys became shorter and wider. The shortening of the jaw and the expansion of its posterior ends to the sides, as well as the straightening of the front teeth and the reduction of the chewing apparatus, led to the development of a protruding nose and the lower anterior part of the jaw - the chin. The latter contributed to an increase in the oral cavity and freer movement of the tongue in it.
A close explanation of the transition of anthropoids to upright posture, bradycardia and hairlessness was proposed in 1960 by the English biologist A. Hardy, who suggested that the ancestors of people were seaside monkeys that lived on the sandy shores of lagoons. As you can see, his guess about the hydrogenation of many features of the human body is very thorough. However, marinological passion led the oceanologist to the idea of a seaside settlement of human ancestors and to excessive assimilation of their origin to human marine mammals. As a result, this hypothesis did not find recognition in science, because it led away from the material traces of anthropogenesis known to paleoanthropology and was left without ontological evidence.
Some supporters of the theory of the amphibious origin of Man, for example, L.I. Ibraev, believe that the Lower Olduvai habilises were amphibious monkeys, and that it is not right to consider them themselves “people” (hominids), even if they are the most ancient, and their pebble tools as “culture”. In all of pre-Shell Olduvai, there was one type of tool - a chopper (chopper). Its “making” was limited to splitting stones without any attention to the shape of the split, the variety and randomness of the forms of splitting choppers testify to purely animal actions, like beavers or birds. Pebble axes are devoid of any repetitive, stable form; they have not undergone any improvements over the existence of thousands of generations (more than two million years). The latter indicates the absence of any continuity and accumulation of experience in the technology of making pebble tools. Consequently, there was no accumulation of experience in their manufacture and its transfer from parents to children.
Let me disagree with this opinion. The blindness from the theory of F. Engels is evident here. If perfect tools were not made, then not people. But if L.I. Ibraev to make a chopper, he would be convinced that it is not so simple. Not every rock and not every form of pebble is suitable for this. Pebbles were not just thrown with force against a larger stone, so that it would split in any way. They hit it with another pebble, and many times, beating off a small piece of the origin of a person with each blow. Most of the pebbles found split by ancient man are not choppers at all. A person was looking for the right stone, for this he took a pebble and threw it against the stone with force, looking to see if this stone was suitable for further processing. If you judge by chips and shavings, you will never imagine what masterpieces the carpenters made. And stone tools were probably kept, since their manufacture required a lot of work. Animals that use different items to get food do not store these items later, they usually have them for one-time use.
With an abundance of food in the form of mollusks and fish, in a warm climate where clothing and warm housing were not required, there was no need to manufacture complex mining tools. But this does not mean that the habilis did not communicate with each other using gestures and sounds, that they did not express their feelings in dances and songs, that they did not teach their children where to look for food, how to distinguish edible from poisonous, how to find a cure for illness. where and how best to escape from predators, etc. The presence of very complex technologies in human society does not yet speak of the cultural and spiritual perfection of individual individuals. The spiritual world of an Australian aborigine or Eskimo is often much richer than the spiritual world of a modern European. Let the primitive tools, but the habilis made them themselves, and modern man uses ready-made tools bought in a store, and he himself often cannot hammer a nail into the wall. A person should be considered a creature that, in appearance and level of development of the central nervous system, differed little from a modern person.
These drawings depict early stone tools - choppers - from the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania (East Africa). Not every modern person without a hammer and chisel will be able to process a stone in this way.
But Homo habilis 1.9 million years ago split basalt and quartzite pebbles, gave them shapes that are now called rough choppers (choppers), scrapers, chisels, ax-shaped tools, and according to their outlines they are divided into discoids, polyhedra (polyhedra) or subspheroids .
A - Rough chopped (chopper) from lava; it was used for cutting meat or for splitting bones.
B - Polyhedron (polyhedron) with three or more cutting edges.
B - Discoid with sharp edges.
G - Skreblo for processing skins.
D - Stone hammer.
The use of primitive tools by amphibious habilis lasted for several million years, but this does not mean that the evolution of ancient people has stopped. Over these many millions of years, a plan has been formed for the internal and external structure of man. And this was much more difficult and more important than the improvement of the tools of labor, the origin of man. Without developed dexterous hands and a perfect brain, no evolution in the manufacture of tools would be possible. The foregoing does not mean that the use of tools is not at all a sign of the difference between man and animals. But the manufacture of tools is not the cause of the appearance of man, but a consequence! According to many modern anthropologists, imaginative thinking and imitation serve as the mental basis for learning in animals. I dare to assure my opponents that in Man, especially in childhood, the situation is exactly the same. Logical thinking is based on figurative, not speech. Thoughts in the human brain are first born, and then formulated in the form of words.
The Habilis of the second shell layer of Olduvai (their remains were found at a depth of 90-60 m) used tools such as bifaces - pebbles, already more thinly chipped and on both sides. The crushed bones of giraffes, antelopes, elephants scattered around indicate that the habilis at that time were forced to move, and perhaps already moved to life on land, which was caused by the expansion of the globe, the global regression of the sea and significant climate change. The land area has increased, the climate on the continents has become drier and more continental, the area of shallow water has sharply decreased, many lakes within the continents have dried up. Humid tropical and subtropical forests gave way to savannahs, prairies and steppes. In the savannas lived different types of monkeys - Australopithecus. They were well adapted to the life of the origin of man in the new conditions. Their body was covered with wool, they moved on four limbs, jaws and teeth allowed Australopithecus to chew grass and leaves. Phylogenetically, Australopithecus is not related to Hydropithecus, but to Driopithecus. By the way, modern chimpanzees and gorillas are the result of the evolution of Australopithecus.
What about habilisa hydropithecus? What happened to them? In all likelihood, a significant part of the habilis died out, a few remained to live in the remaining reservoirs - mainly in the estuaries of large rivers and in the shallow waters of lakes. Few were able to begin adaptation to terrestrial life. Here they had to compete with Australopithecus. This is evidenced by the discovered features of the then fauna and palynological data. In connection with the transition to life on land, the physical appearance of the habilis naturally changed. The remains of a new species, the Oldowan Pithecanthropus (Homo erectus), were found in the Olduvai layers at a depth of about 60 meters. What was a person walking upright?
Homo erectus - Homo erectus, an upright man, had a height of 1.5-1.8 m, a body weight of 40-73 kg. His brain and body were larger than those of Homo habilis, and in many respects he would have been similar to modern man. The volume of the brain averaged 880-1100 cm3, which is more than that of a skilled person, although less than that of a modern person. It is believed that the origin of man Homo erectus lived from 1.6 million to 200 thousand years ago, but most likely he appeared much earlier.
His skull retained archaic features, was long and low set, with a bony bulge at the back, with a sloping forehead, thick supraorbital ridges, with a flatter face than ours, with large protruding jaws, more massive teeth than ours. (but still slightly smaller than Homo habilis); the chin was missing.
Strong muscles at the back of the neck were attached to the posterior cranial tubercle and supported the head with a heavy face, preventing it from sagging forward.
Appearing for the first time, probably in Africa, separate groups of this species then spread to Europe, East Asia (Sinanthropus) and Southeast Asia (Pithecanthropus). Apparently, the rates of evolution of individual isolated populations of Homo erectus were different.
Advanced technology, including the use of a standard set of tools, hunting big game, the use of fire, and improved methods of building shelters and temporary shelters, advanced Homo hominids far ahead of the hominids that preceded him, giving this species the opportunity to exist in new natural and climatic conditions. Adapting to life on land, the ancient hydropithecus could no longer return to moving on four limbs. They could escape from predators and hunt successfully thanks to the improvement of tools and methods of hunting, and for this they had free and dexterous forelimbs and a developed brain.
Pithecanthropus hunting tools found in Spain and their possible use.
Pithecanthropes could hit game at a considerable distance. They used wooden spears, they knew how to sharpen them with stone scrapers and fire. A stone tool with teeth along the cutting edge (the so-called “denticule”). quartzite jib; its length is 25cm. double-sided scraper made of jasper. Butchering the carcasses of large mammals was carried out with the help of stone tools, since the teeth and jaws inherited by pithecanthropes from hydropithecus did not allow them to do it otherwise. Pithecanthropes knew how to clean the skins from fat and used them to build dwellings, and possibly for the manufacture of primitive clothing.
However, the progress in the structure and volume of the brain of Homo erectus during their transition from an amphibian lifestyle to life on land was combined with a regression of their skull and hands: chewing the tough raw meat of large animals required an increase in the jaws and a thickening of the supraocular ridge and the walls of the skull almost twice as compared to with hydropithecus, which greatly reduced the possibilities of speech articulation, and the absence of a wooden handle in Acheulean stone tools, squeezing them directly with a hand, led to a monstrous strengthening of the hand. The brushes became wide, paw-shaped, which prevented the subtle manipulation of objects.
Pithecanthropes, judging by the animal bones found at their sites, hunted wild boars, rams, antelopes, horses and even elephants. This became possible thanks to the improvement of tools: the manufacture of large axes (which, as the experiment showed, can be used to skin an animal and dismember the carcass), as well as scrapers and piercings for processing skins. The origin of man is possible, at that time the first spears appeared - simple poles with a fire-burnt and pointed end. Of course, even then hunting for large animals remained difficult and dangerous - ancient people rarely dared to attack them openly, preferring to set up ambushes or drive the beast to swamps and cliffs. Man at that time successfully used traps, all kinds of traps and wine presses. Animals were driven into hunting pits and traps with the help of fire, setting fire to dry grass, birch bark, using torches, etc.
It is characteristic that it was at this time that Australopithecus disappeared, partly unable to withstand competition with unprecedentedly armed hunters, partly because they were exterminated by them like game. Many punctured skulls and burnt bones of Australopithecus have been found at Homo erectus sites. It is possible that cannibalism was also characteristic of a person walking upright.
Fire was known to humans as early as the Homo habilis species: a 2.5 million-year-old area of charred soil is known near Tukana Lake in Kenya. A person could keep and maintain the fire that arose as a result of a lightning strike or during a volcanic eruption. But it can be argued that it was Homo erectus who first began to systematically use fire for heating, hunting, cooking and protection from enemies.
The transition to hunting large animals was associated with the resettlement of people in the steppe. Therefore, the tools of pithecanthropes were more often made not from pebbles, but from unrolled hard rocks: quartzite, quartz, lavas.
This resettlement took place under the pressure of climatic changes, it turned out to be possible only thanks to the development of new production means by people. Very often, the most successful were not the strongest, but the most intelligent, able to unite in large groups.

The progress of tools and methods of hunting also changed the relationship between individuals in the group. If the gathering and catching of small animals was dominated by individual activity, now there is a herd. It is formed not only and not so much on the basis of sexual and parental ties, but on the need for collective hunting and collective protection from enemies. The connecting function is performed by an orientation towards the behavior of a neighbor and a leader, which makes it easier to find food and self-defense from enemies. All people in the primitive herd act as mutual guides and mutual watchmen. Ambush and driven hunting is the first cooperation with the division of roles in search of prey, rutting, encirclement, attack. However, if predators hunt animals that are often much weaker than each of them individually, and their cooperation is purely situational, then ancient people even hunted elephants, rhinoceroses, cave bears and other giants, which were dozens of times larger, stronger and faster than any single person.
Finishing this article, I can say that the origin of man in the evolution of Man is very unclear and contradictory. Most likely, new phenomenal discoveries await us in the coming years. Remains and traces of the vital activity of our very distant ancestors will be found even more ancient than the Uruguayan ones. It turns out that the genus Homo was once represented by dozens of different species, that Homo sapiens is only the surface part of a huge iceberg. We do not yet know what ancient people lived in Antarctica before its glaciation.
Theories about the origin of man appear more and more often, each time more and more complicated and interesting. This question has been relevant for thousands of years. Even before our era, people tried to find out about the nature of their origin. Perhaps they managed to achieve their goal, but it does not matter, because knowledge has not reached us. In any case, most people think so, including us. We propose to consider the 10 most interesting and most likely theories regarding how man appeared on Earth.
10 theories about the origin of man
Currently recognized is only one theory of Darwin about the origin of man. By no means, no one can reliably say that we originated from monkeys. It's just that more facts point to it:
- primates are most similar to humans in terms of anatomy;
- Darwin noticed a similarity in the expression of emotions;
- facial expressions, gestures, movements are similar;
- we are similar not only in the brain, teeth, blood, but also in the psychology of behavior.
According to his theory, people evolved from monkeys, leaving distant ancestors behind beyond the boundaries of civilization. A huge amount of research is currently being carried out. Filmmakers have already released the film "Planet of the Apes", which talks about the war of primates with humans. Probably, until this issue is resolved, people will not stop torturing animals.

Along with Darwin's theory is the aquatic theory of the origin of man. It indicates that people came out of the seas. What facts point to this?
- 70-80% of the human body consists of water;
- The underwater world has not been explored;
- About 90% of the ocean is unexplored;
- Dolphins resemble humans almost like apes;
Indeed, dolphins know about 14,000 signals. They are able to communicate, save people. In history, there was not a single case of an attack by this animal. Dolphins are not fish because they are warm-blooded and breathe oxygen. You can learn more interesting things from the article "10 facts about dolphins" on our portal.

The theory of the origin of man as a result of the Big Bang is quite complex. We will not go into the scientific explanation of all the chains of interaction between atoms and molecules (if only because we do not understand). In general, something went wrong and a celestial body exploded, as a result of which molecules and atoms began to move so chaotically that people appeared. Perhaps everything is completely different or partially, but the essence is the same - this theory does not explain at all why we appeared. If this is a coincidence, then it is very difficult to believe that such developed and complex organisms could have come about as a result of an explosion. One hair is made up of a huge number of atoms.

Many believe that we are not the only race in the universe. Probably the creators of the franchise "Transformers" are among such people. In general, there is a hypothesis about the origin of man from aliens. Someone thinks that we were brought in a test tube and populated the Earth. Others believe that we are children of UFOs. Still others are sure that aliens are exploiting us. As if we are slaves, therefore we do not know the meaning of life. Probably, in this way, they simply explain the misunderstanding of their nature. However, it is not for us to judge whether this is a fairy tale or a reality.
How man appeared: myths about the gods
Speaking about the origin of man, it is impossible not to mention religion. Perhaps the answer is in the bible. For centuries, the book has been handed down from old people to heirs. At the same time, one truth is visible among different peoples, calling to value neighbors, to do good and not to commit sins. And most importantly, God created us. We do not urge to choose a religion, we are not going to hurt the feelings of believers. In this article, we only emphasize that one of the most popular theories of origin is belief in God.

In my opinion, the most interesting theory of the origin of man. It says that evolution is nothing more than "dust in the eyes" of modern society. In fact, there were civilizations before us, advanced technologies. We just do not understand them, because knowledge was lost along with the Apocalypse. Perhaps our predecessors knew the answers, but something happened. How else to explain the fact that the pyramids have existed on Earth for a huge number of years? At the same time, they are arranged butt-to-butt. Even current technologies do not allow the creation of such structures. Not to mention the fact that inside the pyramids there is a favorable atmosphere for the development of plants. They do not contain viruses and microbes. Amazing, isn't it?

It is difficult to explain this hypothesis. Briefly speaking about how a person appeared, it is worth highlighting the following assumptions:
- thoughts materialize;
- our dreams are sent to the center of the universe, after which they return to our world, materializing;
- there is an invisible energy;
- everything that we invent exists, but in other realities.
Thus, this hypothesis says that all previous theories are real. That is, every law, assumption is a partial truth. At the same time, parallel worlds are different segments of the time line. Difficult, isn't it?

Another tricky theory. According to this hypothesis, there are several worlds. Some scientists indicate the number 9, others 3. Someone believes that there are countless parallel worlds. Imagine there is a time machine. Now you are reading this text (fixed the picture). After some time, we moved into the past and went for a walk. What about the story when you read the text? According to this theory, all time periods are fixed. You have created 2 stories with your journey. One of them in one world, the second in another.
In general, another complex theory in which a certain logic is still visible.

Perhaps the most modern theory about the origin of man. What if the world is a game? Osho, Khayyam, many successful people said to treat life as a game, a performance. Maybe they wanted us to take these phrases literally? Imagine that all emotions, our conclusions and views are a programmed program. This reminds me of the movie The Matrix. Imagine that everything in the world is fiction, a game in which we only perform our tasks. In this case, there is no fate. All this is a cold calculation of the creators. It's hard to believe, but a certain essence is visible.
10

Carlos Castaneda studied for a long time with a shaman named Don Juan Matos "The Art of Dreaming". According to his theory, sleep is an integral part of life. It is as real as our reality. It also talks about parallel worlds and the materialization of thoughts.
The point is the following. The Creator, the center of the universe or God laid the program. Our task is to learn, to learn new things, to discover knowledge and create the unseen before. After death, all our knowledge, along with memory, goes to the creator. This is the essence of our existence. That's what the man came for. You can learn more by reading the works of Carlos.
11 Hypotheses about the origin of man.
There are several hypotheses of athropogenesis: creationism, simial, labor. Simial hypothesis of anthropogenesis According to the adherents of the theory of evolution, about 60 million years ago, semi-monkeys developed from insectivorous mammals on Earth as a result of the influence of the natural environment and natural selection, which then quickly divided into two branches. The first of them led to the broad-nosed monkeys, and the second to the narrow-nosed ones, from which, as if later, a man was formed. Depending on this approach, there are hypotheses of anthropogenesis, which consider the ancestors of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees. The evolutionary branch of man separated from the trunk common with other primates about 4 million years ago. Man and his closest ancestors are called hominids. Currently, they are represented by only one species of rational man. 2 million years ago there were at least three of them. Labor theory of anthropogenesis in its original classical version was presented by F. Engels in his famous work “The role of labor in the process of turning a monkey into a man”. In this work, the sequence of the main stages of hominization is established, highlighting bipedalism as a decisive step towards the humanization of the monkey; the definition of the hand as an organ and product of labor is given; the emergence of a sound language and articulate speech, human thinking as a consequence of social development is considered; emphasizes the qualitative originality of anthropogenesis as a process of active adaptation of man to the environment, the ecological superiority of Homo sapiens over other species. The main position of the labor theory of anthropogenesis - about the decisive role of tool making in the processes of hominization - is now shared by the vast majority of anthropologists of the world, although the concept of “cultural adaptation” common in foreign anthropology does not fully correspond to the basic principles of labor theory; in this case, we are usually talking about an “autocatalytic reaction” or a “cybernetic mechanism” of feedback between the development of biology (the brain) and culture, with the leading role of genetic factors. It is necessary to establish the moment when labor "joined" in the process of human evolution as one of its important stimuli. If we mean by the "first man" a being who started making tools, then, by virtue of simple logic, his formation could not be determined by the labor factor in the sense that otherwise the "chicken and egg" paradox inevitably arises, the conclusion suggests itself about some kind of "working monkey" (or, in any case, a working Australopithecus), which, according to the basic idea, should at the same time be called a man. The direct shaping force of anthropogenesis, as in any process of speciation, is natural selection. Labor activity played an important role in the evolution of the genus Homo and its creation of an “artificial environment” that determined the direction of adaptive processes, but they could not directly “sculpt” the morphological and physiological specifics of the emerging new taxon. Ignoring natural selection, we will not go further in this matter than the Lamarckian understanding of evolution long abandoned by science. The main attention is now being paid to the search for the reasons that led to the transition to upright walking as a key adaptation of human ancestors, as well as the problem of hominization criteria, the “edge” separating the prehuman and human phases of evolution.
12 The problem of determining the absolute geological age of man and his ancestors
In order for an archaeologist to be able to correctly assess the finds that he has to hold in his hands, he must imagine their age. Determination of age is the most important and at the same time the most difficult task facing the researcher of antiquities. For scientists studying the ancient history of mankind, this task becomes doubly difficult, because they cannot use written sources that describe the events of that era. There are simply no such documents, because writing began to spread between peoples much later, at the time of the emergence of the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt. Willy-nilly, one has to use other methods to determine the antiquity of what can be found during excavations. In the first place among the assistants of archaeologists in this difficult task is geology. All currently known geological layers of the earth's crust are referred by geologists to five eras: Archean, Proterozoic, Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The oldest era is the Archean, the youngest is the Cenozoic. The remains of man and traces of his life, which are studied by archaeologists, lie in the upper part of the Cenozoic layers. These layers, in turn, belong to the periods of the Upper Pliocene, Eopleistocene and Pleistocene. Each of these periods is also divided into shorter time periods. Their chronology has been established using various natural scientific methods. According to this chronology, the Upper Pliocene is not younger than 1.6 million years, the Eopleistocene ended about 800 thousand years ago, and the Pleistocene - about 10 thousand years ago. The Pleistocene was replaced by the modern geological epoch - the Holocene. In 1922, A.P. Pavlov proposed to call the geological period, which is characterized by the existence of man, the anthropogen. Geologists use another name - the Quaternary period, thereby emphasizing the ordinal place in the geological record of the era of mammals. the archaeological epoch, which unites the time from the most ancient settlement of people, fixed by science, to the spread of modern humans across the territory of all continents, is called the Paleolithic. The word Paleolithic refers to the ancient stone age. The very allocation of the Stone Age was made by the director of the museum in Copenhagen, the archaeologist Christian Jürgensen Thomsen 1788-1865. In 1836 Thomsen published a Guide to Northern Antiquities. In this book, he attributed the primitive monuments to three ages: stone, bronze and iron. Stone Age monuments differed from the rest in that only stone and bone items were found here, and most of all stone tools were found. The Paleolithic is the beginning of the Stone Age and coincides with the existence of the geological epochs of the Upper Pliocene, Eopleistocene and Pleistocene. The oldest settlement of people and their development of the occupied areas of the earth's land fell on the time from 200-300 thousand to 2.6 million years ago. Despite the ongoing debate about human ancestors, one thing is certain - the time of separation of people from the animal world is determined by the appearance of the first tools of labor. At the present time, scientists recognize the items discovered during excavations on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana in Kenya at the site of Koobi Fora as the most ancient tools. Their age is determined at 2.6 million years, this is the time of the geological epoch of the Upper Pliocene. The following epochs, the Eopleistocene and Lower Pleistocene, include finds that are common both in Africa and in Eurasia. Very ancient tools are found in Ubeidiya Israel. Some scientists even considered it possible to date them with a time of 2 million years. But those layers in which the discovered objects lie cannot be subjected to potassium-argon analysis, therefore the dispute about their age continues. However, their Upper Pliocene age is not questioned. In this sense, the tools from Ubeidiya are very close in time to the oldest tools from East Africa.
13Archaeological division of the Quaternary period
The age of the Earth is approximately equal to 5 billion years. The history of the Earth is divided into four eras: Archean, Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The Cenozoic era, the era of new life, the time of the dominance of mammals, which lasted 60-70 million years, is divided into two periods - Tertiary and Quaternary. In the Tertiary period, monkeys appeared and developed, including anthropomorphic anthropoid, in the Quaternary period, a person appeared, which is why this period is also called anthropogenic. The Quaternary period is divided into two epochs: 1 pre-glacial and glacial, called the Pleistocene, and 2 post-glacial - Holocene, or modern.
The first wave of cold came to Europe at the end of the Tertiary period. Recently, geologists have also referred to the Quaternary period the Villafranchian time,2 which, together with the early stages of the Quaternary period, is called the Eopleistocene, or the oldest Pleistocene. The boundary between the Tertiary and Quaternary periods is conditionally defined as 2.5-2 million years3. The Holocene is only 10-12 thousand years old.
The Quaternary period is characterized by successive advances and retreats of the glacier, which determine its geological periodization.
Based on the study of geological deposits in the Alps, A. Penk and E. Brückner established four glacial and three interglacial epochs for the Pleistocene of Western Europe4. According to the rivers at the foot of the Alps, where they carried out their research, four glacial epochs are named: gunz, mindel, riss and wurm. Penck and Brückner's scheme was widely adopted and accepted5. However, attempts to establish absolute dates for these epochs cause constant controversy. One such more or less successful attempt was made by the English scientist Zeiner6. There is no single point of view among geologists, not only on the question of the duration of glaciations, but also on the question of their number. Polyglacialists believe that during the Quaternary period there were several glaciations, each time accompanied by a change in flora and fauna in those areas of the globe that were influenced by the advance and retreat of the glacier. Some polyglacialists believe that there were six glaciations and introduce two more glacial epochs between the almond and the riss - kander and glitch.
Monoglacialists believe that there was only one ice age and we can only talk about its various stages, about the change of cooling and warming. Some scientists generally deny the fact of glaciation. But this hypothesis was not accepted.
14. Modern scientific data on the origin of man
There are two concepts - phylogeny and ontogenesis - this is the problem of the origin of man and his consciousness. There are various approaches to solving this problem. One is modern scientific ideas about social. the origin of primitive man, another, hypotheses about the origin of man.
Phylogeny is the development of man in the course of his development in history as a man. Ontogeny - the process of individual development of a person from his birth to death
There are many views on the origin of man. In 1969, scientists formulated the missing link between apes and humans. This was formulated by Haeckel and Fak. The main versions of the origin of man are:
1. God created in his own image and likeness - the religious version. 2. The transformation under his influence of the body of a monkey into a man - the version of Shelenga. 3. The idea of aliens from outer space - Bekhterev's version.
4. Man descended from a common ancestor with monkeys, the factor of which was labor - the work of Engels.
Menforth believes that other beings are also suitable for the labor of some kind of activity. He says that man was originally capable of self-perfection.
Academician Moiseev gives some explanations for the origin of man in the Paleolithic era, about 3 million years ago, the temperature began to drop, the tropical forests decreased and Telanthropithecus was forced to go out into the savannas. It was not competitive in the tropics. Academician Moiseev refers on the basis of the works of the spouses Lekki. They faced the question: either die or live. And the man began to eat meat, as before that he had eaten vegetable food.
Moiseev says that resourceful individuals survived at these stages. Under these conditions, the development of the brain was of an explosive nature, after which a person began to master fire and other things. After that, a person organizes hordes to defend themselves from stronger animals.
The process of becoming a man from Australopithecus to the formation of modern man begins about 15 thousand years ago.
The Cro-Magnon man is no longer inferior to a modern person; he has the same brain size and other body capabilities. At this stage of development, a taboo arises in a person - a ban on killing their own kind and on marriages with close relatives, these were the beginnings of morality.
At this time, competition between the hordes is born. Moiseev says that tools of labor gradually appear and the need for the transfer of information gradually appears. A higher degree of development is the degree of transmission of information to other generations.
30 - 40 thousand years ago, the natural recruitment stopped and due to this, a person develops the inner world. It was during the Paleolithic period that man was already formed. The Paleolithic itself was 1.5 million years ago.
Moiseev's version is that there was a classic Neanderthal and two branches went from him, one of which is a dead end. These branches are as follows, Neanderthals arise at the same time as the Cro-Magnons. But Neanderthals will cease to exist in the future. And so he believes that the Neanderthals were very aggressive, and did not give their ancestors the opportunity to develop. This is confirmed by excavations, i.e. many excavated skulls were broken.
Melyushov's point of view is that the first were Australopithecus, which appeared more than 5 million years ago in southeast Africa, after which they settled. He considers a more realistic version that the real ancestor of man lived 15 - 20 million years ago. And 4 - 6 million years ago there was a splitting. In Ethiopia, remains were found belonging to the most ancient man who lived 4 - 5 million years ago. According to the assumption, adults should have weighed 30 - 40 kg, and a height of 120 - 140 cm. According to Melyukov, the appearance of a person is as follows:
Afarensis - brain volume 400 - 500 ml, erect, lived in family groups. Afreki's scientific name is Lucy. Afrecanus - descendant of Lucy, brain volume 400 - 500 ml. Adroit and skillful lived in social groups. Robustus is a native of Afrecanus. Brain volume 530 ml. He left no offspring.
Homo Habiles is the first known species belonging to the Homo family. He was the first to use tools. Brain volume 500 - 600 ml. Homo Erectus is the first species to go outside of Africa. Colonized the nearest and middle east as far as China. Brain volume 1050 - 1250 ml. Lived 1.5 million years ago.
Homo Sapiens - brain volume 1200 - 1700 ml. Cro-Magnon, found in 1767 in Cra-Magnon, France. Appeared about 40 thousand years ago.
There are two theories of human appearance in the world: MONOCENTRISM from mono ... and lat. centrum - focus, center, theory of the origin of the modern human species Homo sapiens and its races monogenism in one area of the globe from one form of ancient people. POLYCENTRISM from poly... and ... center, the theory of the origin of modern man Homo sapiens and his races in several regions of the globe from different forms of ancient people. Most domestic anthropologists are not accepted.
15. Modern methods for determining the relationship between humans and animals. The data of comparative embryology and anatomy clearly show similarities in the structure and development of the human body with animals.
A person is characterized by the main features inherent in the Chordata type and the Vertebrate subtype. In humans, as in all chordates, in the early stages of embryonic development, the internal skeleton is represented by a notochord, the neural tube is laid on the dorsal side, and the body has bilateral symmetry. As the embryo develops, the notochord is replaced by the spinal column, the skull and five sections of the brain are formed. The heart is located on the ventral side, a skeleton of paired free limbs appears.
Humans are characterized by the main features of the class Mammals. The human spine is divided into five sections, the skin is covered with hair and contains sweat and sebaceous glands. Like other mammals, humans are characterized by live birth, the presence of a diaphragm, mammary glands and the feeding of young with milk, a four-chambered heart, and warm-bloodedness.
For a person, the main features of the subclass Placental are characteristic. The mother carries the fetus inside her body, and the fetus is nourished through the placenta.
Humans are characterized by the main features of the order Primates. These include limbs of a grasping type, the presence of nails, the location of the eyes in the same plane, which provides three-dimensional vision, the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones, etc.
There are many common features in humans and with great apes: a similar structure of the brain and facial parts of the skull, well-developed frontal lobes of the brain, a large number of convolutions of the cerebral cortex, the disappearance of the caudal spine, the development of facial muscles, etc. Fig. 104. In addition to morphological features, a number of other data testify to the similarity of humans and great apes: similar Rh factors, ABO blood group antigens; the presence of a menstrual period and pregnancy lasting 9 months, as in chimpanzees and gorillas; similar sensitivity to pathogens of the same diseases, etc.
Recently, methods for determining the evolutionary relationship of organisms by comparing their chromosomes and proteins have been widely used. The relationship between species is greater, the greater the similarity between proteins. Studies have shown that human and chimpanzee proteins are 99% similar.
The kinship of man with animals is also evidenced by the presence in man of atavisms of the outer tail, polynipple, abundant hair on the face, etc., and vestiges of the appendix, ear muscles, third eyelid, etc.
The systematic position of modern man. Kingdom Animals, sub-kingdom Multicellular, phylum Chordata, subtype Vertebrate Cranial, class Mammals, subclass Placental, order Primates, suborder Anthropoid, family Hominids, genus Homo Homo, species Homo sapiens Homo sapiens, subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens.
Since Homo sapiens sapiens, an extinct subspecies of Homo sapiens, is currently also referred to as Homo sapiens, the full name of modern man is Homo sapiens sapiens.
16. Dynamics of the primitive herd The primitive human herd, the conditional name of the original human collective, which directly replaced the zoological associations of the closest animal ancestors of man. The period of the Primitive human herd, as most scientists assume, is the time of the formation of a modern type of man, the struggle of emerging social institutions with zoological instincts inherited from animal ancestors. Archaeologically, the era of the primitive human herd covers the Lower and partly the Middle Paleolithic. Anthropologically, this is the period of existence of emerging people: archanthropes pithecanthropes, sinanthropes and paleoanthropes of Neanderthals. Their economy was based on a combination of hunting and gathering. Hand axes, coarse chopping tools, choppers, flakes, points, etc. were typical tools. Marriage relations may have been initially disorderly, see Promiscuity. Gradually, sexual relations between members of the same herd ceased to be practiced and were prohibited, see Exogamy. With the transition to marriage relations exclusively with members of other herds, a clan is formed. Primitive communal system, the first socio-economic formation in the history of mankind. Fundamentals of the doctrine of P. s. as a special socio-economic formation were laid down by K. Marx and F. Engels and further developed by V. I. Lenin. According to the most common opinion in Soviet science, P. s. covers the time from the appearance of the very first people to the emergence of a class society, which, according to archaeological periodization, coincides mainly with the Stone Age. For P. s. it is characteristic that all members of society were in the same relation to the means of production, and, accordingly, the method of obtaining a share of the social product was the same for all, which is why the use of the term primitive communism to designate it is connected. From the stages of social development of P. following it with. characterized by the absence of private property, classes and the state. 17. Australopithecus. The family of hominids includes modern man and his immediate predecessors. Usually, the most ancient boundary of this group is conditionally considered the moment of division of the general evolutionary line into branches leading to modern great apes and modern man. The most accepted in modern science is the allocation of two subfamilies in the Hominidae family:
1. Australopithecinae Australopithecinae. Australopithecus is usually considered the oldest hominin.
The Australopithecus were a very peculiar group. Who were they - bipedal monkeys or people with a monkey head And how to relate to this combination of signs
Australopithecus appeared about 6-7 million years ago, and the last of them died out only about 900 thousand years ago, during the existence of much more advanced forms. As far as is known, Australopithecus never left Africa, although some finds made on the island of Java are sometimes attributed to this group.
The complexity of the position of Australopithecus among primates lies in the fact that their structure mosaically combines features that are characteristic of both modern great apes and humans.
The Australopithecus skull is similar to that of a chimpanzee. Characterized by large jaws, massive bony ridges for the attachment of chewing muscles, a small brain and a large flattened face. Australopithecus teeth were very large, but the fangs were short, and the details of the structure of the teeth were more human than monkey.
The skeletal structure of Australopithecus is characterized by a wide low pelvis, relatively long legs and short arms, a grasping hand and a non-grasping foot, and a vertical spine. Such a structure is already almost human, the differences are only in the details of the structure and in small sizes.
The growth of Australopithecus ranged from a meter to one and a half. It is characteristic that the size of the brain was about 350-550 cm3, that is, like that of modern gorillas and chimpanzees. For comparison, the brain of a modern person has a volume of about 1200-1500 cm3. The brain structure of Australopithecus was also very primitive and differed little from that of a chimp.
The way of life of Australopithecus, apparently, was unlike that known among modern primates. They lived in tropical forests and savannahs, feeding mainly on plants. However, later Australopithecus hunted antelopes or took prey from large predators - lions and hyenas.
Australopithecus lived in groups of several individuals and, apparently, constantly roamed the expanses of Africa in search of food. Australopithecus tools were unlikely to be able to manufacture, although they were used for sure. Their hands were very similar to human ones, but the fingers were more curved and narrower. As already mentioned, the oldest tools are known from layers in Ethiopia dated 2.7 million years ago, that is, 4 million years after the appearance of Australopithecus. In South Africa, Australopithecus or their immediate descendants used bone fragments to catch termites from termite mounds about 2-1.5 million years ago. . 18. Transitional forms from Australopithecus to the species Homo The most accepted in modern science is the allocation of two subfamilies in the Hominidae family:
o Australopithecinae Australopithecinae - hominids with many typical pongid features;
o hominins Homininae - hominids without pongid features.
Hominins Homininae. The oldest representatives of the subfamily, which includes modern man, are known from the deposits of time about 2.5 million years ago. They are often called early Homo, emphasizing their similarity to humans and their difference from monkeys. They were rather small creatures, completely upright, with a relatively large brain, but still with a monkey face. Of course, the last comparison should not be taken literally. Large protruding jaws and a wide nose gave these creatures a resemblance to modern chimpanzees, but it would be impossible to confuse them. The fundamental difference between early Homo and Pongida and Australopithecus was a large developed brain and hand, fully adapted to the manufacture of tools, although they were not completely modern in form. During the million years in which these first people existed, there was a sharp jump in both biological and social organization. The rate of evolution has increased dramatically. The growth and size of the brain increased, the size of the teeth decreased.
Along with all these progressive features, early Homo retained many very primitive features in their morphology, including the structure of the hand and brain. Because of this, some scientists consider them only a progressive late variety of gracile australopithecines. The majority distinguishes among them two types: a smaller one - Homo habilis and a larger one - Rudolf Man Homo rudolfensis.
Hominins switched from being herbivorous to carnivorous. They probably first took prey from predators or picked up the remains of their feasts. This is evidenced by traces of stone tools on the bones, imprinted over the traces of the teeth of lions and hyenas. Early Homo learned how to make stone tools. At first it was just pebbles split in half, then the first people began to beat off several chips from the stones, making out a sharp cutting edge. Such primitive tools are called pebble or Olduvai tools, after the place of the first finds.
Early Homo may have been able to make simple windscreens out of branches pressed down to the ground with rocks. In the future, the development of culture went at an accelerating pace. Early Homo is the common name for the first representatives of the genus, to which modern man also belongs. The first Homo - H. habilis Homo habilis and H. rudolfensis Man Rudolf, lived about 2.5-1.5 million years ago in East and South Africa. They are descendants of the gracile australopithecines and direct ancestors of later humans. For a long time groups of early Homo coexisted with massive Australopithecus.
The main distinguishing features from the representatives of Australopithecus:
relatively large and progressive brain with a volume of 500-750 cm3;
the jaws and teeth are much smaller than those of Australopithecus, but larger than those of more advanced humans.
At the same time, there are still many primitive features in the structure of the body, including in the foot, hand and brain. The arms are relatively long compared to modern humans.
The so-called stone tools were made and used. Olduvai culture. Switched from herbivorous to omnivorous. They probably knew how to make the simplest dwellings such as huts from branches, the foundations of which were found in Olduvai. The time of appearance and existence of early Homo is characterized by a significant rate of evolutionary rearrangements.
1. Homo habilis Homo habilis is a smaller version of early Homo. Described in 1964 based on a sensational find from the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. Later, similar finds were made at Koobi Fora, Swartkrans, and other localities in East and South Africa. Named skillful because stone tools from the Olduvai culture were found nearby.
It differs from Rudolf Man in a smaller brain size of 500-640 cm3 and smaller jaws and teeth. Height was 1.0-1.5 m, weight - about 30-50 kg.
2. Homo rudolfensis Rudolf Man is a large variant of early Homo. Described in 1978 from skull KNM-ER 1470 from Koobi Fora in Ethiopia. Dozens of remains of representatives of this species are now known. A lower jaw has also been found in Malawi, between East and South Africa.
It differs from Homo habilis in a slightly larger brain volume up to 750 cm3, but at the same time with massive jaws and large teeth. Height 1.5-1.8 m, weight 45-80 kg
Everything around you is saturated with life: people talking, birds chirping, insects buzzing. Life is seething everywhere: in the water, on the ground, in the air.
How did life originate and develop? Perhaps you think it doesn't matter? But man differs from animals in that he thinks, strives to know what is hidden in the depths of centuries or in the infinity of the Universe.
Since the time when primitive people united in society, there have always been questions that human civilization has not yet found an unambiguous answer: where did we come from? Why are we like this? Throughout history, many theories of the origin of man have been created, but among them main consider such theories And hypotheses:
- the creation of man by God;
- evolutionary origin of man;
- extraterrestrial origin of man.
theories divine origin of the world and man adheres to religion. According to this theory, the world and people were created by God. At the same time, each religion - Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Shintoism, etc., expounds this hypothesis in its own way. In particular, the Bible says that the world was created in 3760 BC. e. However, the followers of each of the religions have their own point of view on this issue.
theory evolutionary origin of man first formulated by an English scientist Charles Darwin. In the middle of the XIX century. in his book The Origin of Species, he showed that man and all life on the planet was formed as a result of the gradual, very slow development of living organisms from the simplest forms to modern species. This process is called evolution.
This theory is now supported by most scientists. Even the Catholic Church recognizes it as interesting. In particular, Pope Pius XII noted back in 1950 that this theory deserves serious study. And Pope John Paul II, in his speech at a meeting of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, indicated that "the church considers the theory of evolution seriously substantiated and confirmed by scientific facts." However, he noticed that only God could give a soul to a person. material from the site
Many scientists, based on research, adhere to the theory cosmic origin of man. They claim that all life on our planet is brought from outer space.
Evolution (from Latin.evolution - development)- gradual, over millions of years, the development of living organisms from the simplest forms to modern species.
On this page, material on the topics:
There are currently many theories of human origin on our planet. The question of the emergence of intelligent life on Earth has always attracted the attention of scientists from various fields. In this lecture, the main versions of the origin of man will be considered, although none of them has a 100% guarantee of its veracity. Archaeologists, together with astrologers from different countries, have explored the most diverse sources of the origin of life (morphological, biological, chemical). But all these efforts, unfortunately, did not help to find out in which century BC. the first people appeared.
Darwin's theory
The most probable and close to the truth version of the origin of man is the theory of Charles Darwin (a British scientist). It was this scientist who managed to make a huge contribution to biological science. Darwin's theory is based on the definition of natural selection. According to him, natural selection plays a big role in evolution. The foundation of Darwin's theory was created from numerous observations of nature, in the process of traveling around the world. The project began in 1837 and lasted for over 20 years. Another scientist A. Wallace supported Darwin at the end of the 19th century. At his report in London, he stated that it was Charles who inspired him, after which a direction appeared that had the name "Darwinism".
All followers of this movement argue that each representative of the flora and fauna is changeable and comes from pre-existing species. It turns out that Darwin's theory is based on the impermanence of living things in nature, and the reason for this process is natural selection. It turns out that only the strongest forms survive on the planet, capable of quickly adapting to the environment. Man is one of these beings. Evolution and the desire to survive contributed to the development of a variety of skills and abilities.
evolutionary theory
According to the followers of this theory, the appearance of people on Earth is associated with the modification of primates. In our time, evolutionary theory is one of the most discussed and widespread. Its essence lies in the fact that people are descendants of certain species of monkeys. As for evolution itself, it began from time immemorial under the influence of natural selection and other external factors. This version of the origin of man is confirmed by many testimonies and evidence (psychological, paleontological, archaeological). On the other hand, the ambiguity of many facts does not give the right to consider it 100% correct.
Rice. 1 - The evolutionary theory of the origin of man
Space anomalies
This theory is the most fantastic and controversial. Her followers are sure that man appeared on planet Earth by chance. Its essence lies in the fact that man is the fruit of parallel anomalous spaces. The forefathers of modern people were representatives of other civilizations, representing a combination of energy, aura and matter. The theory assumes that in the Universe there are a huge number of planets with the same biospheres as the Earth, which were created by the information substance. If the conditions for this were favorable, then they contributed to the emergence of life.
This offshoot is called "creationism". All his followers deny the main theories of the appearance of man. They are sure that it was God who created all people, who represents the highest link. At the same time, he created a person in his own image.

Rice. 2 - Theory of creation
If we consider biblical theory of the origin of man on earth, then the first people are Adam and Eve. For example, in countries like Egypt, religion goes deep into ancient myths. A large number of skeptics consider this version impossible. This version is not supported by any evidence, it just exists.
The basis of this version is the activity of extraneous civilizations. In other words, people are the descendants of alien creatures that arrived on our planet millions of years ago. There are several outcomes in this version of the origin of mankind. One of them is the crossing of progenitors with aliens. Other outcomes are to blame for the genetic engineering of a higher mind, which created a thinking person from its own DNA. The version about the intervention of aliens in the evolutionary development of people is considered very interesting. Archaeologists are still finding various evidence (records, drawings) that supernatural forces helped ancient people.

Rice. 3 - Intervention Theory
Stages of evolution
Whatever the history of human origins, most scientists agree on the identity of the stages of development. Australopithecus are considered the first prototypes of people. They communicated with each other with the help of their hands, and their height did not exceed 130 cm.
In the next stage of evolution, a Pithecanthropus appears, which has already learned to use fire and use the gifts of nature for its own needs (bones, skins, stones). The next stage of evolution is the paleoanthropist. Such prototypes of people already knew how to think collectively and communicate using sounds.
Before the appearance of a thinking person, neoanthropes are considered the last stage in evolution. Visually, they were very similar to modern people, they created tools, chose leaders, united in tribes, etc.
Ancestral home of people
While there are disputes about which theory of the origin of man is correct, it was possible to establish exactly where the mind originated. We are talking about the African continent. A large number of archaeologists believe that the location can be safely narrowed down to the northeastern part of the mainland. Although, there are scientists who suggest that humanity began its development from Asia, namely from India and other neighboring countries.
The fact that the first people lived precisely in Africa is confirmed by numerous finds in large-scale excavations. It can be noted that at that time there were several types of prototypes of man.
 Why does a person cry for no reason
Why does a person cry for no reason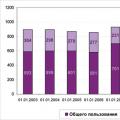 General data on the length of roads in the Russian Federation Trans-Siberian Highway, Russia
General data on the length of roads in the Russian Federation Trans-Siberian Highway, Russia How to calculate the volume of a box?
How to calculate the volume of a box?