Biography of Ivan Sergeyevich Turgenev
Ivan Sergeevich Turgenev - famous Russian writer, poet, translator, member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1860).

Orel city
Lithography. 1850s
“On October 28, 1818, on Monday, the son Ivan was born, 12 inches tall, in Orel, in his house, at 12 o’clock in the morning,” Varvara Petrovna Turgeneva made such an entry in her memorial book.
Ivan Sergeevich was her second son. The first - Nikolai - was born two years earlier, and in 1821 another boy appeared in the Turgenev family - Sergey.

Parents
It is difficult to imagine more dissimilar people than the parents of the future writer.
Mother - Varvara Petrovna, nee Lutovinova - a domineering, intelligent and sufficiently educated woman, did not shine with beauty. She was small, squat, with a broad face, spoiled by smallpox. And only the eyes were good: large, dark and shiny.
Varvara Petrovna was already thirty years old when she met the young officer Sergei Nikolaevich Turgenev. He came from an old noble family, which, however, had already become impoverished by that time. From the former wealth, only a small estate remained. Sergei Nikolaevich was handsome, graceful, smart. And it is not surprising that he made an irresistible impression on Varvara Petrovna, and she made it clear that if Sergei Nikolayevich wooed, then there would be no refusal.
The young officer thought for a moment. And although the bride was six years older than him and did not differ in attractiveness, however, the vast lands and thousands of serf souls that she owned determined the decision of Sergei Nikolayevich.
At the beginning of 1816, the marriage took place, and the young people settled in Orel.
Varvara Petrovna idolized and feared her husband. She gave him complete freedom and did not restrict anything. Sergei Nikolaevich lived the way he wanted, not burdening himself with worries about his family and household. In 1821, he retired and moved with his family to the estate of his wife, Spasskoe-Lutovinovo, seventy miles from Orel.

The childhood of the future writer passed in Spassky-Lutovinovo near the city of Mtsensk, Oryol province. With this family estate of his mother Varvara Petrovna, a stern and domineering woman, much is connected in the work of Turgenev. In the estates and estates described by him, the features of his native "nest" are invariably visible. Turgenev considered himself indebted to the Oryol region, its nature and inhabitants.

The Turgenev estate Spasskoe-Lutovinovo was located in a birch grove on a gentle hill. Around a spacious two-story manor house with columns, to which semicircular galleries adjoined, a huge park was laid out with linden alleys, orchards and flower beds.
Years of study
Varvara Petrovna was mainly engaged in the upbringing of children at an early age. Outbursts of solicitude, attention and tenderness gave way to attacks of bitterness and petty tyranny. On her orders, children were punished for the slightest misconduct, and sometimes for no reason. “I have nothing to remember my childhood,” Turgenev said many years later. “Not a single bright memory. I was afraid of my mother like fire. I was punished for every trifle - in a word, they drilled me like a recruit.
There was a fairly large library in the Turgenevs' house. Huge cabinets kept the works of ancient writers and poets, the works of French encyclopedists: Voltaire, Rousseau, Montesquieu, novels by V. Scott, de Stael, Chateaubriand; works of Russian writers: Lomonosov, Sumarokov, Karamzin, Dmitriev, Zhukovsky, as well as books on history, natural science, botany. Soon the library became for Turgenev the most favorite place in the house, where he sometimes spent whole days. To a large extent, the boy’s interest in literature was supported by his mother, who read quite a lot and knew French literature and Russian poetry of the late 18th and early 19th centuries well.
At the beginning of 1827, the Turgenev family moved to Moscow: it was time to prepare children for entering educational institutions. First, Nikolai and Ivan were placed in the private Winterkeller boarding house, and then in the Krause boarding house, later called the Lazarev Institute of Oriental Languages. Here the brothers did not study for long - only a few months.
Their further education was entrusted to home teachers. With them they studied Russian literature, history, geography, mathematics, foreign languages - German, French, English - drawing. Russian history was taught by the poet I. P. Klyushnikov, and the Russian language was taught by D. N. Dubensky, a well-known researcher of The Tale of Igor's Campaign.

University years. 1833-1837.
Turgenev was not yet fifteen years old when, having successfully passed the entrance exams, he became a student of the verbal department of Moscow University.
Moscow University at that time was the main center of advanced Russian thought. Among the young people who came to the university in the late 1820s and early 1830s, the memory of the Decembrists, who opposed the autocracy with weapons in their hands, was sacredly kept. Students closely followed the events taking place then in Russia and in Europe. Turgenev later said that it was during these years that “very free, almost republican convictions” began to take shape in him.
Of course, Turgenev had not yet developed a coherent and consistent worldview in those years. He was barely sixteen years old. It was a period of growth, a period of search and doubt.
Turgenev studied at Moscow University for only one year. After his older brother Nikolai entered the Guards Artillery stationed in St. Petersburg, his father decided that the brothers should not be separated, and therefore, in the summer of 1834, Turgenev applied for a transfer to the philological department of the philosophical faculty of St. Petersburg University.
No sooner had the Turgenev family settled in the capital than Sergei Nikolaevich suddenly died. The death of his father deeply shocked Turgenev and made him think for the first time seriously about life and death, about the place of man in the eternal movement of nature. The thoughts and experiences of the young man were reflected in a number of lyrical poems, as well as in the dramatic poem "Steno" (1834). The first literary experiments of Turgenev were created under the strongest influence of the then dominant romanticism in literature, and above all Byron's poetry. The hero of Turgenev is an ardent, passionate, full of enthusiastic aspirations man who does not want to put up with the world of evil around him, but cannot find application for his powers and eventually dies tragically. Later, Turgenev was very skeptical about this poem, calling it "an absurd work in which, with childish ineptitude, a slavish imitation of Byron's Manfred was expressed."
However, it should be noted that the poem "Steno" reflected the thoughts of the young poet about the meaning of life and the purpose of a person in it, that is, questions that many great poets of that time tried to resolve: Goethe, Schiller, Byron.
After the Moscow Metropolitan University, Turgenev seemed colorless. Here everything was different: there was no atmosphere of friendship and comradeship to which he was accustomed, there was no desire for lively communication and disputes, few people were interested in issues of public life. And the composition of the students was different. Among them were many young men from aristocratic families who had little interest in science.
Teaching at St. Petersburg University was carried out according to a rather broad program. But students did not receive serious knowledge. There were no interesting teachers. Only the professor of Russian literature Pyotr Aleksandrovich Pletnev turned out to be closer to Turgenev than others.
During his studies at the university, Turgenev showed a deep interest in music and theater. He often visited concerts, opera and drama theaters.
After graduating from university, Turgenev decided to continue his education and in May 1838 went to Berlin.

Studying abroad. 1838-1940.
After St. Petersburg, Berlin seemed to Turgenev a prim and a little boring city. “What do you want to say about the city,” he wrote, “where they get up at six o’clock in the morning, have dinner at two and go to bed before chickens, about the city where at ten o’clock in the evening only melancholic watchmen laden with beer roam the deserted streets ...”
But the university classrooms at the University of Berlin were always crowded. The lecture was attended not only by students, but also by volunteers - officers, officials, who aspired to join science.
Already the first classes at the University of Berlin revealed gaps in Turgenev's education. Later he wrote: “I studied philosophy, ancient languages, history and studied Hegel with particular zeal ... and at home I was forced to cram Latin grammar and Greek, which I knew poorly. And I wasn't one of the worst candidates."
Turgenev diligently comprehended the wisdom of German philosophy, and in his spare time he attended theaters and concerts. Music and theater became a true need for him. He listened to the operas of Mozart and Gluck, the symphonies of Beethoven, watched the dramas of Shakespeare and Schiller.
Living abroad, Turgenev did not stop thinking about his homeland, about his people, about their present and future.
Even then, in 1840, Turgenev believed in the great destiny of his people, in their strength and steadfastness.
Finally, the course of lectures at the University of Berlin ended, and in May 1841 Turgenev returned to Russia and in the most serious way began to prepare himself for scientific activity. He dreamed of becoming a professor of philosophy.
Return to Russia. Service.
Passion for philosophical sciences is one of the characteristic features of the social movement in Russia in the late 1830s and early 1840s. The progressive people of that time tried with the help of abstract philosophical categories to explain the world around them and the contradictions of Russian reality, to find answers to the burning questions of the present that worried them.
However, Turgenev's plans changed. He became disillusioned with idealistic philosophy and gave up hope with its help to solve the questions that worried him. In addition, Turgenev came to the conclusion that science was not his vocation.
At the beginning of 1842, Ivan Sergeevich filed a petition addressed to the Minister of the Interior to enroll him in the service and was soon accepted as an official for special assignments in the office under the command of V. I. Dahl, a famous writer and ethnographer. However, Turgenev did not serve long, and in May 1845 he retired.
Being in the public service gave him the opportunity to collect a lot of vital material, connected primarily with the tragic situation of the peasants and with the destructive power of serfdom, since in the office where Turgenev served, cases of punishment of serfs, all kinds of abuse of officials, etc. It was at this time that Turgenev developed a sharply negative attitude towards the bureaucratic orders that prevail in state institutions, towards the callousness and selfishness of St. Petersburg officials. In general, Petersburg life made a depressing impression on Turgenev.
Creativity I. S. Turgenev.
The first work I. S. Turgenev can be considered the dramatic poem "Steno" (1834), which he wrote in iambic pentameter as a student, and in 1836 showed it to his university teacher P. A. Pletnev.
The first publication in print was a small review of the book by A. N. Muravyov "Journey to Russian Holy Places" (1836). Many years later, Turgenev explained the appearance of this first printed work in this way: “I had just passed seventeen years then, I was a student at St. Petersburg University; my relatives, in order to ensure my future career, introduced me to Serbinovich, the then publisher of the Journal of the Ministry of Education. Serbinovich, whom I saw only once, probably wanting to test my abilities, handed me ... Muravyov's book so that I could take it apart; I wrote something about it - and now, almost forty years later, I find out that this "something" has been embossed.
His first works were poetic. His poems, beginning in the late 1830s, began to appear in the journals Sovremennik and Otechestvennye Zapiski. They clearly heard the motifs of the then dominant romantic trend, echoes of the poetry of Zhukovsky, Kozlov, Benediktov. Most of the poems are elegiac reflections about love, about a wasted youth. They, as a rule, were permeated with motives of sadness, sadness, longing. Turgenev himself was later very skeptical about his poems and poems written at this time, and never included them in collected works. “I feel a positive, almost physical antipathy to my poems...,” he wrote in 1874, “I would give dearly if they didn’t exist at all.”
Turgenev was unfair when he spoke so harshly about his poetic experiments. Among them you can find many talentedly written poems, many of which were highly appreciated by readers and critics: "Ballad", "One Again, One...", "Spring Evening", "Misty Morning, Gray Morning..." and others . Some of them were later set to music and became popular romances.
The beginning of his literary activity Turgenev considered 1843 the year when his poem Parasha appeared in print, which opened a whole series of works dedicated to the debunking of the romantic hero. Parasha met with a very sympathetic review from Belinsky, who saw in the young author "an extraordinary poetic talent", "true observation, deep thought", "a son of our time, carrying all his sorrows and questions in his chest."
First prose work I. S. Turgenev - essay "Khor and Kalinych" (1847), published in the journal "Sovremennik" and opened a whole cycle of works under the general title "Notes of a Hunter" (1847-1852). "Notes of a Hunter" were created by Turgenev at the turn of the forties and early fifties and appeared in print in the form of separate stories and essays. In 1852, they were combined by the writer into a book that became a major event in Russian social and literary life. According to M. E. Saltykov-Shchedrin, “Notes of a Hunter” “laid the foundation of a whole literature that has as its object the people and their needs.”
"Hunter's Notes"- This is a book about people's life in the era of serfdom. The images of peasants, distinguished by a sharp practical mind, a deep understanding of life, a sober look at the world around them, capable of feeling and understanding the beautiful, responding to someone else's grief and suffering, rise up alive from the pages of the Hunter's Notes. Before Turgenev, no one portrayed a people like this in Russian literature. And it is no coincidence that after reading the first essay from the Hunter's Notes - "Khor and Kalinich", "Belinsky noticed that Turgenev "came to the people from such a side, from which no one had come before him."
Turgenev wrote most of the "Notes of a Hunter" in France.
Works by I. S. Turgenev
Stories: a collection of short stories "Notes of a Hunter" (1847-1852), "Mumu" (1852), "The Story of Father Alexei" (1877), etc.;
Tales:"Asya" (1858), "First Love" (1860), "Spring Waters" (1872) and others;
Novels: Rudin (1856), Noble Nest (1859), On the Eve (1860), Fathers and Sons (1862), Smoke (1867), New (1877);
Plays:"Breakfast at the leader" (1846), "Where it is thin, there it breaks" (1847), "Bachelor" (1849), "Provincial" (1850), "A month in the country" (1854) and others;
Poetry: the dramatic poem "The Wall" (1834), poems (1834-1849), the poem "Parasha" (1843) and others, the literary and philosophical "Poems in Prose" (1882);
Translations Byron D., Goethe I., Whitman W., Flaubert G.
As well as criticism, journalism, memoirs and correspondence.

Love through life
Turgenev met the famous French singer Polina Viardot back in 1843, in St. Petersburg, where she came on tour. The singer performed a lot and successfully, Turgenev attended all her performances, told everyone about her, praised her everywhere, and quickly separated from the crowd of her countless fans. Their relationship developed and soon reached a climax. The summer of 1848 (like the previous one, like the next one) he spent in Courtavenel, on the estate of Pauline.
Love for Polina Viardot remained both happiness and torment for Turgenev until his last days: Viardot was married, she was not going to divorce her husband, but Turgenev was not driven either. He felt tied. but he was powerless to break the thread. For more than thirty years, the writer, in fact, has become a member of the Viardot family. Pauline's husband (a man, apparently, of angelic patience), Louis Viardot, he survived by only three months.

Sovremennik magazine
Belinsky and his like-minded people have long dreamed of having their own printed organ. This dream came true only in 1846, when Nekrasov and Panaev managed to rent the Sovremennik magazine, founded at one time by A. S. Pushkin and published by P. A. Pletnev after his death. Turgenev took a direct part in the organization of the new journal. According to P. V. Annenkov, Turgenev was “the soul of the whole plan, its organizer ... Nekrasov consulted with him every day; The journal was filled with his works.
In January 1847, the first issue of the updated Sovremennik was published. Turgenev published several works in it: a cycle of poems, a review of the tragedy by N.V. Kukolnik "Lieutenant General Patkul ...", "Modern Notes" (together with Nekrasov). But the real decoration of the first book of the magazine was the essay “Khor and Kalinich”, which opened a whole cycle of works under the general title “Notes of a Hunter”.
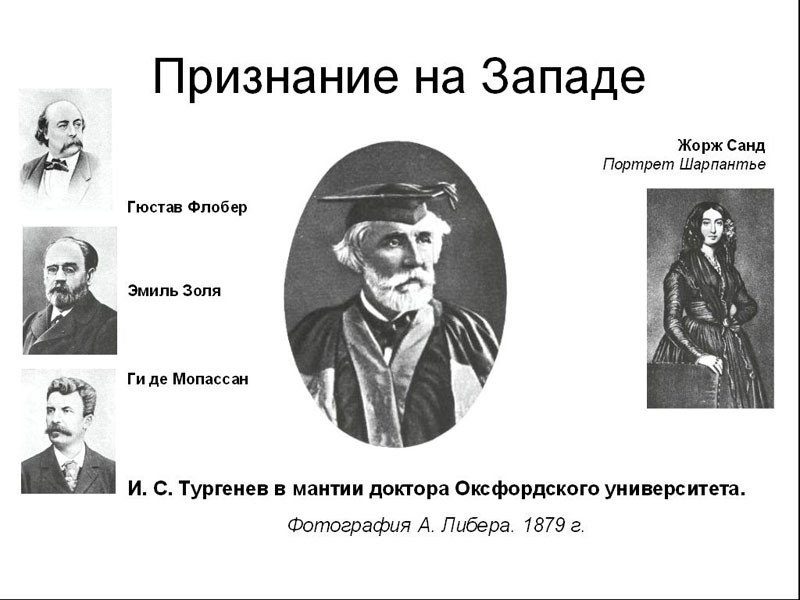
Recognition in the West
Beginning in the 60s, the name of Turgenev became widely known in the West. Turgenev maintained close friendly relations with many Western European writers. He was well acquainted with P. Mérimée, J. Sand, G. Flaubert, E. Zola, A. Daudet, Guy de Maupassant, and knew many figures of English and German culture closely. All of them considered Turgenev an outstanding realist artist and not only highly appreciated his works, but also learned from him. Addressing Turgenev, J. Sand said: “Teacher! “We all have to go through your school!”
Turgenev spent almost his entire life in Europe, only occasionally visiting Russia. He was a prominent figure in the literary life of the West. He closely communicated with many French writers, and in 1878 he even chaired (together with Victor Hugo) the International Literary Congress in Paris. It is no coincidence that it was with Turgenev that the worldwide recognition of Russian literature began.
The greatest merit of Turgenev was that he was an active propagandist of Russian literature and culture in the West: he himself translated the works of Russian writers into French and German, edited the translations of Russian authors, in every possible way contributed to the publication of the works of his compatriots in various countries of Western Europe, introduced the Western European public to works of Russian composers and artists. About this side of his activity, Turgenev, not without pride, said: “I consider it a great happiness of my life that I brought my fatherland somewhat closer to the perception of the European public.”
Connection with Russia
Almost every spring or summer, Turgenev came to Russia. Each of his visits became a whole event. The writer was a welcome guest everywhere. He was invited to speak at all kinds of literary and charity evenings, at friendly meetings.
At the same time, Ivan Sergeevich retained the "lordly" habits of a native Russian nobleman until the end of his life. The appearance itself betrayed its origin to the inhabitants of European resorts, despite the impeccable command of foreign languages. In the best pages of his prose, there is much from the silence of the estate life of landlord Russia. Hardly any of the writers - contemporaries of Turgenev's Russian language is so pure and correct, capable, as he himself used to say, "perform miracles in capable hands." Turgenev often wrote his novels "on the topic of the day."
The last time Turgenev visited his homeland was in May 1881. To his friends, he repeatedly "expressed his determination to return to Russia and settle there." However, this dream did not come true. In early 1882, Turgenev fell seriously ill, and there was no question of moving. But all his thoughts were at home, in Russia. He thought about her, bedridden by a serious illness, about her future, about the glory of Russian literature.
Shortly before his death, he expressed a wish to be buried in St. Petersburg, at the Volkov cemetery, next to Belinsky.
The last will of the writer was carried out

"Poems in Prose".
"Poems in prose" are rightly considered the final chord of the writer's literary activity. They reflected almost all the themes and motives of his work, as if re-felt by Turgenev in his declining years. He himself considered "Poems in Prose" only sketches of his future works.
Turgenev called his lyrical miniatures "Selenia" ("Old Man"), but the editor of "Bulletin of Europe" Stasyulevich replaced it with another one that remained forever - "Poems in Prose". In his letters, Turgenev sometimes called them "Zigzags", thereby emphasizing the contrast of themes and motives, images and intonations, and the unusual nature of the genre. The writer was afraid that "the river of time in its course" "will carry away these light sheets." But "Poems in Prose" met with the most cordial reception and forever entered the golden fund of our literature. No wonder P. V. Annenkov called them "a fabric of the sun, rainbows and diamonds, women's tears and the nobility of men's thought", expressing the general opinion of the reading public.
"Poems in Prose" is an amazing fusion of poetry and prose into a kind of unity that allows you to fit the "whole world" into the grain of small reflections, called by the author "the last breaths ... of an old man." But these "sighs" have conveyed to our days the inexhaustibility of the writer's vital energy.

Monuments to I. S. Turgenev
 “Lefty” - a summary of the work N
“Lefty” - a summary of the work N Turgenev, "Biryuk": a summary
Turgenev, "Biryuk": a summary Comedy A.N. Ostrovsky "Poverty is not a vice": a summary of the work
Comedy A.N. Ostrovsky "Poverty is not a vice": a summary of the work