Losses in the Second World War of all countries. Civilian losses and total losses of the German population in the Second World War
Military losses during the Second World War and the Great Patriotic War have been the subject of both controversy and speculation for many years. Moreover, the attitude towards these losses changes exactly the opposite. So, in the 70s, the propaganda apparatus of the CPSU Central Committee for some reason almost proudly broadcast about the heavy human losses of the USSR during the war. And not so much about the victims of the Nazi genocide, but about the combat losses of the Red Army. With completely incomprehensible pride, the propaganda “canard” was exaggerated about supposedly only three percent of front-line soldiers born in 1923 who survived the war. They talked with ecstasy about entire graduating classes, where all the young men went to the front and not a single one returned. An almost socialist competition was launched among rural areas to see who had more villages, where all the men who went to the front died. Although, according to demographic statistics, on the eve of the Great Patriotic War there were 8.6 million men of 1919-1923. birth, and in 1949, during the All-Union Population Census, there were 5.05 million of them alive, that is, the decline in the male population of 1919-1923. births during this period amounted to 3.55 million people. Thus, if we accept that for each of the ages 1919-1923. If the male population is equal, then there were 1.72 million men in each year of birth. Then it turns out that conscripts born in 1923 killed 1.67 million people (97%), and conscripts born in 1919-1922. births - 1.88 million people, i.e. about 450 thousand people. of those born in each of these four years (about 27% of their total number). And this despite the fact that the military personnel of 1919-1922. births made up the personnel Red Army, which took on the blow of the Wehrmacht in June 1941 and was almost completely burned out in the battles of the summer and autumn of the same year. This alone easily refutes all the speculations of the notorious “sixties” about the supposed three percent of surviving front-line soldiers born in 1923.
During “perestroika” and the so-called. “reforms” the pendulum swung in the other direction. The unimaginable figures of 30 and 40 million military personnel who died during the war were enthusiastically cited; the notorious B. Sokolov, a doctor of philology, by the way, and not a mathematician, is especially zealous with statistical methods. Absurd ideas were voiced that Germany lost only almost 100 thousand people killed during the entire war, about the monstrous ratio of 1:14 dead German and Soviet soldiers, etc. Statistical data on the losses of the Soviet Armed Forces, given in the reference book “The Classification of Secrecy Has Been Removed,” published in 1993, and in the fundamental work “Russia and the USSR in the Wars of the 20th Century (Loss of the Armed Forces),” were categorically declared falsification. Moreover, according to the principle: since it does not correspond to someone’s speculative concept of the losses of the Red Army, it means falsification. At the same time, enemy losses were and are being underestimated in every possible way. With calf delight, numbers are announced that do not fit into any goal. For example, the losses of the 4th Panzer Army and Task Force Kempf during the German offensive near Kursk in July 1943 were given as only 6,900 killed soldiers and officers and 12 burned tanks. At the same time, poor and ridiculous arguments were invented to explain why the tank army, which had practically retained 100% combat capability, suddenly retreated back: from the Allied landings in Italy, to the lack of fuel and spare parts, or even about the beginning of the rains.
Therefore, the question of the human losses of Germany during the Second World War is quite relevant. Moreover, interestingly, in Germany itself there is still no fundamental research on this issue. There is only indirect information. Most researchers, when analyzing German losses during the Second World War, use the monograph of the German researcher B. Muller-Hillebrandt “German Land Army. 1933-1945". However, this historian resorted to outright falsification. Thus, indicating the number of conscripts into the Wehrmacht and SS troops, Müller-Hillebrand provided information only for the period from 06/01/1939 to 04/30/1945, modestly keeping silent about the contingents previously called up for military service. But by June 1, 1939, Germany had already been deploying its armed forces for four years, and by June 1 of that year there were 3214.0 thousand people in the Wehrmacht! Therefore, the number of men mobilized into the Wehrmacht and SS in 1935-1945. takes on a different appearance (see Table 1).
Thus, the total number mobilized into the Wehrmacht and SS troops is not 17,893.2 thousand people, but about 21,107.2 thousand people, which immediately gives a completely different picture of Germany’s losses during the Second World War.
Now let's turn to the actual losses of the Wehrmacht. The Wehrmacht operated three different systems for recording losses:
1) via channel “IIa” - military service;
2) through the health service channel;
3) through the channel of personal accounting of losses in the territorial bodies for the list of military personnel in Germany.
But at the same time, there was an interesting feature - the losses of units and subunits were not taken into account in total, but according to their combat mission. This was done so that the Reserve Army had comprehensive information about which contingents of military personnel needed to be submitted for replenishment in each specific division. A fairly reasonable principle, but today this method of accounting for the loss of personnel makes it possible to manipulate the figures for German losses.
Firstly, separate records were kept of the so-called personnel losses. “combat strength” - Kampfwstaerke - and support units. Thus, in the German infantry division of the state in 1944, the “combat strength” was 7160 people, the number of combat support and logistics units was 5609 people, and the total strength - Tagesstaerke - 12,769 people. In the tank division according to the 1944 staff, the “combat strength” was 9,307 people, the number of combat support and logistics units was 5,420 people, and the total strength was 14,727 people. The "combat strength" of the active Wehrmacht army was approximately 40-45% of the total number of personnel. By the way, this makes it possible to very cleverly falsify the course of the war, when the Soviet troops at the front indicate their total strength, while the German troops only indicate their combat strength. Like, signalmen, sappers, repairmen, they don’t go into attacks...
Secondly, in the “combat strength” itself - Kampfwstaerke - the units “directly leading the battle” - Gefechtstaerke - were separately distinguished. The units and subunits “directly leading the battle” within the divisions were considered to be infantry (motorized rifle, tank-grenadier) regiments, tank regiments and battalions, and reconnaissance battalions. Artillery regiments and divisions, anti-tank and anti-aircraft divisions belonged to combat support units. In the Air Force - Luftwaffe - the flying personnel were considered “units directly leading the battle”, in the Navy - Kriegsmarine - the sailing personnel belonged to this category. And the accounting for the losses of “combat strength” personnel was kept separately for the personnel “directly leading the battle” and for the personnel of the combat support units.
It is also interesting to note that only those killed directly on the battlefield were taken into account in combat losses, but military personnel who died from severe wounds during the evacuation stages were already included in the losses of the Reserve Army and were excluded from the total number of irretrievable losses of the active army. That is, as soon as the injury was determined to require more than 6 weeks to heal, the Wehrmacht soldier was immediately transferred to the Reserve Army. And even if they did not have time to take him to the rear and he died close to the front line, he was still counted as an irretrievable loss in the Reserve Army and this serviceman was excluded from the number of irretrievable combat losses of a particular front (Eastern, African, Western, etc.) . That is why almost only the killed and missing appear in the accounting of Wehrmacht losses.
There was another specific feature of accounting for losses in the Wehrmacht. Czechs drafted into the Wehrmacht from the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, Poles drafted into the Wehrmacht from the Poznań and Pomeranian regions of Poland, as well as Alsatians and Lorraineers through personal registration of losses in the territorial bodies of the list of military personnel in Germany were not taken into account, since they did not belong to the so-called . "Imperial Germans" In the same way, ethnic Germans (Volksdeutsche) conscripted into the Wehrmacht from occupied European countries were not taken into account through the personal registration channel. In other words, the losses of these categories of military personnel were excluded from the total accounting of irretrievable losses of the Wehrmacht. Although more than 1,200 thousand people were drafted from these territories into the Wehrmacht and SS, not counting the ethnic Germans - Volksdoche - of the occupied countries of Europe. Six SS divisions were formed from the ethnic Germans of Croatia, Hungary and the Czech Republic alone, not counting a large number of military police units.
The Wehrmacht also did not take into account the losses of auxiliary paramilitary forces: the National Socialist Automobile Corps, the Speer Transport Corps, the Imperial Labor Service and the Todt Organization. Although the personnel of these formations took a direct part in ensuring combat operations, and at the final stage of the war, units and units of these auxiliary formations rushed into battle against Soviet troops on German territory. Often, the personnel of these formations were added as reinforcements to the Wehrmacht formations right at the front, but since this was not a reinforcement sent through the Reserve Army, a centralized record of this replenishment was not kept, and the combat losses of these personnel were not taken into account through the official channels of loss accounting.
Separately from the Wehrmacht, records were kept of the losses of the Volkssturm and the Hitler Youth, which were widely involved in the fighting in East Prussia, East Pomerania, Silesia, Brandenburg, West Pomerania, Saxony and Berlin. The Volksshurm and the Hitler Youth were under the jurisdiction of the NSDAP. Often, units of both the Volkssturm and the Hitler Youth also joined the Wehrmacht units and formations directly at the front as reinforcements, but for the same reason as with other paramilitary formations, personal registration of this reinforcement was not carried out.
The Wehrmacht also did not take into account the losses of the SS military-police units (primarily the Felgendarmerie), which fought the partisan movement, and at the final stage of the war rushed into battle against units of the Red Army.
In addition, the so-called German troops took part in the hostilities. “voluntary helpers” - Hilfswillige (“hiwi”, Hiwi), but the losses of this category of personnel were also not taken into account in the total combat losses of the Wehrmacht. Special attention should be paid to “voluntary assistants”. These “assistants” were recruited from all countries of Europe and the occupied part of the USSR, in total in 1939-1945. Up to 2 million people joined the Wehrmacht and SS as “voluntary assistants” (including about 500 thousand people from the occupied territories of the USSR). And although most of the Hiwi were service personnel from the rear structures and commandant's offices of the Wehrmacht in the occupied territories, a significant part of them were directly included in the combat units and formations.
Thus, unscrupulous researchers excluded from the total number of irretrievable losses in Germany a large number of lost personnel who directly participated in the hostilities, but were not formally related to the Wehrmacht. Although the auxiliary paramilitary formations, the Volkssturm, and the “voluntary assistants” suffered losses during the battles, these losses can rightfully be attributed to Germany’s combat losses.
Table 2 given here attempts to bring together the numbers of both the Wehrmacht and German paramilitary forces, and to roughly calculate the loss of personnel in the armed forces of Nazi Germany during the Second World War.
The number of German military personnel who were captured by the Allies and capitulated to them may be surprising, despite the fact that 2/3 of the Wehrmacht troops operated on the Eastern Front. The bottom line is that in captivity by the Allies, both the Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS military personnel (the designation of the SS field troops operating on the fronts of World War II) and the personnel of all kinds of paramilitary formations, Volkssturm, NSDAP functionaries, employees were taken into account in the general cauldron territorial divisions of the RSHA and police territorial formations, up to firefighters. As a result, the allies counted up to 4032.3 thousand people as prisoners, although the real number of prisoners of war from the Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS was significantly lower than the allies indicated in their documents - about 3000.0 thousand people, but in our We will use official data in our calculations. In addition, in April-May 1945, German troops, fearing retribution for the atrocities committed on the territory of the USSR, quickly rolled back to the west, trying to surrender to the Anglo-American troops. Also at the end of April - beginning of May 1945, formations of the Wehrmacht Reserve Army and all kinds of paramilitary formations, as well as police units, surrendered en masse to the Anglo-American troops.
Thus, the table clearly shows that the total losses of the Third Reich on the Eastern Front in killed and died from wounds, missing, and died in captivity reach 6,071 thousand people.
However, as is known, not only German troops, foreign volunteers and German paramilitary forces fought against the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front, but also the troops of their satellites. It is also necessary to take into account the losses of “volunteer helpers - “Hiwi”. Therefore, taking into account the losses of these categories of personnel, the overall picture of losses of Germany and its satellites on the Eastern Front takes on the picture shown in Table 3.
Thus, the total irretrievable losses of Nazi Germany and its satellites on the Eastern Front in 1941-1945. reach 7 million 625 thousand people. If we take losses only on the battlefield, without taking into account those who died in captivity and the losses of “voluntary assistants”, then the losses are: for Germany - about 5620.4 thousand people and for satellite countries - 959 thousand people, in total - about 6579.4 thousands of people. Soviet losses on the battlefield amounted to 6885.1 thousand people. Thus, the losses of Germany and its satellites on the battlefield, taking into account all factors, are only slightly less than the combat losses of the Soviet Armed Forces on the battlefield (about 5%), and there is no ratio of 1:8 or 1:14 to the combat losses of Germany and its satellites there is no question of USSR losses.
The figures given in the tables above are, of course, very approximate and have serious errors, but they give, to a certain approximation, the order of losses of Nazi Germany and its satellites on the Eastern Front and during the war in general. Moreover, of course, if not for the inhumane treatment of Soviet prisoners of war by the Nazis, the total number of losses of Soviet military personnel would have been significantly lower. With an appropriate attitude towards Soviet prisoners of war, at least one and a half to two million people from among those who died in German captivity could have remained alive.
Nevertheless, a detailed and detailed study of the real human losses of Germany during the Second World War does not exist to date, because there is no political order, and many data regarding German losses are still classified under the pretext that they can cause “moral trauma” to the current German society (it would be better to remain in blissful ignorance of how many Germans died during the Second World War). Contrary to the popular picture of the domestic media in Germany, which is actively falsifying history. The main goal of these actions is to introduce into public opinion the idea that in the war with the USSR, Nazi Germany was the defending side, and the Wehrmacht was the “advanced detachment of European civilization” in the fight against “Bolshevik barbarism.” And there they actively praise the “brilliant” German generals, who held back the “Asian hordes of the Bolsheviks” for four years, with minimal losses of German troops, and only the “twenty-fold numerical superiority of the Bolsheviks,” who filled the Wehrmacht with corpses, broke the resistance of the “valiant” Wehrmacht soldiers. And the thesis is constantly being exaggerated that more “civilian” German population died than soldiers at the front, and most of the civilian deaths allegedly occurred in the eastern part of Germany, where Soviet troops allegedly committed atrocities.
In light of the problems discussed above, it is necessary to touch upon the clichés persistently imposed by pseudo-historians that the USSR won by “filling the Germans with the corpses of its soldiers.” The USSR simply did not have such a quantity of human resources. As of June 22, 1941, the population of the USSR was about 190-194 million people. Including the male population was about 48-49% - approximately 91-93 million people, of this number men 1891-1927. births were about 51-53 million people. We exclude approximately 10% of men who are unfit for military service even in wartime - this is about 5 million people. We exclude 18-20% of the “reserved” - highly qualified specialists who are not subject to conscription - this is about another 10 million people. Thus, the conscription resource of the USSR was about 36-38 million people. This is what the USSR actually demonstrated by conscripting 34,476.7 thousand people into the Armed Forces. In addition, it must be taken into account that a significant part of the conscript contingent remained in the occupied territories. And many of these people were either driven to Germany, or died, or took the path of collaboration, and after the liberation by Soviet troops from the territories subject to occupation, much fewer people were drafted into the army (40-45%) than could have been drafted before the occupation. In addition, the economy of the USSR simply could not stand it if almost all men capable of bearing arms - 48-49 million people - were drafted into the army. Then there would be no one to melt steel, produce T-34 and Il-2, or grow grain.
To have an Armed Forces of 11,390.6 thousand people in May 1945, to have 1,046 thousand people being treated in hospitals, to demobilize 3,798.2 thousand people due to wounds and illnesses, to lose 4,600 thousand people. captured and lost 26,400 thousand people killed, exactly 48,632.3 thousand people should have been mobilized into the Armed Forces. That is, with the exception of cripples completely unfit for military service, not a single man from 1891-1927. births should not have remained in the rear! Moreover, taking into account that some men of military age ended up in the occupied territories, and some worked at industrial enterprises, older and younger men inevitably had to be mobilized. However, the mobilization of men older than 1891 was not carried out, nor was the mobilization of conscripts younger than 1927. In general, if Doctor of Philology B. Sokolov had been engaged in analyzing poetry or prose, perhaps he would not have become a laughing stock.
Returning to the losses of the Wehrmacht and the Third Reich as a whole, it should be noted that the issue of accounting for losses there is quite interesting and specific. Thus, the data on losses of armored vehicles given by B. Muller-Hillebrandt are very interesting and noteworthy. For example, in April-June 1943, when there was a lull on the Eastern Front and fighting took place only in North Africa, 1019 tanks and assault guns were counted as irretrievable losses. Despite the fact that by the end of March, Army Africa had barely 200 tanks and assault guns, and in April and May, at most 100 units of armored vehicles were delivered to Tunisia. Those. in North Africa in April and May, the Wehrmacht could have lost at most 300 tanks and assault guns. Where did another 700-750 lost armored vehicles come from? Were there really secret tank battles on the Eastern Front? Or did the Wehrmacht tank army find its end in Yugoslavia these days?
Similar to the losses of armored vehicles in December 1942, when there were fierce tank battles on the Don, or the losses in January 1943, when German troops rolled back from the Caucasus, abandoning their equipment, Müller-Hillebrand cites only 184 and 446 tanks and assault guns. But in February-March 1943, when the Wehrmacht launched a counteroffensive in the Donbass, the losses of the German armored vehicles suddenly reached 2069 units in February and 759 units in March. It must be taken into account that the Wehrmacht was advancing, the battlefield remained with the German troops, and all armored vehicles damaged in the battles were delivered to the Wehrmacht tank repair units. In Africa, the Wehrmacht could not suffer such losses; by the beginning of February, Army Africa consisted of no more than 350-400 tanks and assault guns, and in February-March it received only about 200 units of armored vehicles for replenishment. Those. even with the destruction of all German tanks in Africa, the losses of Army Africa in February-March could not exceed 600 units; the remaining 2,228 tanks and assault guns were lost on the Eastern Front. How could this happen? Why did the Germans lose five times more tanks during the offensive than during the retreat, although war experience shows that the opposite always happens?
The answer is simple: in February 1943, the 6th German Army under Field Marshal Paulus capitulated in Stalingrad. And the Wehrmacht had to transfer to the list of irretrievable losses all the armored vehicles that it had long ago lost in the Don steppes, but which continued to be modestly listed in medium- and long-term repairs in the 6th Army.
It is impossible to explain why, gnawing through the deeply echeloned defenses of Soviet troops near Kursk in July 1943, saturated with anti-tank artillery and tanks, German troops lost fewer tanks than in February 1943, when they launched counterattacks on the lined-up troops of the South-Western and Voronezh fronts. Even if we assume that in February 1943 German troops lost 50% of their tanks in Africa, it is difficult to admit that in February 1943 in the Donbass the small Soviet troops were able to knock out more than 1000 tanks, and in July near Belgorod and Orel - only 925.
It is no coincidence that for a long time, when the documents of the German “Panzerdivisions” were captured in the “cauldrons,” serious questions arose about where the German equipment went if no one broke through from the encirclement, and the amount of abandoned and broken equipment did not correspond to what was written in the documents. Each time, the Germans had significantly fewer tanks and assault guns than were listed according to the documents. And only by mid-1944 did they realize that the actual composition of German tank divisions must be determined by the “combat ready” column. Situations often arose when in the German tank and tank-grenadier divisions there were more “dead tank souls” than actually available combat-ready tanks and assault guns. And burnt-out tanks, with turrets twisted on their sides, with gaping holes in their armor, stood in the courtyards of tank repair plants, on paper moving from vehicles of one repair category to another, waiting either to be sent for melting down, or to be captured by Soviet troops. But at that time, German industrial corporations were quietly “sawing” the finances allocated for supposedly long-term repairs or repairs “to be sent to Germany.” In addition, if Soviet documents immediately and clearly indicated that an irretrievably lost tank was burned out or broken so that it could not be restored, then German documents indicated only the disabled unit or unit (engine, transmission, chassis), or indicated location of combat damage (hull, turret, bottom, etc.). Moreover, even a tank that was completely burned out by a shell hitting the engine compartment was listed as having engine damage.
If we analyze the same B. Müller-Hillebrandt’s data on the losses of the “Royal Tigers”, an even more striking picture emerges. At the beginning of February 1945, the Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS had 219 Pz tanks. Kpfw. VI Ausf. B "Tiger II" ("Royal Tiger"). By this time, 417 tanks of this type had been produced. And according to Muller-Hillebrandt, 57 were lost. In total, the difference between produced and lost tanks is 350 units. In stock - 219. Where did 131 cars go? And that is not all. According to the same retired general, in August 1944 there were no lost Royal Tigers at all. And many other researchers of the history of the Panzerwaffe also find themselves in an awkward position when almost everyone points out that German troops admitted the loss of only 6 (six) Pz. Kpfw. VI Ausf. B "Tiger II". But what then to do with the situation when, near the town of Szydłów and the village of Oglendów near Sandomierz, Soviet trophy groups and special groups from the armored department of the 1st Ukrainian Front studied in detail and described, indicating serial numbers, 10 knocked out and burned out and 3 fully operational “Royal Tigers” ? We can only assume that the knocked out and burned out “Royal Tigers”, standing within the direct line of sight of the German troops, were considered by the Wehrmacht to be undergoing long-term repairs under the pretext that, theoretically, these tanks could be repulsed during a counterattack and then returned to service. Original logic, but nothing else comes to mind.
According to B. Müller-Hillebrandt, by February 1, 1945, 5840 Pz heavy tanks were produced. Kpfw. V "Panther" ("Panther"), lost - 3059 units, 1964 units were available. If we take the difference between the Panthers produced and their losses, the balance is 2781 units. There were, as already indicated, 1964 units. At the same time, Panther tanks were not transferred to Germany’s satellites. Where did the 817 units go?
With Pz tanks. Kpfw. IV is exactly the same picture. According to Müller-Hillebrandt, 8,428 units of these vehicles were produced by February 1, 1945, 6,151 were lost, the difference is 2,277 units, and 1,517 units were available on February 1, 1945. No more than 300 vehicles of this type were transferred to the Allies. Thus, up to 460 vehicles are left unaccounted for and disappeared to God knows where.
Tanks Pz. Kpfw. III. Produced - 5681 units, lost by February 1, 1945 - 4808 units, difference - 873 units, available on the same date - 534 tanks. No more than 100 units were transferred to the satellites, so, who knows where, about 250 tanks disappeared from the register.
In total, more than 1,700 tanks “Royal Tiger”, “Panther”, Pz. Kpfw. IV and Pz. Kpfw. III.
Paradoxically, to date, not a single attempt to deal with the irretrievable losses of the Wehrmacht in technology has been successful. No one has been able to analyze in detail by month and year what real irretrievable losses the Panzerwaffe suffered. And all because of the peculiar method of “accounting” for the losses of military equipment in the German Wehrmacht.
Similarly, in the Luftwaffe, the existing method of accounting for losses made it possible for a long time to list in the “repair” column the aircraft that were shot down but fell on their territory. Sometimes even a plane smashed to smithereens that fell in the disposition of German troops was not immediately included in the lists of irretrievable losses, but was listed as damaged. All this led to the fact that in Luftwaffe squadrons up to 30-40%, and even more, of equipment was constantly listed as not combat-ready, smoothly moving from the category of damaged to the category subject to write-off.
One example: when in July 1943, on the southern front of the Kursk Bulge, pilot A. Gorovets shot down 9 Ju-87 dive bombers in one battle, the Soviet infantry examined the crash sites of the Junkers and reported detailed data on the downed aircraft: tactical and serial numbers given on dead crew members, etc. However, the Luftwaffe admitted the loss of only two dive bombers that day. How could this happen? The answer is simple: by the evening of the day of the air battle, the territory where the Luftwaffe bombers fell was occupied by German troops. And the downed planes ended up in territory controlled by the Germans. And out of nine bombers, only two disintegrated in the air, the rest fell, but retained relative integrity, although they were mangled. And the Luftwaffe, with a calm soul, classified the downed planes as those that had only received combat damage. Surprisingly, this is a real fact.
And in general, when considering the issue of losses of Wehrmacht equipment, we must take into account that huge amounts of money were made on repairing equipment. And when it came to the financial interests of the financial-industrial oligarchy, the entire repressive apparatus of the Third Reich stood at attention in front of it. The interests of industrial corporations and banks were looked after sacredly. Moreover, most of the Nazi bosses had their own selfish interests in this.
One more specific point should be noted. Contrary to popular belief about the pedantry, accuracy and scrupulousness of the Germans, the Nazi elite understood perfectly well that a complete and accurate accounting of losses could become a weapon against them. After all, there is always a possibility that information about the true scale of losses will fall into the hands of the enemy and will be used in the propaganda war against the Reich. Therefore, in Nazi Germany they turned a blind eye to the confusion in accounting for losses. At first there was a calculation that the victors would not be judged, then it became a deliberate policy so as not to give the victors, in the event of the complete defeat of the Third Reich, arguments for exposing the scale of the disaster to the German people. In addition, it cannot be ruled out that at the final stage of the war, a special erasure of the archives was carried out so as not to provide the victors with additional arguments in accusing the leaders of the Nazi regime of crimes not only against other nations, but also against their own, German. After all, the death of several million young men in a senseless massacre for the sake of realizing delusional ideas about world domination is a very compelling argument for the prosecution.
Therefore, the true scale of human losses in Germany during the Second World War is still awaiting its scrupulous researchers, and then very interesting facts may be revealed to them. But on condition that these will be conscientious historians, and not all kinds of corned beef, mlechina, Svanidze, Afanasyev, Gavriilpopov and Sokolov. Paradoxically, the commission to combat the falsification of history will find more work to do inside Russia than outside its borders.
Before we go into explanations, statistics, etc., let’s immediately clarify what we mean. This article examines the losses suffered by the Red Army, the Wehrmacht and the troops of the satellite countries of the Third Reich, as well as the civilian population of the USSR and Germany, only in the period from 06/22/1941 until the end of hostilities in Europe (unfortunately, in the case of Germany this is practically unenforceable). The Soviet-Finnish war and the “liberation” campaign of the Red Army were deliberately excluded. The issue of losses of the USSR and Germany has been repeatedly raised in the press, there are endless debates on the Internet and on television, but researchers on this issue cannot come to a common denominator, because, as a rule, all arguments ultimately come down to emotional and politicized statements. This once again proves how painful this issue is in our country. The purpose of the article is not to “clarify” the final truth in this matter, but to attempt to summarize the various data contained in disparate sources. We will leave the right to draw conclusions to the reader.
With all the variety of literature and online resources about the Great Patriotic War, ideas about it largely suffer from a certain superficiality. The main reason for this is the ideological nature of this or that research or work, and it does not matter what kind of ideology it is - communist or anti-communist. The interpretation of such a grandiose event in the light of any ideology is obviously false.
It is especially bitter to read recently that the war of 1941–45. was just a clash between two totalitarian regimes, where one, they say, was completely consistent with the other. We will try to look at this war from the most justified point of view - geopolitical.
Germany in the 1930s, for all its Nazi “peculiarities,” directly and unswervingly continued that powerful desire for primacy in Europe, which for centuries determined the path of the German nation. Even the purely liberal German sociologist Max Weber wrote during World War I: “...we, 70 million Germans...are obliged to be an empire. We must do this, even if we are afraid of failure.” The roots of this aspiration of the Germans go back centuries; as a rule, the Nazis’ appeal to medieval and even pagan Germany is interpreted as a purely ideological event, as the construction of a myth mobilizing the nation.
From my point of view, everything is more complicated: it was the German tribes that created the empire of Charlemagne, and later on its foundation the Holy Roman Empire of the German nation was formed. And it was the “empire of the German nation” that created what is called “European civilization” and began the aggressive policy of the Europeans with the sacramental “Drang nach osten” - “onslaught to the east”, because half of the “original” German lands, up until the 8th–10th centuries, belonged to Slavic tribes. Therefore, giving the plan of war against the “barbaric” USSR the name “Plan Barbarossa” is not a coincidence. This ideology of German “primacy” as the fundamental force of “European” civilization was the original cause of two world wars. Moreover, at the beginning of World War II, Germany was able to truly (albeit briefly) realize its aspiration.
Invading the borders of one or another European country, German troops met resistance that was amazing in its weakness and indecisiveness. Short-term battles between the armies of European countries and the German troops invading their borders, with the exception of Poland, were more likely compliance with a certain “custom” of war than actual resistance.
Extremely much has been written about the exaggerated European “Resistance Movement,” which supposedly caused enormous damage to Germany and testified that Europe flatly rejected its unification under German leadership. But, with the exception of Yugoslavia, Albania, Poland and Greece, the scale of the Resistance is the same ideological myth. Undoubtedly, the regime established by Germany in the occupied countries did not suit large sections of the population. In Germany itself there was also resistance to the regime, but in neither case was it resistance of the country and the nation as a whole. For example, in the Resistance movement in France, 20 thousand people died in 5 years; Over the same 5 years, about 50 thousand Frenchmen died who fought on the side of the Germans, that is, 2.5 times more!

In Soviet times, the exaggeration of the Resistance was introduced into the minds as a useful ideological myth, saying that our fight with Germany was supported by all of Europe. In fact, as already mentioned, only 4 countries offered serious resistance to the invaders, which is explained by their “patriarchal” nature: they were alien not so much to the “German” order imposed by the Reich, but to the pan-European one, because these countries, in their way of life and consciousness, were largely not belonged to European civilization (although geographically included in Europe).
Thus, by 1941, almost all of continental Europe, one way or another, but without any major shocks, became part of the new empire with Germany at its head. Of the existing two dozen European countries, almost half - Spain, Italy, Denmark, Norway, Hungary, Romania, Slovakia, Finland, Croatia - together with Germany entered the war against the USSR, sending their armed forces to the Eastern Front (Denmark and Spain without a formal announcement war). The rest of the European countries did not take part in military operations against the USSR, but one way or another “worked” for Germany, or, rather, for the newly formed European Empire. Misconceptions about events in Europe have made us completely forget about many of the real events of that time. So, for example, the Anglo-American troops under the command of Eisenhower in November 1942 in North Africa initially fought not with the Germans, but with a 200,000-strong French army, despite the quick “victory” (Jean Darlan, due to the clear superiority of the Allied forces, ordered the surrender of the French troops), 584 Americans, 597 British and 1,600 French were killed in action. Of course, these are miniscule losses on the scale of the entire Second World War, but they show that the situation was somewhat more complicated than is usually thought.
In battles on the Eastern Front, the Red Army captured half a million prisoners, who were citizens of countries that did not seem to be at war with the USSR! It can be argued that these are “victims” of German violence, which drove them into Russian spaces. But the Germans were no more stupid than you and me and would hardly have allowed an unreliable contingent to the front. And while the next great and multinational army was winning victories in Russia, Europe was, by and large, on its side. Franz Halder, in his diary on June 30, 1941, wrote down Hitler's words: "European unity as a result of a joint war against Russia." And Hitler assessed the situation quite correctly. In fact, the geopolitical goals of the war against the USSR were carried out not only by the Germans, but by 300 million Europeans, united on various grounds - from forced submission to desired cooperation - but, one way or another, acting together. Only thanks to their reliance on continental Europe were the Germans able to mobilize 25% of the total population into the army (for reference: the USSR mobilized 17% of its citizens). In a word, the strength and technical equipment of the army that invaded the USSR was provided by tens of millions of skilled workers throughout Europe.

Why did I need such a long introduction? The answer is simple. Finally, we must realize that the USSR fought not only with the German Third Reich, but with almost all of Europe. Unfortunately, the eternal “Russophobia” of Europe was superimposed by the fear of the “terrible beast” - Bolshevism. Many volunteers from European countries who fought in Russia fought precisely against a communist ideology that was alien to them. No less of them were conscious haters of the “inferior” Slavs, infected with the plague of racial superiority. The modern German historian R. Rurup writes:
“Many documents of the Third Reich captured the image of the enemy - the Russian, deeply rooted in German history and society. Such views were characteristic even of those officers and soldiers who were not convinced or enthusiastic Nazis. They (these soldiers and officers) also shared ideas about “ "the eternal struggle" of the Germans... about the defense of European culture from the "Asian hordes", about the cultural vocation and right of domination of the Germans in the East. The image of an enemy of this type was widespread in Germany, it belonged to "spiritual values."
And this geopolitical consciousness was not unique to the Germans as such. After June 22, 1941, volunteer legions appeared by leaps and bounds, later turning into the SS divisions “Nordland” (Scandinavian), “Langemarck” (Belgian-Flemish), “Charlemagne” (French). Guess where they defended “European civilization”? That’s right, quite far from Western Europe, in Belarus, Ukraine, Russia. German professor K. Pfeffer wrote in 1953: “Most of the volunteers from Western European countries went to the Eastern Front because they saw this as a COMMON task for the entire West...” It was with the forces of almost all of Europe that the USSR was destined to face, and not just with Germany, and this clash was not “two totalitarianisms,” but “civilized and progressive” Europe with the “barbaric state of subhumans” that had frightened Europeans from the east for so long.

1. USSR losses
According to official data from the 1939 population census, 170 million people lived in the USSR - significantly more than in any other single country in Europe. The entire population of Europe (without the USSR) was 400 million people. By the beginning of World War II, the population of the Soviet Union differed from the population of future enemies and allies in its high mortality rate and low life expectancy. However, the high birth rate ensured significant population growth (2% in 1938–39). Also different from Europe was the youth of the USSR population: the proportion of children under 15 years old was 35%. It was this feature that made it possible to restore the pre-war population relatively quickly (within 10 years). The share of the urban population was only 32% (for comparison: in Great Britain - more than 80%, in France - 50%, in Germany - 70%, in the USA - 60%, and only in Japan it had the same value as in THE USSR).
In 1939, the population of the USSR increased noticeably after the entry into the country of new regions (Western Ukraine and Belarus, the Baltics, Bukovina and Bessarabia), whose population ranged from 20 to 22.5 million people. The total population of the USSR, according to a certificate from the Central Statistical Office as of January 1, 1941, was determined to be 198,588 thousand people (including the RSFSR - 111,745 thousand people). According to modern estimates, it was still smaller, and on June 1, 1941 it was 196.7 million people.
Population of some countries for 1938–40
USSR - 170.6 (196.7) million people;
Germany - 77.4 million people;
France - 40.1 million people;
Great Britain - 51.1 million people;
Italy - 42.4 million people;
Finland - 3.8 million people;
USA - 132.1 million people;
Japan - 71.9 million people.
By 1940, the population of the Reich had increased to 90 million people, and taking into account the satellites and conquered countries - 297 million people. By December 1941, the USSR had lost 7% of the country's territory, where 74.5 million people lived before the start of the Second World War. This once again emphasizes that despite Hitler’s assurances, the USSR did not have an advantage in human resources over the Third Reich.
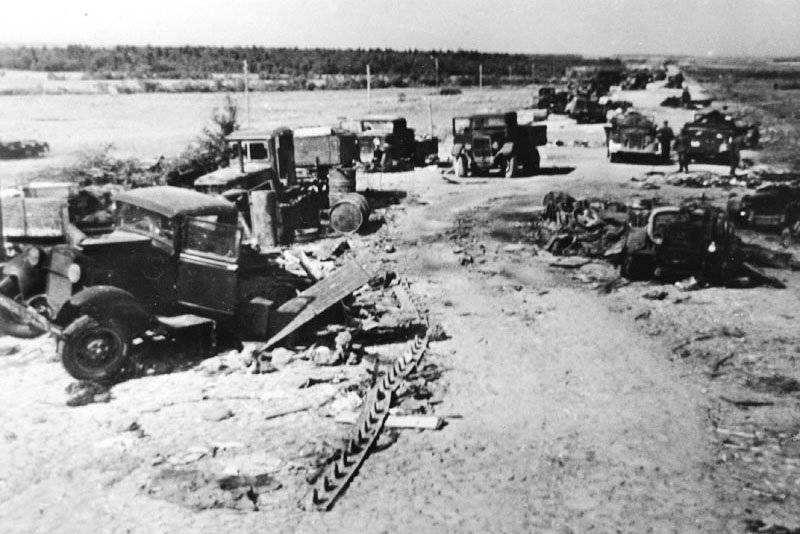

During the entire Great Patriotic War in our country, 34.5 million people put on military uniforms. This amounted to about 70% of the total number of men aged 15–49 years in 1941. The number of women in the Red Army was approximately 500 thousand. The percentage of conscripts was higher only in Germany, but as we said earlier, the Germans covered the labor shortage at the expense of European workers and prisoners of war. In the USSR, such a deficit was covered by increased working hours and the widespread use of labor by women, children and the elderly.
For a long time, the USSR did not talk about direct irretrievable losses of the Red Army. In a private conversation, Marshal Konev in 1962 named the figure 10 million people, a famous defector - Colonel Kalinov, who fled to the West in 1949 - 13.6 million people. The figure of 10 million people was published in the French version of the book “Wars and Population” by B. Ts. Urlanis, a famous Soviet demographer. The authors of the famous monograph “The Classification of Secrecy Has Been Removed” (edited by G. Krivosheev) in 1993 and in 2001 published the figure of 8.7 million people; at the moment, this is precisely what is indicated in most reference literature. But the authors themselves state that it does not include: 500 thousand people liable for military service, called up for mobilization and captured by the enemy, but not included in the lists of units and formations. Also, the almost completely dead militias of Moscow, Leningrad, Kyiv and other large cities are not taken into account. Currently, the most complete lists of irretrievable losses of Soviet soldiers amount to 13.7 million people, but approximately 12-15% of the records are repeated. According to the article “Dead Souls of the Great Patriotic War” (“NG”, 06.22.99), the historical and archival search center “Fate” of the “War Memorials” association established that due to double and even triple counting, the number of dead soldiers of the 43rd and 2nd of the Shock Armies in the battles studied by the center was overestimated by 10-12%. Since these figures refer to a period when the accounting of losses in the Red Army was not careful enough, it can be assumed that in the war as a whole, due to double counting, the number of Red Army soldiers killed was overestimated by approximately 5–7%, i.e. by 0.2– 0.4 million people

On the issue of prisoners. American researcher A. Dallin, based on archival German data, estimates their number at 5.7 million people. Of these, 3.8 million died in captivity, that is, 63%. Domestic historians estimate the number of captured Red Army soldiers at 4.6 million people, of which 2.9 million died. Unlike German sources, this does not include civilians (for example, railway workers), as well as seriously wounded people who remained on the battlefield occupied by the enemy, and subsequently died from wounds or were shot (about 470-500 thousand). The situation of prisoners of war was especially desperate in the first year of the war, when more than half of their total number (2.8 million people) was captured, and their labor had not yet been used in interests of the Reich. Open-air camps, hunger and cold, illness and lack of medicine, cruel treatment, mass executions of the sick and unable to work, and simply all those unwanted, primarily commissars and Jews. Unable to cope with the flow of prisoners and guided by political and propaganda motives, the occupiers in 1941 sent home over 300 thousand prisoners of war, mainly natives of western Ukraine and Belarus. This practice was subsequently discontinued.
Also, do not forget that approximately 1 million prisoners of war were transferred from captivity to the auxiliary units of the Wehrmacht. In many cases, this was the only chance for prisoners to survive. Again, most of these people, according to German data, tried to desert from Wehrmacht units and formations at the first opportunity. The local auxiliary forces of the German army included:
1) volunteer helpers (hivi)
2) order service (odi)
3) front auxiliary parts (noise)
4) police and defense teams (gema).
At the beginning of 1943, the Wehrmacht operated: up to 400 thousand Khivi, from 60 to 70 thousand Odi, and 80 thousand in the eastern battalions.
Some of the prisoners of war and the population of the occupied territories made a conscious choice in favor of cooperation with the Germans. Thus, in the SS division “Galicia” there were 82,000 volunteers for 13,000 “places”. More than 100 thousand Latvians, 36 thousand Lithuanians and 10 thousand Estonians served in the German army, mainly in the SS troops.
In addition, several million people from the occupied territories were taken to forced labor in the Reich. The ChGK (Emergency State Commission) immediately after the war estimated their number at 4.259 million people. More recent studies give a figure of 5.45 million people, of whom 850-1000 thousand died.
Estimates of direct physical extermination of the civilian population, according to the ChGK data from 1946.
RSFSR - 706 thousand people.
Ukrainian SSR - 3256.2 thousand people.
BSSR - 1547 thousand people.
Lit. SSR - 437.5 thousand people.
Lat. SSR - 313.8 thousand people.
Est. SSR - 61.3 thousand people.
Mold. USSR - 61 thousand people.
Karelo-Fin. SSR - 8 thousand people. (10)
Such high figures for Lithuania and Latvia are explained by the fact that there were death camps and concentration camps for prisoners of war there. The population losses in the front line during the fighting were also enormous. However, it is virtually impossible to determine them. The minimum acceptable value is the number of deaths in besieged Leningrad, i.e. 800 thousand people. In 1942, the infant mortality rate in Leningrad reached 74.8%, that is, out of 100 newborns, about 75 babies died!

Another important question. How many former Soviet citizens chose not to return to the USSR after the end of the Great Patriotic War? According to Soviet archival data, the number of the “second emigration” was 620 thousand people. 170,000 are Germans, Bessarabians and Bukovinians, 150,000 are Ukrainians, 109,000 are Latvians, 230,000 are Estonians and Lithuanians, and only 32,000 are Russians. Today this estimate seems clearly underestimated. According to modern data, emigration from the USSR amounted to 1.3 million people. Which gives us a difference of almost 700 thousand, previously attributed to irreversible population losses.
So, what are the losses of the Red Army, the civilian population of the USSR and the general demographic losses in the Great Patriotic War. For twenty years, the main estimate was the far-fetched figure of 20 million people by N. Khrushchev. In 1990, as a result of the work of a special commission of the General Staff and the State Statistics Committee of the USSR, a more reasonable estimate of 26.6 million people appeared. At the moment it is official. Noteworthy is the fact that back in 1948, the American sociologist Timashev gave an assessment of the USSR's losses in the war, which practically coincided with the assessment of the General Staff commission. Maksudov’s assessment made in 1977 also coincides with the data of the Krivosheev Commission. According to the commission of G.F. Krivosheev.
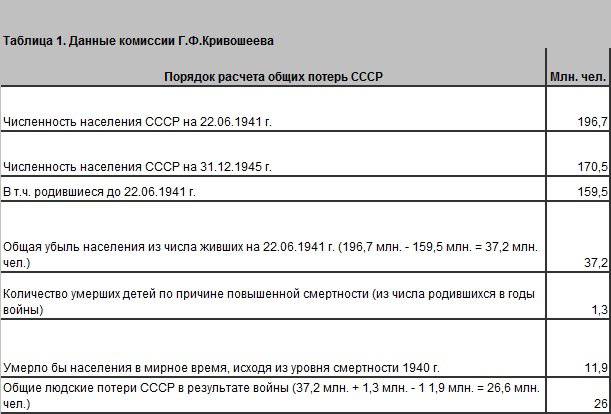
So let's summarize:
Post-war estimate of Red Army losses: 7 million people.
Timashev: Red Army - 12.2 million people, civilian population 14.2 million people, direct human losses 26.4 million people, total demographic 37.3 million.
Arntz and Khrushchev: direct human: 20 million people.
Biraben and Solzhenitsyn: Red Army 20 million people, civilian population 22.6 million people, direct human 42.6 million, general demographic 62.9 million people.
Maksudov: Red Army - 11.8 million people, civilian population 12.7 million people, direct casualties 24.5 million people. It is impossible not to make a reservation that S. Maksudov (A.P. Babenyshev, Harvard University USA) determined the purely combat losses of the spacecraft at 8.8 million people
Rybakovsky: direct human 30 million people.
Andreev, Darsky, Kharkov (General Staff, Krivosheev Commission): direct combat losses of the Red Army 8.7 million (11,994 including prisoners of war) people. Civilian population (including prisoners of war) 17.9 million people. Direct human losses: 26.6 million people.
B. Sokolov: losses of the Red Army - 26 million people
M. Harrison: total losses of the USSR - 23.9 - 25.8 million people.
What do we have in the “dry” residue? We will be guided by simple logic.
The estimate of the losses of the Red Army given in 1947 (7 million) does not inspire confidence, since not all calculations, even with the imperfections of the Soviet system, were completed.
Khrushchev's assessment is also not confirmed. On the other hand, “Solzhenitsyn’s” 20 million casualties in the army alone, or even 44 million, are just as unfounded (without denying some of A. Solzhenitsyn’s talent as a writer, all the facts and figures in his works are not confirmed by a single document and it’s difficult to understand where he comes from took - impossible).
Boris Sokolov is trying to explain to us that the losses of the USSR armed forces alone amounted to 26 million people. He is guided by the indirect method of calculations. The losses of the officers of the Red Army are known quite accurately; according to Sokolov, this is 784 thousand people (1941–44). Mr. Sokolov, referring to the average statistical losses of Wehrmacht officers on the Eastern Front of 62,500 people (1941–44), and data from Müller-Hillebrandt , displays the ratio of losses of the officer corps to the rank and file of the Wehrmacht as 1:25, that is, 4%. And, without hesitation, he extrapolates this technique to the Red Army, receiving his 26 million irretrievable losses. However, upon closer examination, this approach turns out to be initially false. Firstly, 4% of officer losses is not an upper limit, for example, in the Polish campaign, the Wehrmacht lost 12% of officers to the total losses of the Armed Forces. Secondly, it would be useful for Mr. Sokolov to know that with the regular strength of the German infantry regiment being 3049 officers, there were 75 officers, that is, 2.5%. And in the Soviet infantry regiment, with a strength of 1582 people, there are 159 officers, i.e. 10%. Thirdly, appealing to the Wehrmacht, Sokolov forgets that the more combat experience in the troops, the fewer losses among officers. In the Polish campaign, the loss of German officers was −12%, in the French campaign - 7%, and on the Eastern Front already 4%.
The same can be applied to the Red Army: if at the end of the war the losses of officers (not according to Sokolov, but according to statistics) were 8-9%, then at the beginning of the Second World War they could have been 24%. It turns out, like a schizophrenic, everything is logical and correct, only the initial premise is incorrect. Why did we dwell on Sokolov’s theory in such detail? Yes, because Mr. Sokolov very often presents his figures in the media.
Taking into account the above, discarding the obviously underestimated and overestimated estimates of losses, we get: Krivosheev Commission - 8.7 million people (with prisoners of war 11.994 million, 2001 data), Maksudov - losses are even slightly lower than the official ones - 11.8 million people. (1977−93), Timashev - 12.2 million people. (1948). This can also include the opinion of M. Harrison, with the level of total losses indicated by him, the losses of the army should fit into this period. These data were obtained using different calculation methods, since Timashev and Maksudov, respectively, did not have access to the archives of the USSR and Russian Defense Ministry. It seems that the losses of the USSR Armed Forces in the Second World War lie very close to such a “heaped” group of results. Let's not forget that these figures include 2.6–3.2 million destroyed Soviet prisoners of war.

In conclusion, we should probably agree with Maksudov’s opinion that the emigration outflow, which amounted to 1.3 million people, which was not taken into account in the General Staff study, should be excluded from the number of losses. The losses of the USSR in the Second World War should be reduced by this amount. In percentage terms, the structure of USSR losses looks like this:
41% - aircraft losses (including prisoners of war)
35% - aircraft losses (without prisoners of war, i.e. direct combat)
39% - losses of the population of the occupied territories and the front line (45% with prisoners of war)
8% - rear population
6% - GULAG
6% - emigration outflow.

2. Losses of the Wehrmacht and SS troops
To date, there are no sufficiently reliable figures for the losses of the German army obtained by direct statistical calculation. This is explained by the absence, for various reasons, of reliable initial statistical materials on German losses.
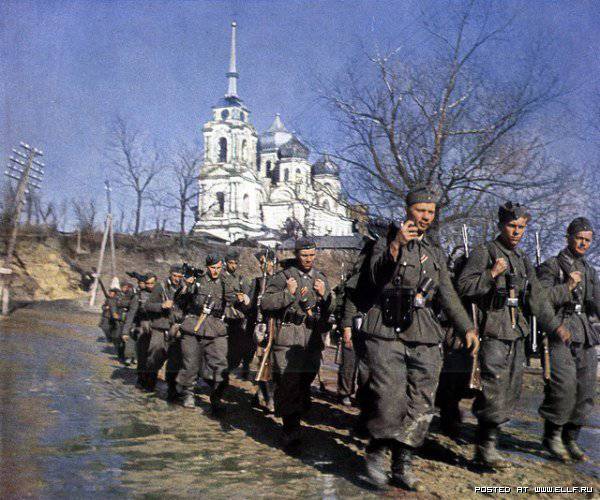

The picture is more or less clear regarding the number of Wehrmacht prisoners of war on the Soviet-German front. According to Russian sources, Soviet troops captured 3,172,300 Wehrmacht soldiers, of which 2,388,443 were Germans in NKVD camps. According to the calculations of German historians, there were about 3.1 million German military personnel alone in Soviet prisoner-of-war camps. The discrepancy, as you can see, is approximately 0.7 million people. This discrepancy is explained by differences in estimates of the number of Germans who died in captivity: according to Russian archival documents, 356,700 Germans died in Soviet captivity, and according to German researchers, approximately 1.1 million people. It seems that the Russian figure of Germans killed in captivity is more reliable, and the missing 0.7 million Germans who went missing and did not return from captivity actually died not in captivity, but on the battlefield.

The vast majority of publications devoted to calculations of combat demographic losses of the Wehrmacht and SS troops are based on data from the central bureau (department) for recording losses of armed forces personnel, part of the German General Staff of the Supreme High Command. Moreover, while denying the reliability of Soviet statistics, German data are regarded as absolutely reliable. But upon closer examination, it turned out that the opinion about the high reliability of the information from this department was greatly exaggerated. Thus, the German historian R. Overmans, in the article “Human casualties of the Second World War in Germany,” came to the conclusion that “... the channels of information in the Wehrmacht do not reveal the degree of reliability that some authors attribute to them.” As an example, he reports that “... an official report from the casualty department at Wehrmacht headquarters dating back to 1944 documented that the losses that were incurred during the Polish, French and Norwegian campaigns, and the identification of which did not present any technical difficulties, were almost twice as high as originally reported." According to Müller-Hillebrand data, which many researchers believe, the demographic losses of the Wehrmacht amounted to 3.2 million people. Another 0.8 million died in captivity. However, according to a certificate from the OKH organizational department dated May 1, 1945, the ground forces alone, including the SS troops (without the Air Force and Navy), lost 4 million 617.0 thousand during the period from September 1, 1939 to May 1, 1945. people This is the latest report of German Armed Forces losses. In addition, since mid-April 1945, there was no centralized accounting of losses. And since the beginning of 1945, the data is incomplete. The fact remains that in one of the last radio broadcasts with his participation, Hitler announced the figure of 12.5 million total losses of the German Armed Forces, of which 6.7 million are irrevocable, which is approximately twice the data of Müller-Hillebrand. This happened in March 1945. I don’t think that in two months the soldiers of the Red Army did not kill a single German.
In general, the information from the Wehrmacht loss department cannot serve as the initial data for calculating the losses of the German Armed Forces in the Great Patriotic War.

There is another statistics on losses - statistics on the burials of Wehrmacht soldiers. According to the annex to the German law “On the Preservation of Burial Sites”, the total number of German soldiers located in recorded burial sites on the territory of the Soviet Union and Eastern European countries is 3 million 226 thousand people. (on the territory of the USSR alone - 2,330,000 burials). This figure can be taken as a starting point for calculating the demographic losses of the Wehrmacht, however, it also needs to be adjusted.
Firstly, this figure takes into account only the burials of Germans, and a large number of soldiers of other nationalities fought in the Wehrmacht: Austrians (270 thousand of them died), Sudeten Germans and Alsatians (230 thousand people died) and representatives of other nationalities and states (357 thousand people died). Of the total number of dead Wehrmacht soldiers of non-German nationality, the Soviet-German front accounts for 75-80%, i.e. 0.6–0.7 million people.
Secondly, this figure dates back to the early 90s of the last century. Since then, the search for German burials in Russia, the CIS countries and Eastern European countries has continued. And the messages that appeared on this topic were not informative enough. For example, the Russian Association of War Memorials, created in 1992, reported that over the 10 years of its existence it transferred information about the burials of 400 thousand Wehrmacht soldiers to the German Association for the Care of Military Graves. However, whether these were newly discovered burials or whether they had already been taken into account in the figure of 3 million 226 thousand is unclear. Unfortunately, it was not possible to find generalized statistics of newly discovered burials of Wehrmacht soldiers. Tentatively, we can assume that the number of graves of Wehrmacht soldiers newly discovered over the past 10 years is in the range of 0.2–0.4 million people.
Thirdly, many graves of dead Wehrmacht soldiers on Soviet soil have disappeared or were deliberately destroyed. Approximately 0.4–0.6 million Wehrmacht soldiers could have been buried in such disappeared and unmarked graves.
Fourthly, these data do not include the burials of German soldiers killed in battles with Soviet troops on the territory of Germany and Western European countries. According to R. Overmans, in the last three spring months of the war alone, about 1 million people died. (minimum estimate 700 thousand) In general, approximately 1.2–1.5 million Wehrmacht soldiers died on German soil and in Western European countries in battles with the Red Army.
Finally, fifthly, the number of those buried also included Wehrmacht soldiers who died a “natural” death (0.1–0.2 million people)
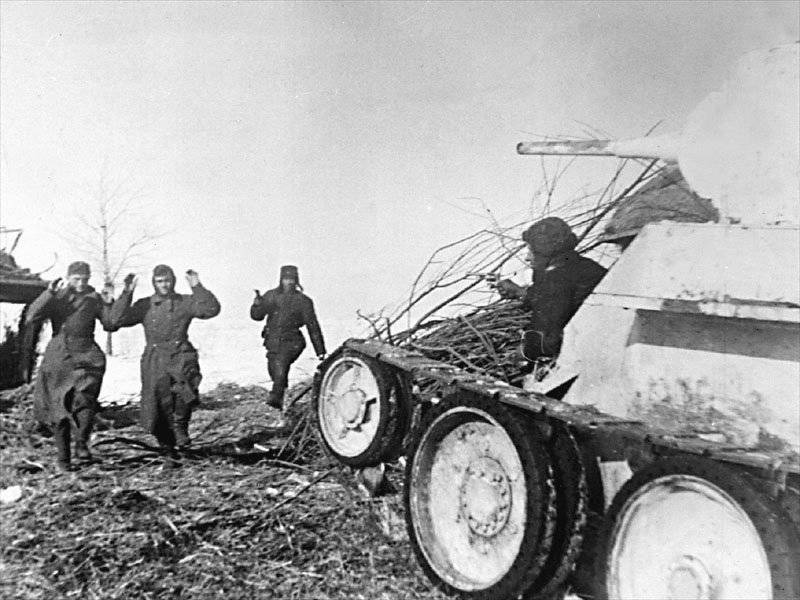

Articles by Major General V. Gurkin are devoted to assessing Wehrmacht losses using the balance of the German armed forces during the war years. His calculated figures are given in the second column of the table. 4. Here two figures are noteworthy, characterizing the number of those mobilized into the Wehrmacht during the war, and the number of prisoners of war of Wehrmacht soldiers. The number of those mobilized during the war (17.9 million people) is taken from the book by B. Müller-Hillebrand “German Land Army 1933–1945,” Vol. At the same time, V.P. Bohar believes that more were drafted into the Wehrmacht - 19 million people.
The number of Wehrmacht prisoners of war was determined by V. Gurkin by summing up the prisoners of war taken by the Red Army (3.178 million people) and the Allied forces (4.209 million people) before May 9, 1945. In my opinion, this number is overestimated: it also included prisoners of war who were not Wehrmacht soldiers. The book “German Prisoners of War of the Second World War” by Paul Karel and Ponter Boeddeker reports: “...In June 1945, the Allied Command became aware that there were 7,614,794 prisoners of war and unarmed military personnel in the “camps, of which 4,209,000 by the time capitulation were already in captivity." Among the indicated 4.2 million German prisoners of war, in addition to Wehrmacht soldiers, there were many other people. For example, in the French camp of Vitril-Francois, among the prisoners, “the youngest was 15 years old, the oldest was almost 70.” The authors write about captured Volksturm soldiers, about the organization by the Americans of special “children’s” camps, where captured twelve- to thirteen-year-old boys from the “Hitler Youth” and “Werewolf” were collected. Mention is made of placing even disabled people in camps. In the article “My path to Ryazan captivity” (“ Map" No. 1, 1992) Heinrich Schippmann noted:

“It should be taken into account that at first, although predominantly, but not exclusively, not only Wehrmacht soldiers or SS troops were taken prisoner, but also Air Force service personnel, members of the Volkssturm or paramilitary unions (the Todt organization, the Service labor of the Reich", etc.) Among them were not only men, but also women - and not only Germans, but also the so-called "Volksdeutsche" and "aliens" - Croats, Serbs, Cossacks, Northern and Western Europeans, who "fought in any way on the side of the German Wehrmacht or were assigned to it. In addition, during the occupation of Germany in 1945, anyone who wore a uniform was arrested, even if it was a question of the head of a railway station."
Overall, among the 4.2 million prisoners of war taken by the Allies before May 9, 1945, approximately 20–25% were not Wehrmacht soldiers. This means that the Allies had 3.1–3.3 million Wehrmacht soldiers in captivity.
The total number of Wehrmacht soldiers captured before the surrender was 6.3–6.5 million people.

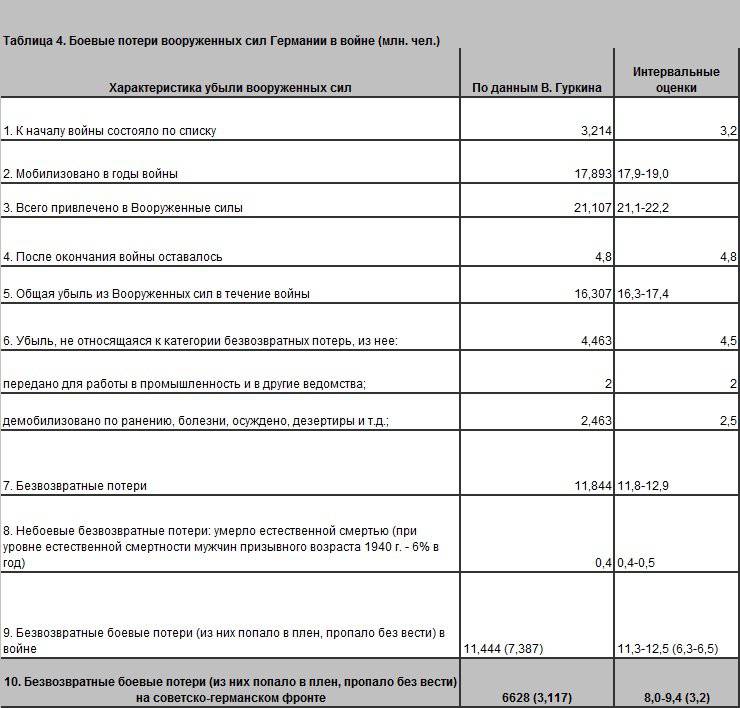
In general, the demographic combat losses of the Wehrmacht and SS troops on the Soviet-German front amount to 5.2–6.3 million people, of which 0.36 million died in captivity, and irretrievable losses (including prisoners) 8.2 –9.1 million people It should also be noted that until recent years, Russian historiography did not mention some data on the number of Wehrmacht prisoners of war at the end of hostilities in Europe, apparently for ideological reasons, because it is much more pleasant to believe that Europe “fought” fascism than to realize that that a certain and very large number of Europeans deliberately fought in the Wehrmacht. So, according to a note from General Antonov, on May 25, 1945. The Red Army captured 5 million 20 thousand Wehrmacht soldiers alone, of which 600 thousand people (Austrians, Czechs, Slovaks, Slovenes, Poles, etc.) were released before August after filtration measures, and these prisoners of war were sent to camps The NKVD was not sent. Thus, the irretrievable losses of the Wehrmacht in battles with the Red Army could be even higher (about 0.6 - 0.8 million people).
There is another way to “calculate” the losses of Germany and the Third Reich in the war against the USSR. Quite correct, by the way. Let’s try to “substitute” the figures relating to Germany into the methodology for calculating the total demographic losses of the USSR. Moreover, we will use ONLY official data from the German side. So, the population of Germany in 1939, according to Müller-Hillebrandt (p. 700 of his work, so beloved by supporters of the “filling up with corpses” theory), was 80.6 million people. At the same time, you and I, the reader, must take into account that this includes 6.76 million Austrians, and the population of the Sudetenland - another 3.64 million people. That is, the population of Germany proper within the borders of 1933 in 1939 was (80.6 - 6.76 - 3.64) 70.2 million people. We figured out these simple mathematical operations. Further: natural mortality in the USSR was 1.5% per year, but in Western European countries the mortality rate was much lower and amounted to 0.6 - 0.8% per year, Germany was no exception. However, the birth rate in the USSR was approximately the same proportion as it was in Europe, due to which the USSR had consistently high population growth throughout the pre-war years, starting from 1934.

We know about the results of the post-war population census in the USSR, but few people know that a similar population census was conducted by the Allied occupation authorities on October 29, 1946 in Germany. The census gave the following results:
Soviet occupation zone (without East Berlin): men - 7.419 million, women - 9.914 million, total: 17.333 million people.
All western zones of occupation (without western Berlin): men - 20.614 million, women - 24.804 million, total: 45.418 million people.
Berlin (all sectors of occupation), men - 1.29 million, women - 1.89 million, total: 3.18 million people.
The total population of Germany is 65,931,000 people. A purely arithmetic operation of 70.2 million - 66 million seems to give a loss of only 4.2 million. However, everything is not so simple.
At the time of the population census in the USSR, the number of children born since the beginning of 1941 was about 11 million; the birth rate in the USSR during the war years fell sharply and amounted to only 1.37% per year of the pre-war population. The birth rate in Germany even in peacetime did not exceed 2% per year of the population. Suppose it fell only 2 times, and not 3, as in the USSR. That is, the natural population growth during the war years and the first post-war year was about 5% of the pre-war population, and in figures amounted to 3.5–3.8 million children. This figure must be added to the final figure for the population decline in Germany. Now the arithmetic is different: the total population decline is 4.2 million + 3.5 million = 7.7 million people. But this is not the final figure; To complete the calculations, we need to subtract from the population decline figure the figure of natural mortality during the war years and 1946, which is 2.8 million people (let’s take the figure 0.8% to make it “higher”). Now the total population loss in Germany caused by the war is 4.9 million people. Which, in general, is very “similar” to the figure for irretrievable losses of the Reich ground forces given by Müller-Hillebrandt. So did the USSR, which lost 26.6 million of its citizens in the war, really “fill up with corpses” of its enemy? Patience, dear reader, let’s bring our calculations to their logical conclusion.
The fact is that the population of Germany proper in 1946 grew by at least another 6.5 million people, and presumably even by 8 million! By the time of the 1946 census (according to German data, by the way, published back in 1996 by the “Union of Expellees”, and in total about 15 million Germans were “forcibly displaced”) only from the Sudetenland, Poznan and Upper Silesia were evicted to German territory 6.5 million Germans. About 1 - 1.5 million Germans fled from Alsace and Lorraine (unfortunately, there are no more accurate data). That is, these 6.5 - 8 million must be added to the losses of Germany itself. And these are “slightly” different numbers: 4.9 million + 7.25 million (arithmetic average of the number of Germans “expelled” to their homeland) = 12.15 million. Actually, this is 17.3% (!) of the German population in 1939. Well, that's not all!

Let me emphasize once again: the Third Reich is NOT JUST Germany! By the time of the attack on the USSR, the Third Reich “officially” included: Germany (70.2 million people), Austria (6.76 million people), the Sudetenland (3.64 million people), captured from Poland “Baltic corridor”, Poznan and Upper Silesia (9.36 million people), Luxembourg, Lorraine and Alsace (2.2 million people), and even Upper Corinthia cut off from Yugoslavia, a total of 92.16 million people.
These are all territories that were officially included in the Reich, and whose inhabitants were subject to conscription into the Wehrmacht. We will not take into account the “Imperial Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia” and the “Government General of Poland” here (although ethnic Germans were drafted into the Wehrmacht from these territories). And ALL of these territories remained under Nazi control until the beginning of 1945. Now we get the “final calculation” if we take into account that Austria’s losses are known to us and amount to 300,000 people, that is, 4.43% of the country’s population (which in %, of course, is much less than that of Germany). It would not be much of a stretch to assume that the population of the remaining regions of the Reich suffered the same percentage losses as a result of the war, which would give us another 673,000 people. As a result, the total human losses of the Third Reich are 12.15 million + 0.3 million + 0.6 million people. = 13.05 million people. This “number” is already more like the truth. Taking into account the fact that these losses include 0.5 - 0.75 million dead civilians (and not 3.5 million), we obtain the losses of the Third Reich Armed Forces equal to 12.3 million people irrevocably. If we consider that even the Germans admit the losses of their Armed Forces in the East at 75-80% of all losses on all fronts, then the Reich Armed Forces lost about 9.2 million (75% of 12.3 million) in battles with the Red Army. person irrevocably. Of course, not all of them were killed, but having data on those released (2.35 million), as well as prisoners of war who died in captivity (0.38 million), we can say quite accurately that those actually killed and those who died from wounds and in captivity, and also missing, but not captured (read “killed”, which is 0.7 million!), the Armed Forces of the Third Reich lost approximately 5.6-6 million people during the campaign to the East. According to these calculations, the irretrievable losses of the USSR Armed Forces and the Third Reich (without allies) are correlated as 1.3:1, and the combat losses of the Red Army (data from the team led by Krivosheev) and the Reich Armed Forces as 1.6:1.
The procedure for calculating the total human losses in Germany
The population in 1939 was 70.2 million people.
The population in 1946 was 65.93 million people.
Natural mortality 2.8 million people.
Natural increase (birth rate) 3.5 million people.
Emigration influx of 7.25 million people.
Total losses ((70.2 - 65.93 - 2.8) + 3.5 + 7.25 = 12.22) 12.15 million people.
Every tenth German died! Every twelfth person was captured!!!

Conclusion
In this article, the author does not pretend to seek out the “golden ratio” and “ultimate truth”. The data presented in it are available in the scientific literature and on the Internet. It’s just that they are all scattered and scattered across various sources. The author expresses his personal opinion: you cannot trust German and Soviet sources during the war, because your losses are underestimated by at least 2–3 times, while the enemy’s losses are exaggerated by the same 2–3 times. It is even more strange that German sources, unlike Soviet ones, are considered to be completely “reliable”, although, as a simple analysis shows, this is not the case.
The irretrievable losses of the USSR Armed Forces in the Second World War amount to 11.5 - 12.0 million irrevocably, with actual combat demographic losses of 8.7–9.3 million people. The losses of the Wehrmacht and SS troops on the Eastern Front amount to 8.0 - 8.9 million irrevocably, of which purely combat demographic 5.2-6.1 million people (including those who died in captivity) people. Plus, to the losses of the German Armed Forces proper on the Eastern Front, it is necessary to add the losses of the satellite countries, and this is no less than 850 thousand (including those who died in captivity) people killed and more than 600 thousand captured. Total 12.0 (largest number) million versus 9.05 (smallest number) million people.
A logical question: where is the “filling with corpses” that Western and now domestic “open” and “democratic” sources talk about so much? The percentage of dead Soviet prisoners of war, even according to the most gentle estimates, is no less than 55%, and of German prisoners, according to the largest, no more than 23%. Maybe the whole difference in losses is explained simply by the inhumane conditions in which the prisoners were kept?
The author is aware that these articles differ from the latest officially announced version of losses: losses of the USSR Armed Forces - 6.8 million military personnel killed, and 4.4 million captured and missing, German losses - 4.046 million military personnel killed, died from wounds, missing in action (including 442.1 thousand killed in captivity), losses of satellite countries - 806 thousand killed and 662 thousand captured. Irreversible losses of the armies of the USSR and Germany (including prisoners of war) - 11.5 million and 8.6 million people. The total losses of Germany are 11.2 million people. (for example on Wikipedia)
The issue with the civilian population is more terrible against the 14.4 (smallest number) million victims of the Second World War in the USSR - 3.2 million people (largest number) of victims on the German side. So who fought and with whom? It is also necessary to mention that without denying the Holocaust of the Jews, German society still does not perceive the “Slavic” Holocaust; if everything is known about the suffering of the Jewish people in the West (thousands of works), then they prefer to “modestly” remain silent about the crimes against the Slavic peoples. The non-participation of our researchers, for example, in the all-German “dispute of historians” only aggravates this situation.
I would like to end the article with a phrase from an unknown British officer. When he saw a column of Soviet prisoners of war being driven past the “international” camp, he said: “I forgive the Russians in advance for everything they will do to Germany.”
The article was written in 2007. Since then, the author has not changed his opinion. That is, there was no “stupid” inundation of corpses on the part of the Red Army, however, there was no special numerical superiority. This is also proven by the recent emergence of a large layer of Russian “oral history,” that is, memoirs of ordinary participants in the Second World War. For example, Elektron Priklonsky, the author of “The Diary of a Self-propelled Gun,” mentions that throughout the war he saw two “death fields”: when our troops attacked in the Baltic states and came under flanking fire from machine guns, and when the Germans broke through from the Korsun-Shevchenkovsky pocket. This is an isolated example, but nevertheless, it is valuable because it is a wartime diary, and therefore quite objective.
Estimation of the loss ratio based on the results of a comparative analysis of losses in wars of the last two centuries
The application of the method of comparative analysis, the foundations of which were laid by Jomini, to assess the ratio of losses requires statistical data on wars of different eras. Unfortunately, more or less complete statistics are available only for wars of the last two centuries. Data on irretrievable combat losses in the wars of the 19th and 20th centuries, summarized based on the results of the work of domestic and foreign historians, are given in Table. The last three columns of the table demonstrate the obvious dependence of the results of the war on the magnitude of relative losses (losses expressed as a percentage of the total army strength) - the relative losses of the winner in a war are always less than those of the vanquished, and this dependence has a stable, repeating character (it is valid for all types of wars), that is, it has all the signs of law.

This law - let's call it the law of relative losses - can be formulated as follows: in any war, victory goes to the army that has fewer relative losses.
Note that the absolute numbers of irretrievable losses for the victorious side can be either less (Patriotic War of 1812, Russian-Turkish, Franco-Prussian wars) or greater than for the defeated side (Crimean, World War I, Soviet-Finnish) , but the relative losses of the winner are always less than those of the loser.
The difference between the relative losses of the winner and the loser characterizes the degree of convincingness of the victory. Wars with close relative losses of the parties end in peace treaties with the defeated side retaining the existing political system and army (for example, the Russo-Japanese War). In wars that end, like the Great Patriotic War, with the complete surrender of the enemy (Napoleonic Wars, Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871), the relative losses of the winner are significantly less than the relative losses of the vanquished (by no less than 30%). In other words, the greater the losses, the larger the army must be in order to win a landslide victory. If the army's losses are 2 times greater than those of the enemy, then to win the war its strength must be at least 2.6 times greater than the size of the opposing army.
Now let’s return to the Great Patriotic War and see what human resources the USSR and Nazi Germany had during the war. Available data on the numbers of warring parties on the Soviet-German front are given in Table. 6.

From the table 6 it follows that the number of Soviet participants in the war was only 1.4–1.5 times larger than the total number of opposing troops and 1.6–1.8 times larger than the regular German army. In accordance with the law of relative losses, with such an excess in the number of participants in the war, the losses of the Red Army, which destroyed the fascist military machine, in principle could not exceed the losses of the armies of the fascist bloc by more than 10-15%, and the losses of regular German troops by more than 25-30 %. This means that the upper limit of the ratio of irretrievable combat losses of the Red Army and the Wehrmacht is the ratio of 1.3:1.
The figures for the ratio of irretrievable combat losses given in table. 6, do not exceed the upper limit of the loss ratio obtained above. This, however, does not mean that they are final and cannot be changed. As new documents, statistical materials, and research results appear, the figures for the losses of the Red Army and the Wehrmacht (Tables 1-5) may be clarified, change in one direction or another, their ratio may also change, but it cannot be higher than the value of 1.3 :1.

Sources:
1. Central Statistical Office of the USSR “Number, composition and movement of the population of the USSR” M 1965
2. “Population of Russia in the 20th century” M. 2001
3. Arntz “Human losses in the Second World War” M. 1957
4. Frumkin G. Population Changes in Europe since 1939 N.Y. 1951
5. Dallin A. German rule in Russia 1941–1945 N.Y.- London 1957
6. “Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century” M. 2001
7. Polyan P. Victims of two dictatorships M. 1996.
8. Thorwald J. The Illusion. Soviet soldiers in Hitler,s Army N. Y. 1975
9. Collection of messages of the Extraordinary State Commission M. 1946
10. Zemskov. Birth of the second emigration 1944–1952 SI 1991 No. 4
11. Timasheff N. S. The postwar population of the Soviet Union 1948
13 Timasheff N. S. The postwar population of the Soviet Union 1948
14. Arntz. Human losses in the Second World War M. 1957; "International Affairs" 1961 No. 12
15. Biraben J. N. Population 1976.
16. Maksudov S. Population losses of the USSR Benson (Vt) 1989; “On the front-line losses of the SA during the Second World War” “Free Thought” 1993. No. 10
17. Population of the USSR over 70 years. Edited by Rybakovsky L. L. M 1988
18. Andreev, Darsky, Kharkov. "Population of the Soviet Union 1922–1991." M 1993
19. Sokolov B. “Novaya Gazeta” No. 22, 2005, “The Price of Victory -” M. 1991.
20. “Germany’s War against the Soviet Union 1941-1945” edited by Reinhard Rürup 1991. Berlin
21. Müller-Hillebrand. “German Land Army 1933-1945” M. 1998
22. “Germany’s War against the Soviet Union 1941-1945” edited by Reinhard Rürup 1991. Berlin
23. Gurkin V.V. About human losses on the Soviet-German front 1941–45. NiNI No. 3 1992
24. M. B. Denisenko. WWII in the demographic dimension "Eksmo" 2005
25. S. Maksudov. Population losses of the USSR during the Second World War. "Population and Society" 1995
26. Yu. Mukhin. If it weren't for the generals. "Yauza" 2006
27. V. Kozhinov. The Great Russian War. A series of lectures on the 1000th anniversary of the Russian wars. "Yauza" 2005
28. Materials from the newspaper “Duel”
29. E. Beevor “The Fall of Berlin” M. 2003
Our planet has known many bloody battles and battles. Our entire history consisted of various internecine conflicts. But only the human and material losses in the Second World War made humanity think about the importance of everyone’s life. Only after it did people begin to understand how easy it is to start a bloodbath and how difficult it is to stop it. This war showed all the peoples of the Earth how important peace is for everyone.
The importance of studying the history of the twentieth century
The younger generation sometimes does not understand the differences. History has been rewritten many times in the years since they ended, so young people are no longer so interested in those distant events. Often these people do not even really know who took part in those events and what losses humanity suffered in World War II. But we must not forget the history of our country. If you watch American films about World War II today, you might think that only thanks to the US Army did victory over Nazi Germany become possible. That is why it is so necessary to convey to our younger generation the role of the Soviet Union in these sad events. In fact, it was the people of the USSR who suffered the greatest losses in World War II.
Prerequisites for the bloodiest war

This armed conflict between two world military-political coalitions, which became the biggest massacre in human history, began on September 1, 1939 (in contrast to the Great Patriotic War, which lasted from June 22, 1941 to May 8, 1945 G.). It ended only on September 2, 1945. Thus, this war lasted 6 long years. There are several reasons for this conflict. These include: a deep global economic crisis, the aggressive policies of some states, and the negative consequences of the Versailles-Washington system in force at that time.
Participants in an international conflict
62 countries were involved in this conflict to one degree or another. And this despite the fact that at that time there were only 73 sovereign states on Earth. Fierce battles took place on three continents. Naval battles were fought in four oceans (Atlantic, Indian, Pacific and Arctic). The number of warring countries changed several times throughout the war. Some states participated in active military operations, while others simply helped their coalition allies in any way (equipment, equipment, food).
Anti-Hitler coalition

Initially, there were 3 states in this coalition: Poland, France, Great Britain. This is due to the fact that it was after the attack on these countries that Germany began to conduct active military operations on the territory of these countries. In 1941, countries such as the USSR, USA, and China were drawn into the war. Further, Australia, Norway, Canada, Nepal, Yugoslavia, the Netherlands, Czechoslovakia, Greece, Belgium, New Zealand, Denmark, Luxembourg, Albania, the Union of South Africa, San Marino, and Turkey joined the coalition. To one degree or another, countries such as Guatemala, Peru, Costa Rica, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Brazil, Panama, Mexico, Argentina, Honduras, Chile, Paraguay, Cuba, Ecuador, Venezuela, Uruguay, Nicaragua also became coalition allies. , Haiti, El Salvador, Bolivia. They were also joined by Saudi Arabia, Ethiopia, Lebanon, Liberia, and Mongolia. During the war years, those states that had ceased to be allies of Germany joined the anti-Hitler coalition. These are Iran (since 1941), Iraq and Italy (since 1943), Bulgaria and Romania (since 1944), Finland and Hungary (since 1945).

On the side of the Nazi bloc were such states as Germany, Japan, Slovakia, Croatia, Iraq and Iran (until 1941), Finland, Bulgaria, Romania (until 1944), Italy (until 1943), Hungary (until 1945), Thailand (Siam), Manchukuo. In some occupied territories, this coalition created puppet states that had virtually no influence on the world battlefield. These include: the Italian Social Republic, Vichy France, Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, the Philippines, Burma, Cambodia, Vietnam and Laos. Various collaborationist troops created from among the inhabitants of the opposing countries often fought on the side of the Nazi bloc. The largest of them were RONA, ROA, SS divisions created from foreigners (Ukrainian, Belarusian, Russian, Estonian, Norwegian-Danish, 2 Belgian, Dutch, Latvian, Bosnian, Albanian and French). Volunteer armies of neutral countries such as Spain, Portugal and Sweden fought on the side of this bloc.
Consequences of the war

Despite the fact that over the long years of World War II the situation on the world stage changed several times, its result was the complete victory of the anti-Hitler coalition. Following this, the largest international organization, the United Nations (abbreviated as UN), was created. The result of victory in this war was the condemnation of fascist ideology and the prohibition of Nazism during the Nuremberg trials. After the end of this world conflict, the role of France and Great Britain in world politics decreased significantly, and the USA and the USSR became real superpowers, dividing new spheres of influence among themselves. Two camps of countries with diametrically opposed socio-political systems (capitalist and socialist) were created. After World War II, a period of decolonization of empires began throughout the planet.
Theater of Operations

Germany, for which World War II was an attempt to become the only superpower, fought in five directions at once:
- Western European: Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, Great Britain, France.
- Mediterranean: Greece, Yugoslavia, Albania, Italy, Cyprus, Malta, Libya, Egypt, North Africa, Lebanon, Syria, Iran, Iraq.
- Eastern European: USSR, Poland, Norway, Finland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Austria, Yugoslavia, Barents, Baltic and Black Sea.
- African: Ethiopia, Somalia, Madagascar, Kenya, Sudan, Equatorial Africa.
- Pacific (in commonwealth with Japan): China, Korea, South Sakhalin, Far East, Mongolia, Kuril Islands, Aleutian Islands, Hong Kong, Indochina, Burma, Malaya, Sarawak, Singapore, Dutch East Indies, Brunei, New Guinea, Sabah, Papua, Guam, Solomon Islands, Hawaii, Philippines, Midway, Marianas and other numerous Pacific Islands.
The beginning and end of the war
They began to be calculated from the moment of the invasion of German troops into the territory of Poland. Hitler had been preparing the ground for an attack on this state for a long time. On August 31, 1939, the German press reported the seizure of a radio station in Gleiwitz by the Polish military (although this was a provocation of saboteurs), and already at 4 o’clock in the morning on September 1, 1939, the warship Schleswig-Holstein began shelling the fortifications in Westerplatte (Poland). Together with the troops of Slovakia, Germany began to occupy foreign territories. France and Great Britain demanded that Hitler withdraw troops from Poland, but he refused. Already on September 3, 1939, France, Australia, England, and New Zealand declared war on Germany. Then they were joined by Canada, Newfoundland, the Union of South Africa, and Nepal. This is how the bloody Second World War began to quickly gain momentum. The USSR, although it urgently introduced universal conscription, did not declare war on Germany until June 22, 1941.

In the spring of 1940, Hitler's troops began the occupation of Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Next I headed to France. In June 1940, Italy began to fight on Hitler's side. In the spring of 1941, it quickly captured Greece and Yugoslavia. On June 22, 1941, she attacked the USSR. On the side of Germany in these military actions were Romania, Finland, Hungary, and Italy. Up to 70% of all active Nazi divisions fought on all Soviet-German fronts. The defeat of the enemy in the battle for Moscow thwarted Hitler's notorious plan - “Blitzkrieg” (lightning war). Thanks to this, already in 1941 the creation of an anti-Hitler coalition began. On December 7, 1941, after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States also entered this war. For a long time, the army of this country fought its enemies only in the Pacific Ocean. The so-called second front, Great Britain and the United States, promised to open in the summer of 1942. But, despite the fierce fighting on the territory of the Soviet Union, the partners in the anti-Hitler coalition were in no hurry to engage in hostilities in Western Europe. This is due to the fact that the USA and England were waiting for the complete weakening of the USSR. Only when it became obvious that not only their territory, but also the countries of Eastern Europe began to be liberated at a rapid pace, the Allies hastened to open a Second Front. This happened on June 6, 1944 (2 years after the promised date). From that moment on, the Anglo-American coalition sought to be the first to liberate Europe from German troops. Despite all the efforts of the allies, the Soviet Army was the first to occupy the Reichstag, where it erected its own. But even the unconditional surrender of Germany did not stop the Second World War. Military operations continued in Czechoslovakia for some time. Also in the Pacific, hostilities almost never ceased. Only after the bombing of the cities of Hiroshima (August 6, 1945) and Nagasaki (August 9, 1945) with atomic bombs by the Americans did the Japanese emperor realize the futility of further resistance. As a result of this attack, about 300 thousand civilians died. This bloody international conflict ended only on September 2, 1945. It was on this day that Japan signed the act of surrender.
Victims of the world conflict
The Polish people suffered the first large-scale losses in World War II. The army of this country was unable to withstand a stronger enemy in the form of German troops. This war had an unprecedented impact on all of humanity. About 80% of all people living on Earth at that time (more than 1.7 billion people) were drawn into the war. Military actions took place on the territory of more than 40 states. Over the 6 years of this world conflict, about 110 million people were mobilized into the armed forces of all armies. According to the latest data, human losses amount to about 50 million people. At the same time, only 27 million people were killed on the fronts. The remaining victims were civilians. Countries such as the USSR (27 million), Germany (13 million), Poland (6 million), Japan (2.5 million), and China (5 million) lost the most human lives. The human losses of other warring countries were: Yugoslavia (1.7 million), Italy (0.5 million), Romania (0.5 million), Great Britain (0.4 million), Greece (0.4 million). ), Hungary (0.43 million), France (0.6 million), USA (0.3 million), New Zealand, Australia (40 thousand), Belgium (88 thousand), Africa (10 thousand .), Canada (40 thousand). More than 11 million people were killed in fascist concentration camps.
Losses from international conflict
It is simply amazing what losses the Second World War brought to humanity. History shows the $4 trillion that went into military spending. For the warring states, material costs amounted to about 70% of national income. For several years, the industry of many countries was completely reoriented to the production of military equipment. Thus, the USA, USSR, Great Britain and Germany produced more than 600 thousand combat and transport aircraft during the war years. The weapons of World War II became even more effective and deadly in 6 years. The most brilliant minds of the warring countries were busy only with its improvement. The Second World War forced us to come up with a lot of new weapons. Tanks from Germany and the Soviet Union were constantly modernized throughout the war. At the same time, more and more advanced machines were created to destroy the enemy. Their number was in the thousands. Thus, more than 280 thousand armored vehicles, tanks, and self-propelled guns alone were produced. More than 1 million different artillery pieces rolled off the assembly lines of military factories; about 5 million machine guns; 53 million machine guns, carbines and rifles. The Second World War brought with it colossal destruction and destruction of several thousand cities and other populated areas. The history of mankind without it could have followed a completely different scenario. Because of it, all countries were set back in their development many years ago. Colossal resources and efforts of millions of people were spent eliminating the consequences of this international military conflict.
USSR losses

A very high price had to be paid for the Second World War to end quickly. USSR losses amounted to about 27 million people. (last count 1990). Unfortunately, it is unlikely that it will ever be possible to obtain accurate data, but this figure is the closest to the truth. There are several different estimates of USSR losses. Thus, according to the latest method, about 6.3 million are considered killed or died from their wounds; 0.5 million died from diseases, sentenced to death, died in accidents; 4.5 million missing and captured. The total demographic losses of the Soviet Union amount to more than 26.6 million people. In addition to the huge number of deaths in this conflict, the USSR suffered enormous material losses. According to estimates, they amounted to more than 2,600 billion rubles. During World War II, hundreds of cities were partially or completely destroyed. More than 70 thousand villages were wiped off the face of the earth. 32 thousand large industrial enterprises were completely destroyed. The agriculture of the European part of the USSR was almost completely destroyed. Restoring the country to pre-war levels took several years of incredible effort and enormous expense.
In 1945, the bloodiest war of the 20th century ended, causing terrible destruction and claiming millions of lives. From our article you can find out what losses the countries participating in World War II suffered.
Total losses
The most global military conflict of the 20th century involved 62 countries, 40 of which were directly involved in hostilities. Their losses in World War II are primarily calculated by casualties among military and civilians, which amounted to about 70 million.
The financial losses (the price of lost property) of all parties to the conflict were significant: about $2,600 billion. The country spent 60% of its income on providing the army and conducting military operations. The total cost reached $4 trillion.
The Second World War led to enormous destruction (about 10 thousand large cities and towns). In the USSR alone, more than 1,700 cities, 70 thousand villages, and 32 thousand enterprises suffered from bombing. The enemy destroyed about 96 thousand Soviet tanks and self-propelled artillery units, 37 thousand armored vehicles.
Historical facts show that it was the USSR that, of all the participants in the anti-Hitler coalition, suffered the most serious losses. Special measures were taken to clarify the number of deaths. In 1959, a population census was conducted (the first after the war). Then the figure of 20 million victims was announced. To date, other specific data are known (26.6 million), announced by the state commission in 2011. They coincided with the figures announced in 1990. Most of the dead were civilians.

Rice. 1. Destroyed city during World War II.
Human casualties
Unfortunately, the exact number of victims is still not known. Objective reasons (lack of official documentation) complicate the count, so many continue to be listed as missing.
TOP 5 articleswho are reading along with this
Before talking about the dead, let us indicate the number of people called up for service by states whose participation in the war was key, and those injured during the fighting:
- Germany : 17,893,200 soldiers, of which: 5,435,000 were wounded, 4,100,000 were captured;
- Japan : 9 058 811: 3 600 000: 1 644 614;
- Italy : 3,100,000: 350 thousand: 620 thousand;
- USSR : 34,476,700: 15,685,593: about 5 million;
- Great Britain : 5,896,000: 280 thousand: 192 thousand;
- USA : 16 112 566: 671 846: 130 201;
- China : 17,250,521: 7 million: 750 thousand;
- France : 6 million: 280 thousand: 2,673,000

Rice. 2. Wounded soldiers from World War II.
For convenience, we present a table of countries' losses in World War II. The death toll is indicated taking into account all causes of death approximately (averages between the minimum and maximum):
|
A country |
Dead military personnel |
Dead civilians |
|
Germany |
About 5 million |
About 3 million |
|
Great Britain |
||
|
Australia |
||
|
Yugoslavia |
||
|
Finland |
||
|
Netherlands |
||
|
Bulgaria |
Editor's note. For 70 years, first the top leadership of the USSR (by rewriting history), and later the government of the Russian Federation, supported a monstrous and cynical lie about the greatest tragedy of the 20th century - World War II
Editor's note . For 70 years, first the top leadership of the USSR (by rewriting history), and later the government of the Russian Federation, supported a monstrous and cynical lie about the greatest tragedy of the 20th century - World War II, mainly by privatizing victory in it and keeping silent about its cost and the role of other countries in the outcome war. Now in Russia they have made a ceremonial picture of victory, they support victory at all levels, and the cult of the St. George’s ribbon has reached such an ugly form that it has actually developed into outright mockery of the memory of millions of fallen people. And while the whole world mourns for those who died fighting Nazism or became its victims, eReFiya is organizing a blasphemous Sabbath. And over these 70 years, the exact number of losses of Soviet citizens in that war has not been finally clarified. The Kremlin is not interested in this, just as it is not interested in publishing statistics on the deaths of Russian military personnel in the Donbass, in the Russian-Ukrainian war, which it unleashed. Only a few who did not succumb to the influence of Russian propaganda are trying to find out the exact number of losses in WWII.
In the article that we bring to your attention, the most important thing is that the Soviet and Russian authorities did not care about the fate of how many millions of people, while promoting their feat in every possible way.

Estimates of the losses of Soviet citizens in World War II have a huge range: from 19 to 36 million. The first detailed calculations were made by the Russian emigrant, demographer Timashev in 1948 - he came up with 19 million. The maximum figure was called by B. Sokolov - 46 million. The latest calculations show , that the USSR military alone lost 13.5 million people, but the total losses were over 27 million.
At the end of the war, long before any historical and demographic studies, Stalin named the figure - 5.3 million military losses. He also included missing persons (obviously, in most cases, prisoners). In March 1946, in an interview with a correspondent of the Pravda newspaper, the generalissimo estimated the human losses at 7 million. The increase was due to civilians who died in the occupied territory or were deported to Germany.
In the West, this figure was perceived with skepticism. Already at the end of the 1940s, the first calculations of the demographic balance of the USSR during the war years appeared, contradicting Soviet data. An illustrative example is the calculations of the Russian emigrant, demographer N. S. Timashev, published in the New York “New Journal” in 1948. Here is his technique.
The All-Union Population Census of the USSR in 1939 determined its number at 170.5 million. Growth in 1937-1940. reached, according to his assumption, almost 2% for each year. Consequently, the population of the USSR by mid-1941 should have reached 178.7 million. But in 1939-1940. Western Ukraine and Belarus, three Baltic states, the Karelian lands of Finland were annexed to the USSR, and Romania returned Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina. Therefore, minus the Karelian population who went to Finland, the Poles who fled to the West, and the Germans repatriated to Germany, these territorial acquisitions gave a population increase of 20.5 million. Considering that the birth rate in the annexed territories was no more than 1% in year, that is, lower than in the USSR, and also taking into account the short time period between their entry into the USSR and the beginning of World War II, the author determined the population growth for these territories by mid-1941 at 300 thousand. Consistently adding up the above figures, he received 200.7 million who lived in the USSR on the eve of June 22, 1941.

Timashev further divided 200 million into three age groups, again relying on data from the 1939 All-Union Census: adults (over 18 years old) - 117.2 million, teenagers (from 8 to 18 years old) - 44.5 million, children (under 8 years) - 38.8 million. At the same time, he took into account two important circumstances. First: in 1939-1940. From childhood, two very weak annual streams moved from childhood to the group of teenagers, born in 1931-1932, during the famine, which covered large areas of the USSR and negatively affected the size of the teenage group. Second: in the former Polish lands and Baltic states there were more people over 20 years of age than in the USSR.
Timashev supplemented these three age groups with the number of Soviet prisoners. He did it in the following way. By the time of the elections of deputies to the Supreme Soviet of the USSR in December 1937, the population of the USSR reached 167 million, of which voters made up 56.36% of the total figure, and the population over 18 years of age, according to the All-Union Census of 1939, reached 58.3%. The resulting difference of 2%, or 3.3 million, in his opinion, was the population of the Gulag (including the number of those executed). This turned out to be close to the truth.
Next, Timashev moved on to post-war figures. The number of voters included in the voting lists for the elections of deputies to the Supreme Soviet of the USSR in the spring of 1946 was 101.7 million. Adding to this figure the 4 million Gulag prisoners he calculated, he received 106 million adult population in the USSR at the beginning of 1946. Calculating the teenage group, he took as a basis 31.3 million primary and secondary school students in the 1947/48 school year, compared them with data from 1939 (31.4 million schoolchildren within the borders of the USSR before September 17, 1939) and obtained a figure of 39 million When calculating the child group, he proceeded from the fact that by the beginning of the war the birth rate in the USSR was approximately 38 per 1000, in the second quarter of 1942 it decreased by 37.5%, and in 1943-1945. - half.

Subtracting from each year group the percentage calculated according to the normal mortality table for the USSR, he received 36 million children at the beginning of 1946. Thus, according to his statistical calculations, in the USSR at the beginning of 1946 there were 106 million adults, 39 million adolescents and 36 million children, and a total of 181 million. Timashev’s conclusion is as follows: the population of the USSR in 1946 was 19 million less than in 1941.
Other Western researchers came to approximately the same results. In 1946, under the auspices of the League of Nations, F. Lorimer’s book “The Population of the USSR” was published. According to one of his hypotheses, during the war the population of the USSR decreased by 20 million.
In the article “Human Losses in the Second World War,” published in 1953, the German researcher G. Arntz came to the conclusion that “20 million people is the closest figure to the truth of the total losses of the Soviet Union in the Second World War.” The collection including this article was translated and published in the USSR in 1957 under the title “Results of the Second World War.” Thus, four years after Stalin’s death, Soviet censorship released the figure of 20 million into the open press, thereby indirectly recognizing it as correct and making it available, at least, to specialists: historians, international affairs experts, etc.
Only in 1961, Khrushchev, in a letter to Swedish Prime Minister Erlander, admitted that the war against fascism “claimed two tens of millions of lives of Soviet people.” Thus, compared to Stalin, Khrushchev increased Soviet casualties by almost 3 times.

In 1965, on the occasion of the 20th anniversary of the Victory, Brezhnev spoke of “more than 20 million” human lives lost by the Soviet people in the war. In the 6th and final volume of the fundamental “History of the Great Patriotic War of the Soviet Union,” published at the same time, it was stated that of the 20 million dead, almost half “were military and civilians killed and tortured by the Nazis in occupied Soviet territory.” In fact, 20 years after the end of the war, the USSR Ministry of Defense recognized the death of 10 million Soviet troops.
Four decades later, the head of the Center for Military History of Russia at the Institute of Russian History of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor G. Kumanev, in a line-by-line commentary, told the truth about the calculations that military historians carried out in the early 1960s when preparing the “History of the Great Patriotic War of the Soviet Union”: “Our losses in the war were then it was determined at 26 million. But the figure “over 20 million” was accepted by high authorities.”
As a result, “20 Million” not only took root in historical literature for decades, but also became part of the national consciousness.
In 1990, M. Gorbachev announced a new figure for losses obtained as a result of research by demographers - “almost 27 million people.”
In 1991, B. Sokolov’s book “The Price of Victory” was published. The Great Patriotic War: the unknown about the known.” It estimated direct military losses of the USSR at approximately 30 million, including 14.7 million military personnel, and “actual and potential losses” at 46 million, including 16 million unborn children.”

A little later, Sokolov clarified these figures (he added new losses). He obtained the loss figure as follows. From the size of the Soviet population at the end of June 1941, which he determined to be 209.3 million, he subtracted 166 million who, in his opinion, lived in the USSR on January 1, 1946, and received 43.3 million dead. Then, from the resulting number, I subtracted the irretrievable losses of the Armed Forces (26.4 million) and received the irretrievable losses of the civilian population - 16.9 million.
“We can name the number of Red Army soldiers killed during the entire war, which is close to reality, if we determine the month of 1942, when the Red Army’s losses in casualties were taken into account most fully and when it had almost no losses in prisoners. For a number of reasons, we chose November 1942 as such a month and extended the ratio of the number of dead and wounded obtained for it to the entire period of the war. As a result, we came to a figure of 22.4 million Soviet military personnel killed in battle and died from wounds, illnesses, accidents and executed by tribunals.”
To the 22.4 million received in this way, he added 4 million soldiers and commanders of the Red Army who died in enemy captivity. This is how it turned out to be 26.4 million irretrievable losses suffered by the Armed Forces.

In addition to B. Sokolov, similar calculations were carried out by L. Polyakov, A. Kvasha, V. Kozlov and others. The methodological weakness of this kind of calculations is obvious: the researchers proceeded from the difference between the size of the Soviet population in 1941, which is known very approximately, and the size of the post-war population USSR, which is almost impossible to accurately determine. It was this difference that they considered the total human losses.
In 1993, a statistical study “The Classification of Secrecy Has Been Removed: Losses of the Armed Forces of the USSR in Wars, Combat Actions and Military Conflicts” was published, prepared by a team of authors headed by General G. Krivosheev. The main source of statistical data was previously secret archival documents, primarily reports of the General Staff. However, the losses of entire fronts and armies in the first months, and the authors specifically stipulated this, were obtained by calculation. In addition, the reporting of the General Staff did not include the losses of units that were not organizationally part of the Soviet Armed Forces (army, navy, border and internal troops of the NKVD of the USSR), but were directly involved in the battles: people's militia, partisan detachments, groups of underground fighters.
Finally, the number of prisoners of war and missing in action is clearly underestimated: this category of losses, according to the reports of the General Staff, totals 4.5 million, of which 2.8 million remained alive (were repatriated after the end of the war or again drafted into the ranks of the Red Army in the liberated from the occupiers of the territory), and, accordingly, the total number of those who did not return from captivity, including those who did not want to return to the USSR, amounted to 1.7 million.
As a result, the statistical data in the “Classified as Classified” directory was immediately perceived as requiring clarification and additions. And in 1998, thanks to the publication of V. Litovkin “During the war years, our army lost 11 million 944 thousand 100 people,” these data were replenished by 500 thousand reservists drafted into the army, but not yet included in the lists of military units and who died along the way to the front.

The study by V. Litovkin states that from 1946 to 1968, a special commission of the General Staff, headed by General S. Shtemenko, prepared a statistical reference book on losses in 1941-1945. At the end of the commission’s work, Shtemenko reported to the Minister of Defense of the USSR, Marshal A. Grechko: “Taking into account that the statistical collection contains information of national importance, the publication of which in the press (including closed ones) or in any other way is currently not necessary and undesirable, the collection is intended to be kept at the General Staff as a special document, to which a strictly limited circle of persons will be allowed to become familiar.” And the prepared collection was kept under seven seals until the team under the leadership of General G. Krivosheev made its information public.
V. Litovkin’s research sowed even greater doubts about the completeness of the information published in the collection “Classified as Classified”, because a logical question arose: were all the data contained in the “statistics collection of the Shtemenko Commission” declassified?
For example, according to the data given in the article, during the war years, military justice authorities convicted 994 thousand people, of whom 422 thousand were sent to penal units, 436 thousand to places of detention. The remaining 136 thousand were apparently shot.
And yet, the reference book “The Classification of Secrecy Has Been Removed” has significantly expanded and supplemented the ideas not only of historians, but also of the entire Russian society about the cost of the 1945 Victory. It is enough to refer to the statistical calculation: from June to November 1941, the Armed Forces of the USSR lost 24 thousand people every day, of which 17 thousand were killed and up to 7 thousand wounded, and from January 1944 to May 1945 - 20 thousand people , of which 5.2 thousand were killed and 14.8 thousand were wounded.

In 2001, a significantly expanded statistical publication appeared - “Russia and the USSR in the wars of the twentieth century. Losses of the armed forces." The authors supplemented the General Staff materials with reports from military headquarters about losses and notifications from military registration and enlistment offices about the dead and missing, which were sent to relatives at their place of residence. And the figure of losses he received increased to 9 million 168 thousand 400 people. These data were reproduced in volume 2 of the collective work of employees of the Institute of Russian History of the Russian Academy of Sciences “Population of Russia in the 20th century. Historical essays”, published under the editorship of academician Yu. Polyakov.
In 2004, the second, corrected and expanded, edition of the book by the head of the Center for Military History of Russia at the Institute of Russian History of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor G. Kumanev, “Feat and Forgery: Pages of the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945,” was published. It provides data on losses: about 27 million Soviet citizens. And in the footnote comments to them, the same addition mentioned above appeared, explaining that the calculations of military historians back in the early 1960s gave a figure of 26 million, but the “high authorities” preferred to accept something else as the “historical truth”: “over 20 million."
Meanwhile, historians and demographers continued to look for new approaches to determining the magnitude of the USSR's losses in the war.
The historian Ilyenkov, who served in the Central Archives of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, followed an interesting path. He tried to calculate the irretrievable losses of the Red Army personnel based on the files of irretrievable losses of privates, sergeants and officers. These files began to be created when, on July 9, 1941, a department for recording personal losses was organized as part of the Main Directorate for the Formation and Recruitment of the Red Army (GUFKKA). The responsibilities of the department included personal accounting of losses and compiling an alphabetical card index of losses.

The records were kept in the following categories: 1) dead - according to reports from military units, 2) dead - according to reports from military registration and enlistment offices, 3) missing in action - according to reports from military units, 4) missing - according to reports from military registration and enlistment offices, 5) dead in German captivity , 6) those who died from illnesses, 7) those who died from wounds - according to reports from military units, those who died from wounds - according to reports from military registration and enlistment offices. At the same time, the following were taken into account: deserters; military personnel sentenced to forced labor camps; sentenced to capital punishment - execution; removed from the register of irretrievable losses as survivors; those on suspicion of having served with the Germans (the so-called “signals”), and those who were captured but survived. These military personnel were not included in the list of irretrievable losses.
After the war, the card files were deposited in the Archive of the USSR Ministry of Defense (now the Central Archive of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation). Since the early 1990s, the archive began counting registration cards by letters of the alphabet and categories of losses. As of November 1, 2000, 20 letters of the alphabet were processed; a preliminary calculation was carried out using the remaining 6 uncounted letters, which had fluctuations up or down by 30-40 thousand persons.
The calculated 20 letters for 8 categories of losses of privates and sergeants of the Red Army gave the following figures: 9 million 524 thousand 398 people. At the same time, 116 thousand 513 people were removed from the register of irretrievable losses as those who turned out to be alive according to reports from military registration and enlistment offices.
A preliminary calculation based on 6 uncounted letters gave 2 million 910 thousand people as irretrievable losses. The result of the calculations was as follows: 12 million 434 thousand 398 Red Army soldiers and sergeants were lost by the Red Army in 1941-1945. (Recall that this is without losses of the Navy, internal and border troops of the NKVD of the USSR.)
Using the same methodology, the alphabetical card index of irretrievable losses of officers of the Red Army was calculated, which is also stored in the TsAMO of the Russian Federation. They amounted to about 1 million 100 thousand people.

Thus, during the Second World War, the Red Army lost 13 million 534 thousand 398 soldiers and commanders killed, missing, died from wounds, diseases and in captivity.
These data are 4 million 865 thousand 998 people higher than the irretrievable losses of the Armed Forces of the USSR (payroll) according to the General Staff, which included the Red Army, sailors, border guards, and internal troops of the NKVD of the USSR.
Finally, we note another new trend in the study of the demographic results of the Second World War. Before the collapse of the USSR, there was no need to estimate human losses for individual republics or nationalities. And only at the end of the twentieth century L. Rybakovsky tried to calculate the approximate amount of human losses of the RSFSR within its then borders. According to his estimates, it amounted to approximately 13 million people - slightly less than half of the total losses of the USSR.
(Quotes: S. Golotik and V. Minaev - “Demographic losses of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War: history of calculations”, “New Historical Bulletin”, No. 16, 2007.)
 Usage and conjugation of the verbs sein and haben
Usage and conjugation of the verbs sein and haben Linguistic means characteristic of reasoning
Linguistic means characteristic of reasoning Personality and self-education Examples of personal self-development in literature
Personality and self-education Examples of personal self-development in literature