How many years did the Russian empire exist. Russian Empire: the beginning of formation
As a result of the Northern War of 1700-1721, the powerful Swedish army was defeated, the Russian lands occupied by Sweden in the late 16th and early 17th centuries were returned. At the mouth of the Neva, the city of St. Petersburg was built, where in 1712 the capital of Russia was transferred. The Muscovite state becomes in 1721 the Russian Empire, headed by the Emperor of All Russia.
Of course, Russia took a long time to create an empire, and not only the victory in the Northern War contributed to this.
Long way
At the beginning of the XIII century, Russia consisted of about 15 principalities. However, the natural course of centralization was crossed out by the Mongol invasion (1237-1240). Further unification of the Russian lands took place in difficult foreign policy conditions and was dictated primarily by political prerequisites.
In the XIV century, most of the Russian lands were united around Vilna - the capital of the emerging Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Russia. During the 13th-15th centuries, the Gorodensky, Polotsk, Vitebsk, Turov-Pinsk, Kiev principalities, as well as most of the Chernihiv region, Volyn, Podolia, Smolensk region and a number of other Russian lands were in the possession of the great Lithuanian princes from the Gediminovich family. Thus, the sole rule of the Rurikovichs and the tribal unity of Russia have gone into the past. Lands were annexed both by military and peaceful means.
The end of the 15th - the beginning of the 16th centuries became a kind of frontier, after which the lands annexed to Russia formed a single whole with it. The process of joining the rest of the legacy of Ancient Russia dragged on for another two centuries, and by this time their own ethnic processes had gained strength there.
In 1654 Left-Bank Ukraine joined Russia. The lands of the Right-Bank Ukraine (without Galicia) and Belarus became part of the Russian Empire as a result of the second division of the Commonwealth in 1793.
“The Russian kingdom (both conceptually, ideologically, and institutionally) had two sources: the “kingdom” (khanate) of the Golden Horde and the Byzantine Orthodox kingdom (empire).”
One of the first to formulate a new idea of the royal power of the Moscow princes was Metropolitan Zosima. In the essay "The Presentation of the Paschal", submitted to the Moscow Cathedral in 1492, he emphasized that Moscow became the new Constantinople thanks to the fidelity of Russia to God. God Himself appointed Ivan III - "the new Tsar Constantine to the new city of Constantine - Moscow and the whole Russian land and many other lands of the sovereign." Thus, Ivan IV was the first tsar crowned king. This happened on January 16, 1547.

Under Ivan IV, Russia managed to significantly expand its possessions. As a result of the campaign against Kazan and its capture in 1552, she gained the middle Volga region, and in 1556, with the capture of Astrakhan, the lower Volga region and access to the Caspian Sea, which opened up new trade opportunities with Persia, the Caucasus and Central Asia. At the same time, the ring of hostile Tatar khanates that hampered Russia was broken, and the road to Siberia was opened.

V. Surikov "Conquest of Siberia by Yermak"
The era of Ivan the Terrible also marked the beginning of the conquest of Siberia. A small detachment of Cossacks Yermak Timofeevich, hired by the Ural industrialists Stroganovs to protect against the raids of the Siberian Tatars, defeated the army of the Siberian Khan Kuchum and took his capital Kashlyk. Despite the fact that due to the attacks of the Tatars, few of the Cossacks managed to return alive, the collapsed Siberian Khanate was no longer restored. A few years later, the tsarist archers of the voivode Voeikov crushed the last resistance. The gradual development of Siberia by the Russians began. Over the next decades, forts and trading settlements began to appear: Tobolsk, Verkhoturye, Mangazeya, Yeniseisk and Bratsk.
Russian empire

P. Zharkov "Portrait of Peter I"
On August 30, 1721, the Treaty of Nystadt was concluded between Russia and Sweden, according to which Russia received access to the Baltic Sea, annexed the territory of Ingria, part of Karelia, Estonia and Livonia.
Russia has become a great European power. Peter I accepted from the Senate the titles "Great" and "Father of the Fatherland", he was proclaimed emperor, and Russia - an empire.
The formation of the Russian Empire was accompanied by a number of reforms.
Public Administration Reform
Creation of the Near Office (or Council of Ministers) in 1699. It was transformed in 1711 into the Governing Senate. Establishment of 12 collegiums with a specific scope of activity and powers.
The system of state administration has become more perfect. The activities of most state bodies became regulated, the collegiums had a clearly defined area of activity. Supervisory bodies were created.
Regional (provincial) reform
At the first stage of the reform, Peter I divided Russia into 8 provinces: Moscow, Kyiv, Kazan, Ingermandland (later St. Petersburg), Arkhangelsk, Smolensk, Azov, Siberia. They were ruled by governors who were in charge of the troops located on the territory of the province, and also possessed full administrative and judicial power. At the second stage of the reform, the provinces were divided into 50 provinces ruled by governors, and those were divided into districts led by zemstvo commissars. The governors were stripped of their administrative power and were in charge of judicial and military matters.
There was a centralization of power. Local governments have almost completely lost influence.
Judicial reform
Peter 1 formed new judicial bodies: the Senate, the Justic College, the Hofgerichts, and the lower courts. Judicial functions were also performed by all colleagues, except for Foreign. The judges were separated from the administration. The court of kissers (an analogue of the jury trial) was canceled, the principle of the inviolability of an unconvicted person was lost.
A large number of judicial bodies and persons who carried out judicial activities (the emperor himself, governors, governors, etc.) brought confusion and confusion to the proceedings, the introduction of the possibility of "knocking out" testimony under torture created grounds for abuse and bias. At the same time, the adversarial nature of the process was established and the need for the verdict to be based on specific articles of the law corresponding to the case under consideration.
Military reforms
The introduction of recruitment, the creation of the navy, the establishment of the Military Collegium, which was in charge of all military affairs. Introduction with the help of the "Table of Ranks" of military ranks, uniform for all of Russia. Creation of military-industrial enterprises, as well as military educational institutions. Introduction of army discipline and military regulations.
With his reforms, Peter 1 created a formidable regular army, numbering up to 212 thousand people by 1725, and a strong navy. Subdivisions were created in the army: regiments, brigades and divisions, in the navy - squadrons. Many military victories were won. These reforms (although ambiguously assessed by different historians) created a springboard for the further success of Russian weapons.

Church reform
The institution of the patriarchate was actually liquidated. In 1701, the management of church and monastery lands was reformed. Peter 1 restored the Monastic order, which controlled church revenues and the trial of the monastery peasants. In 1721, the Spiritual Regulations were adopted, which actually deprived the church of independence. To replace the patriarchate, the Holy Synod was created, whose members were subordinate to Peter 1, by whom they were appointed. Church property was often taken away and spent on the needs of the emperor.
The church reforms of Peter 1 led to the almost complete subordination of the clergy to secular power. In addition to the elimination of the patriarchate, many bishops and ordinary clergy were persecuted. The church could no longer pursue an independent spiritual policy and partly lost its authority in society.
Financial reforms
The introduction of many new (including indirect) taxes, the monopolization of the sale of tar, alcohol, salt and other goods. Damage (reduction in weight) of the coin. The penny becomes the main coin. Transition to the poll tax.
Increase in revenues of the treasury several times. But! It was achieved at the expense of the impoverishment of the bulk of the population, and most of this income was embezzled.
Culture and life
Peter I led the fight against the external manifestations of the "outdated" way of life (the most famous ban on beards), but no less paid attention to the introduction of the nobility to education and secular Europeanized culture. Secular educational institutions began to appear, the first Russian newspaper was founded, translations of many books into Russian appeared. Success in the service of Peter made the nobles dependent on education.

N. Nevrev "Peter I"
A number of measures were taken to develop education: on January 14, 1700, a school of mathematical and navigational sciences was opened in Moscow. In 1701-1721, artillery, engineering and medical schools were opened in Moscow, an engineering school and a naval academy in St. Petersburg, mining schools at the Olonets and Ural factories. In 1705, the first gymnasium in Russia was opened. The goals of mass education were to be served by the digital schools created by decree of 1714 in provincial cities, called " to teach children of all ranks literacy, numbers and geometry". It was supposed to create two such schools in each province, where education was supposed to be free. Garrison schools were opened for soldiers' children, and a network of theological schools was created for the training of priests in 1721. Peter's decrees introduced compulsory education for nobles and clergy, but a similar measure for the urban population met with fierce resistance and was canceled. Peter's attempt to create an all-estate elementary school failed (the creation of a network of schools ceased after his death, most of the digital schools under his successors were redesigned into class schools for the training of the clergy), but nevertheless, during his reign, the foundations were laid for the spread of education in Russia.
Peter I created new printing houses.
In 1724, Peter approved the charter of the Academy of Sciences being organized, which was opened after his death.
Of particular importance was the construction of stone Petersburg, in which foreign architects took part and which was carried out according to the plan developed by the tsar. He created a new urban environment with previously unfamiliar forms of life and pastime (theatre, masquerades). The interior decoration of houses, the way of life, the composition of food, etc. have changed.
By a special decree of the tsar in 1718, assemblies were introduced, representing a new form of communication between people in Russia. At the assemblies, the nobles danced and mingled freely, unlike earlier feasts and feasts.

S. Khlebovsky "Assemblies under Peter I"
Peter invited foreign artists to Russia and at the same time sent talented young people to study "arts" abroad.
On December 30, 1701, Peter issued a decree ordering to write full names in petitions and other documents instead of derogatory half-names (Ivashka, Senka, etc.), not to fall on your knees in front of the tsar, in winter, in the cold, wear a hat in front of the house in which you are king, do not shoot. He explained the need for these innovations in this way: "Less baseness, more zeal for service and loyalty to me and the state - this honor is characteristic of the king ...".
Peter tried to change the position of women in Russian society. He by special decrees (1700, 1702 and 1724) forbade forced marriage and marriage. It was prescribed that there should be at least six weeks between the betrothal and the wedding, "so that the bride and groom could recognize each other." If during this time, the decree said, “the bridegroom does not want to take the bride, or the bride does not want to marry the groom,” no matter how the parents insisted, “there is freedom.”
The transformations of the era of Peter I led to the strengthening of the Russian state, the creation of a modern European army, the development of industry and the spread of education among the upper classes of the population. An absolute monarchy was established, headed by the emperor, to whom the church was also subordinate (through the chief prosecutor of the Holy Synod).
There were many empires in the world, which were famous for their wealth, luxurious palaces and temples, conquests and culture. Among the greatest of them are such powerful states as the Roman, Byzantine, Persian, Holy Roman, Ottoman, British empires.
Russia on the historical map of the world
Empires of the world collapsed, disintegrated, and separate independent states were formed in their place. A similar fate did not bypass the Russian Empire, which lasted 196 years, starting from 1721 and ending in 1917.
It all started with the Moscow principality, which, thanks to the conquests of princes and tsars, grew at the expense of new lands in the west and east. Victorious wars allowed Russia to seize important territories that opened the way for the country to the Baltic and Black Seas.
Russia became an empire in 1721, when Tsar Peter the Great assumed the imperial title by decision of the Senate.
Territory and composition of the Russian Empire
In terms of the size and extent of its possessions, Russia ranked second in the world, second only to the British Empire, which owned numerous colonies. At the beginning of the 20th century, the territory of the Russian Empire included:
- 78 provinces + 8 Finnish;
- 21 regions;
- 2 districts.
The provinces consisted of districts, the latter were divided into camps and sections. The empire had the following administrative-territorial administration:

Many lands joined the Russian Empire voluntarily, and some as a result of aggressive campaigns. The territories that became part of it at their own request were:
- Georgia;
- Armenia;
- Abkhazia;
- Tyva Republic;
- Ossetia;
- Ingushetia;
- Ukraine.
In the course of the foreign colonial policy of Catherine II, the Kuril Islands, Chukotka, Crimea, Kabarda (Kabardino-Balkaria), Belarus and the Baltic states became part of the Russian Empire. Part of Ukraine, Belarus and the Baltic States went to Russia after the division of the Commonwealth (modern Poland).
Russian Empire Square
From the Arctic Ocean to the Black Sea and from the Baltic Sea to the Pacific Ocean, the territory of the state extended, occupying two continents - Europe and Asia. In 1914, before the First World War, the area of the Russian Empire was 69,245 sq. kilometers, and the length of its borders was as follows:

Let's stop and talk about individual territories of the Russian Empire.
Grand Duchy of Finland
Finland became part of the Russian Empire in 1809, after a peace treaty was signed with Sweden, according to which it ceded this territory. The capital of the Russian Empire was now covered by new lands that protected St. Petersburg from the north.

When Finland became part of the Russian Empire, it retained great autonomy, despite Russian absolutism and autocracy. It had its own constitution, according to which power in the principality was divided into executive and legislative. The legislature was the Sejm. Executive power belonged to the Imperial Finnish Senate, it consisted of eleven people elected by the Sejm. Finland had its own currency - Finnish marks, and in 1878 received the right to have a small army.
Finland as part of the Russian Empire was famous for the coastal city of Helsingfors, where not only the Russian intelligentsia, but also the reigning house of the Romanovs, loved to relax. This city, which is now called Helsinki, was chosen by many Russian people who enjoyed relaxing in resorts and renting dachas from local residents.
After the strikes of 1917 and thanks to the February Revolution, the independence of Finland was proclaimed, and it withdrew from Russia.
Accession of Ukraine to Russia
Right-bank Ukraine became part of the Russian Empire during the reign of Catherine II. The Russian Empress first destroyed the Hetmanate, and then the Zaporozhian Sich. In 1795, the Commonwealth was finally divided, and its lands were ceded to Germany, Austria and Russia. So, Belarus and Right-Bank Ukraine became part of the Russian Empire.

After the Russian-Turkish war of 1768-1774. Catherine the Great annexed the territory of modern Dnepropetrovsk, Kherson, Odessa, Nikolaev, Lugansk and Zaporozhye regions. As for the Left-bank Ukraine, it voluntarily became part of Russia in 1654. Ukrainians fled from the social and religious repressions of the Poles and asked for help from the Russian Tsar Alexei Mikhailovich. He, together with Bohdan Khmelnitsky, concluded the Treaty of Pereyaslav, according to which the Left-Bank Ukraine became part of the Muscovite kingdom on the rights of autonomy. Not only Cossacks participated in the Rada, but also ordinary people who made this decision.
Crimea - the pearl of Russia
The Crimean peninsula was incorporated into the Russian Empire in 1783. On July 9, the famous Manifesto was read at the Ak-Kaya rock, and the Crimean Tatars agreed to become subjects of Russia. First, the noble murzas, and then the ordinary inhabitants of the peninsula, took an oath of allegiance to the Russian Empire. After that, festivities, games and festivities began. Crimea became part of the Russian Empire after the successful military campaign of Prince Potemkin.

This was preceded by difficult times. The Crimean coast and the Kuban were the possessions of the Turks and Crimean Tatars from the end of the 15th century. During the wars with the Russian Empire, the latter gained some independence from Turkey. The rulers of the Crimea were replaced quickly, and some occupied the throne two or three times.
Russian soldiers more than once suppressed the rebellions that were organized by the Turks. The last Khan of Crimea, Shahin Giray, dreamed of making the peninsula a European power, he wanted to carry out a military reform, but no one wanted to support his undertakings. Taking advantage of the confusion, Prince Potemkin recommended to Catherine the Great that Crimea be incorporated into the Russian Empire through a military campaign. The empress agreed, but on one condition, that the people themselves express their consent to this. Russian troops peacefully treated the inhabitants of the Crimea, showed them kindness and care. Shahin Giray renounced power, and the Tatars were guaranteed freedom to practice religion and observe local traditions.
The easternmost edge of the empire
The development of Alaska by the Russians began in 1648. Semyon Dezhnev, a Cossack and traveler, led an expedition, reaching Anadyr in Chukotka. Upon learning of this, Peter I sent Bering to verify this information, but the famous navigator did not confirm Dezhnev's facts - fog hid the coast of Alaska from his team.

Only in 1732 the crew of the ship "Saint Gabriel" landed in Alaska for the first time, and in 1741 Bering studied in detail the coast of both her and the Aleutian Islands. Gradually, the exploration of a new area began, merchants sailed and formed settlements, built a capital and called it Sitka. Alaska, as part of the Russian Empire, was not yet famous for gold, but for fur-bearing animals. Furs of various animals were mined here, which were in demand both in Russia and in Europe.
Under Paul I, the Russian-American Company was organized, which had the following powers:
- she ruled Alaska;
- could organize an armed army and ships;
- have your own flag.
The Russian colonialists found a common language with the local people - the Aleuts. The priests learned their language and translated the Bible. The Aleuts were baptized, the girls willingly married Russian men and wore traditional Russian clothes. With another tribe - Koloshi, the Russians did not make friends. It was a warlike and very cruel tribe that practiced cannibalism.
Why was Alaska sold?
These vast territories were sold to the US for $7.2 million. The agreement was signed in the US capital - Washington. The reasons for the sale of Alaska have recently been called different.
Some say that the reason for the sale was the human factor and the reduction in the number of sable and other fur-bearing animals. There were very few Russians living in Alaska, their number was 1000 people. Others hypothesize that Alexander II was afraid of losing the eastern colonies, therefore, before it was too late, he decided to sell Alaska for the price that was offered.

Most researchers agree that the Russian Empire decided to get rid of Alaska because there were no human resources to cope with the development of such distant lands. Thoughts arose in the government as to whether to sell the Ussuri Territory, which was sparsely populated and poorly managed. However, hotheads cooled down, and Primorye remained a part of Russia.
Along with the collapse of the Russian Empire, the majority of the population chose to create independent nation-states. Many of them were never destined to remain sovereign, and they became part of the USSR. Others were incorporated into the Soviet state later. And what was the Russian Empire at the beginning XXcentury?
By the end of the 19th century, the territory of the Russian Empire was 22.4 million km2. According to the 1897 census, the population was 128.2 million people, including the population of European Russia - 93.4 million people; The kingdom of Poland - 9.5 million, - 2.6 million, the Caucasus region - 9.3 million, Siberia - 5.8 million, Central Asia - 7.7 million people. More than 100 peoples lived; 57% of the population were non-Russian peoples. The territory of the Russian Empire in 1914 was divided into 81 provinces and 20 regions; there were 931 cities. Part of the provinces and regions was united into governor-generals (Warsaw, Irkutsk, Kiev, Moscow, Amur, Steppe, Turkestan and Finland).
By 1914, the length of the territory of the Russian Empire was 4,383.2 versts (4,675.9 km) from north to south and 10,060 versts (10,732.3 km) from east to west. The total length of land and sea borders is 64,909.5 versts (69,245 km), of which land borders accounted for 18,639.5 versts (19,941.5 km), and sea borders accounted for about 46,270 versts (49,360 km). .4 km).
The entire population was considered subjects of the Russian Empire, the male population (from 20 years old) swore allegiance to the emperor. The subjects of the Russian Empire were divided into four classes ("states"): the nobility, the clergy, urban and rural inhabitants. The local population of Kazakhstan, Siberia and a number of other regions stood out in an independent "state" (foreigners). The emblem of the Russian Empire was a double-headed eagle with royal regalia; the state flag - a cloth with white, blue and red horizontal stripes; national anthem - "God Save the Tsar". National language - Russian.
In administrative terms, the Russian Empire by 1914 was divided into 78 provinces, 21 regions and 2 independent districts. The provinces and regions were subdivided into 777 counties and districts, and in Finland - into 51 parishes. Counties, districts and parishes, in turn, were divided into camps, departments and sections (2523 in total), as well as 274 Lensmanships in Finland.
Important in the military-political terms of the territory (capital and border) were united in the viceroyalty and general government. Some cities were separated into special administrative units - townships.
Even before the transformation of the Grand Duchy of Moscow into the Russian Tsardom in 1547, at the beginning of the 16th century, Russian expansion began to go beyond its ethnic territory and began to absorb the following territories (the table does not indicate lands lost before the beginning of the 19th century):
|
Territory |
Date (year) of joining the Russian Empire |
Facts |
|
Western Armenia (Asia Minor) |
The territory was ceded in 1917-1918 |
|
|
Eastern Galicia, Bukovina (Eastern Europe) |
In 1915 it was ceded, in 1916 it was partially recaptured, in 1917 it was lost |
|
|
Uryankhai region (Southern Siberia) |
Currently part of the Republic of Tuva |
|
|
Franz Josef Land, Emperor Nicholas II Land, New Siberian Islands (Arctic) |
Archipelagos of the Arctic Ocean, fixed as the territory of Russia by a note of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs |
|
|
Northern Iran (Middle East) |
Lost as a result of revolutionary events and the Civil War in Russia. Currently owned by the State of Iran |
|
|
Concession in Tianjin |
Lost in 1920. At present, the city of central subordination of the People's Republic of China |
|
|
Kwantung Peninsula (Far East) |
Lost as a result of defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905. Currently Liaoning Province, China |
|
|
Badakhshan (Central Asia) |
Currently Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous District of Tajikistan |
|
|
Concession in Hankou (Wuhan, East Asia) |
Currently Hubei Province, China |
|
|
Transcaspian region (Central Asia) |
Currently owned by Turkmenistan |
|
|
Adjarian and Kars-Childyr sanjaks (Transcaucasia) |
In 1921 they were ceded to Turkey. Currently Adjara Autonomous Region of Georgia; silts of Kars and Ardahan in Turkey |
|
|
Bayazet (Dogubayazit) sanjak (Transcaucasia) |
In the same year, 1878, it was ceded to Turkey following the results of the Berlin Congress. |
|
|
Principality of Bulgaria, Eastern Rumelia, Adrianople Sanjak (Balkans) |
Abolished by the results of the Berlin Congress in 1879. Currently Bulgaria, Marmara region of Turkey |
|
|
Khanate of Kokand (Central Asia) |
Currently Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan |
|
|
Khiva (Khorezm) Khanate (Central Asia) |
Currently Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan |
|
|
including Åland |
Currently Finland, Republic of Karelia, Murmansk, Leningrad regions |
|
|
Tarnopol District of Austria (Eastern Europe) |
Currently Ternopil region of Ukraine |
|
|
Bialystok District of Prussia (Eastern Europe) |
Currently Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland |
|
|
Ganja (1804), Karabakh (1805), Sheki (1805), Shirvan (1805), Baku (1806), Quba (1806), Derbent (1806), northern part of the Talysh (1809) khanate (Transcaucasia) |
Vassal khanates of Persia, capture and voluntary entry. Fixed in 1813 by an agreement with Persia following the war. Limited autonomy until 1840s. Currently Azerbaijan, Nagorno-Karabakh Republic |
|
|
Kingdom of Imereti (1810), Megrelian (1803) and Gurian (1804) principalities (Transcaucasia) |
Kingdom and principalities of Western Georgia (since 1774 independent from Turkey). Protectorates and voluntary entry. They were fixed in 1812 by an agreement with Turkey and in 1813 by an agreement with Persia. Self-government until the end of the 1860s. Currently Georgia, the regions of Samegrelo-Upper Svaneti, Guria, Imereti, Samtskhe-Javakheti |
|
|
Minsk, Kiev, Bratslav, eastern parts of the Vilna, Novogrudok, Beresteisky, Volyn and Podolsky voivodeships of the Commonwealth (Eastern Europe) |
Currently Vitebsk, Minsk, Gomel regions of Belarus; Rivne, Khmelnytsky, Zhytomyr, Vinnitsa, Kyiv, Cherkasy, Kirovohrad regions of Ukraine |
|
|
Crimea, Yedisan, Dzhambailuk, Yedishkul, Lesser Nogai Horde (Kuban, Taman) (Northern Black Sea region) |
Khanate (independent from Turkey since 1772) and nomadic Nogai tribal unions. Annexation, secured in 1792 by treaty as a result of the war. Currently Rostov Region, Krasnodar Territory, Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol; Zaporozhye, Kherson, Nikolaev, Odessa regions of Ukraine |
|
|
Kuril Islands (Far East) |
Tribal unions of the Ainu, bringing into Russian citizenship, finally by 1782. Under the treaty of 1855, the South Kuriles in Japan, under the treaty of 1875 - all the islands. Currently, the North Kuril, Kuril and South Kuril urban districts of the Sakhalin Region |
|
|
Chukotka (Far East) |
Currently Chukotka Autonomous Okrug |
|
|
Tarkov shamkhalate (Northern Caucasus) |
Currently the Republic of Dagestan |
|
|
Ossetia (Caucasus) |
Currently Republic of North Ossetia - Alania, Republic of South Ossetia |
|
|
Big and Small Kabarda |
principalities. In 1552-1570, a military alliance with the Russian state, later vassals of Turkey. In 1739-1774, according to the agreement, it was a buffer principality. Since 1774 in Russian citizenship. Currently Stavropol Territory, Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, Chechen Republic |
|
|
Inflyantsky, Mstislavsky, large parts of Polotsk, Vitebsk voivodeships of the Commonwealth (Eastern Europe) |
Currently Vitebsk, Mogilev, Gomel regions of Belarus, Daugavpils region of Latvia, Pskov, Smolensk regions of Russia |
|
|
Kerch, Yenikale, Kinburn (Northern Black Sea region) |
Fortresses, from the Crimean Khanate by agreement. Recognized by Turkey in 1774 by treaty as a result of the war. The Crimean Khanate gained independence from the Ottoman Empire under the auspices of Russia. Currently, the city district of Kerch of the Republic of Crimea of Russia, Ochakovsky district of the Mykolaiv region of Ukraine |
|
|
Ingushetia (Northern Caucasus) |
Currently Republic of Ingushetia |
|
|
Altai (Southern Siberia) |
Currently Altai Territory, Republic of Altai, Novosibirsk, Kemerovo, Tomsk regions of Russia, East Kazakhstan region of Kazakhstan |
|
|
Kymenigord and Neishlot flax - Neishlot, Wilmanstrand and Friedrichsgam (Baltic) |
Len, from Sweden by treaty as a result of the war. Since 1809 in the Russian Grand Duchy of Finland. Currently Leningrad region of Russia, Finland (region of South Karelia) |
|
|
Junior zhuz (Central Asia) |
Currently West Kazakhstan region of Kazakhstan |
|
|
(Kyrgyz land, etc.) (Southern Siberia) |
Currently Republic of Khakassia |
|
|
Novaya Zemlya, Taimyr, Kamchatka, Commander Islands (Arctic, Far East) |
Currently Arkhangelsk Region, Kamchatka, Krasnoyarsk Territory |
The Russian Empire began its existence in 1721, during the reign of Peter I.
Russia became an Empire after the end of the Northern War, the results of which secured new lands for Russia, access to the Baltic Sea, various economic benefits, and other privileges. The capital of the Russian Empire was the city of St. Petersburg, the creation of Petrovo.
Between 1728 and 1730, Moscow was again the capital of Russia. From 1730 to 1917, St. Petersburg was again the main city. The Russian Empire was a large state, whose lands were immense.
In world history, it was the third state by area that ever existed (the palm in the nomination is held by the Mongolian and British Empires).
The Empire was ruled by the EMPEROR, the monarch, whose power was not limited by anything, except for Christian postulates. In 1905, after the first revolution, the State Duma appeared in the Russian Empire, which limited the power of the monarch.
 On the eve of 1917, Russian agriculture was at its peak. Stolypin's land reform had a beneficial effect in many respects. Between the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the First World War, the grain harvest in Russia doubled.
On the eve of 1917, Russian agriculture was at its peak. Stolypin's land reform had a beneficial effect in many respects. Between the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the First World War, the grain harvest in Russia doubled.
Russia harvested one-third more grain than Canada, the US and Argentina combined. For example, the harvest of rye from the fields of the Russian Empire in 1894 yielded a crop of 2 billion poods of grain, and in the last pre-war year (1913) - 4 billion.
The Russian Empire during the reign of Nicholas II provided all of Europe with agricultural products.Between 1894 and 1911, cotton production in Russia increased by 388%.
 During the period 1890-1913, the industry of the Russian Empire quadrupled (!!!) its productivity. The income received by the Russian Empire from industrial enterprises was equal to the receipts to the treasury of income from such an industry as agriculture.
During the period 1890-1913, the industry of the Russian Empire quadrupled (!!!) its productivity. The income received by the Russian Empire from industrial enterprises was equal to the receipts to the treasury of income from such an industry as agriculture.
Goods produced at Russian enterprises covered 4/5 of the domestic market demand for industrial products. In the four years before the First World War, the number of established joint-stock companies in Russia increased by 132%.
The capital invested in joint-stock companies has quadrupled.
 The main principle of budget planning in autocratic Russia was the absence of deficits. The ministers did not forget about the need to accumulate gold reserves. State revenues in the last years of life
The main principle of budget planning in autocratic Russia was the absence of deficits. The ministers did not forget about the need to accumulate gold reserves. State revenues in the last years of life
The formation of the Russian Empire happened on October 22, 1721, according to the old style, or on November 2. It was on this day that the last Russian tsar, Peter the Great, declared himself emperor of Russia. This happened as one of the consequences of the northern war, after which the Senate asked Peter 1 to accept the title of Emperor of the country. The state received the name "Russian Empire". Its capital was the city of St. Petersburg. For all the time, the capital was transferred to Moscow only for 2 years (from 1728 to 1730).
Territory of the Russian Empire
Considering the history of Russia of that era, it must be remembered that at the time of the formation of the empire, large territories were annexed to the country. This became possible thanks to the successful foreign policy of the country, which was led by Peter 1. He created a new history, a history that returned Russia to the ranks of world leaders and powers whose opinion should be reckoned with.
The territory of the Russian Empire was 21.8 million km2. It was the second largest country in the world. In the first place was the British Empire with its numerous colonies. Most of them have retained their status to this day. The first laws of the country divided its territory into 8 provinces, each of which was controlled by a governor. He had full local authority, including the judiciary. Later, Catherine 2 increased the number of provinces to 50. Of course, this was done not by annexing new lands, but by crushing them. This greatly increased the state apparatus and rather significantly reduced the effectiveness of local government in the country. We will talk about this in more detail in the corresponding article. It should be noted that at the time of the collapse of the Russian Empire, its territory consisted of 78 provinces. The largest cities in the country were:
- St. Petersburg.
- Moscow.
- Warsaw.
- Odessa.
- Lodz.
- Riga.
- Kyiv.
- Kharkov.
- Tiflis.
- Tashkent.
The history of the Russian Empire is full of both bright and negative moments. In this time period, which lasted less than two centuries, a huge number of fateful moments were invested in the fate of our country. It was during the period of the Russian Empire that the Patriotic War, campaigns in the Caucasus, campaigns in India, European campaigns took place. The country developed dynamically. The reforms affected absolutely all aspects of life. It was the history of the Russian Empire that gave our country great commanders, whose names are on the lips to this day not only in Russia, but throughout Europe - Mikhail Illarionovich Kutuzov and Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov. These illustrious generals forever inscribed their names in the history of our country and covered Russian weapons with eternal glory.
Map
We present a map of the Russian Empire, a brief history of which we are considering, which shows the European part of the country with all the changes that have occurred in terms of territories over the years of the existence of the state.

Population
By the end of the 18th century, the Russian Empire was the largest country in the world in terms of area. Its scale was such that the messenger, who was sent to all corners of the country to report the death of Catherine 2, arrived in Kamchatka after 3 months! And this despite the fact that the messenger rode almost 200 km daily.
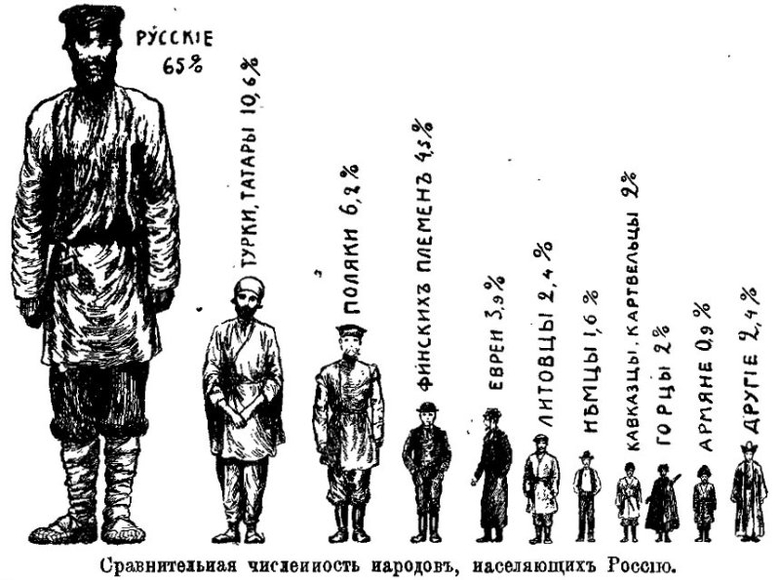
Russia was also the most populous country. In 1800, about 40 million people lived in the Russian Empire, most of them in the European part of the country. A little less than 3 million lived beyond the Urals. The national composition of the country was motley:
- East Slavs. Russians (Great Russians), Ukrainians (Little Russians), Belarusians. For a long time, almost until the very end of the Empire, it was considered a single people.
- Estonians, Latvians, Latvians and Germans lived in the Baltics.
- Finno-Ugric (Mordovians, Karelians, Udmurts, etc.), Altai (Kalmyks) and Turkic (Bashkirs, Tatars, etc.) peoples.
- The peoples of Siberia and the Far East (Yakuts, Evens, Buryats, Chukchi, etc.).
In the course of the formation of the country, part of the Kazakhs and Jews who lived on the territory of Poland, who, after its collapse, went to Russia, turned out to be its citizenship.
The main class in the country were peasants (about 90%). Other classes: philistinism (4%), merchants (1%), and the remaining 5% of the population were distributed among the Cossacks, the clergy and the nobility. This is the classic structure of an agrarian society. Indeed, the main occupation of the Russian Empire was agriculture. It is no coincidence that all the indicators that lovers of the tsarist regime are so proud of today are related to agriculture (we are talking about the import of grain and butter).

By the end of the 19th century, 128.9 million people lived in Russia, of which 16 million lived in cities, and the rest in villages.
Political system
The Russian Empire was autocratic in the form of its government, where all power was concentrated in the hands of one person - the emperor, who was often called, in the old manner, the king. Peter 1 laid down in the laws of Russia precisely the unlimited power of the monarch, which ensured the autocracy. Simultaneously with the state, the autocrat actually controlled the church.
An important point - after the reign of Paul 1, autocracy in Russia could no longer be called absolute. This happened due to the fact that Paul 1 issued a decree that canceled the system for the transfer of the throne, established by Peter 1. Peter Alekseevich Romanov, let me remind you, decided that the ruler himself determines his successor. Some historians today speak of the negative of this document, but this is precisely the essence of autocracy - the ruler makes all decisions, including about his successor. After Paul 1, the system returned, in which the son inherits the throne after his father.
Rulers of the country
Below is a list of all the rulers of the Russian Empire during the period of its existence (1721-1917).
Emperor |
Years of government |
|---|---|
| Peter 1 | 1721-1725 |
| Catherine 1 | 1725-1727 |
| Peter 2 | 1727-1730 |
| Anna Ioannovna | 1730-1740 |
| Ivan 6 | 1740-1741 |
| Elizabeth 1 | 1741-1762 |
| Peter 3 | 1762 |
| Catherine 2 | 1762-1796 |
| Pavel 1 | 1796-1801 |
| Alexander 1 | 1801-1825 |
| Nicholas 1 | 1825-1855 |
| Alexander 2 | 1855-1881 |
| Alexander 3 | 1881-1894 |
| Nicholas 2 | 1894-1917 |
All the rulers were from the Romanov dynasty, and after the overthrow of Nicholas 2 and the murder of himself and his family by the Bolsheviks, the dynasty was interrupted, and the Russian Empire ceased to exist, changing the form of statehood to the USSR.

Main dates
During its existence, and this is almost 200 years, the Russian Empire has experienced many important moments and events that have had an impact on the state and people.
- 1722 - Table of ranks
- 1799 - Suvorov's foreign campaigns in Italy and Switzerland
- 1809 - Accession of Finland
- 1812 - Patriotic War
- 1817-1864 - Caucasian War
- 1825 (December 14) - Decembrist uprising
- 1867 Sale of Alaska
- 1881 (March 1) the murder of Alexander 2
- 1905 (January 9) - Bloody Sunday
- 1914-1918 - World War I
- 1917 - February and October revolutions
End of the Empire
The history of the Russian Empire ended on September 1, 1917, according to the old style. It was on this day that the Republic was proclaimed. This was proclaimed by Kerensky, who by law did not have the right to do so, so declaring Russia a Republic can safely be called illegal. Only the Constituent Assembly had the authority to make such a declaration. The fall of the Russian Empire is closely connected with the history of its last emperor, Nicholas 2. This emperor had all the qualities of a worthy person, but had an indecisive character. It was because of this that the riots occurred in the country that cost Nicholas himself 2 lives, and the Russian Empire - existence. Nicholas 2 failed to severely suppress the revolutionary and terrorist activities of the Bolsheviks in the country. True, there were objective reasons for this. Chief among which, the First World War, in which the Russian Empire was involved and exhausted in it. The Russian Empire was replaced by a new type of state structure of the country - the USSR.
 Two heads and six legs; four walk, and two lie still
Two heads and six legs; four walk, and two lie still Self-esteem - what is it: concept, structure, types and levels
Self-esteem - what is it: concept, structure, types and levels Cassandra's Path, or Pasta Adventures War on Earth and Underground
Cassandra's Path, or Pasta Adventures War on Earth and Underground