What is the temperature in outer space in Celsius? Facts about space that are hard to believe
h do you know what temperature it has space ? In fact, for a person it is cold - about -270 degrees. Space is largely an empty void, so temperature has a big influence. The same objects that are inouter space , acquire its temperature.
There is no air here, and heat transfer occurs due to infrared radiation. That is, heat is gradually lost. An object falling into the depths of space does not lose it instantly, but gradually, several degrees at a time. To freeze completely outer space It will take a person several hours, but he is unlikely to die from freezing, since in a vacuum there are many other phenomena that will kill you much earlier. Objects traveling in space have a very low temperature. If you touch them, you will die immediately, as they will take all your heat.
T However, wind in space can be very hot. Take the Sun, which emits high-temperature infrared waves. And it’s not the only one, there is a large number of star clouds between stars, heating up to several thousand degrees.
That the surface of the Sun has high temperature, influences life on Earth. The side of our planet’s orbit that is turned toward it can heat up above 100 degrees; the other side of the orbit, located in the shadow, on the contrary, has a temperature of about -100 degrees. For humans, both options are considered unacceptable. It is also unable to withstand rapid temperature changes.

The surface temperature of other bodies depends on many factors. The mass of the body, its shape, distance from the Sun, and the influence of other space objects play a role. For example, if you send aluminum towards the Sun, being at a distance from the star, equal to the distance, on which our planet is located from it, it will acquire a temperature of up to 850 F. If you take an opaque element and cover it with paint white, it will not heat up above -40 F. This is why going into outer space without using a spacesuit is extremely dangerous for humans. Concerning aliens, perhaps they are designed differently, so they can live in a vacuum without additional devices.
The boiling point of liquid in space is not constant. It depends on the pressure affecting it. In high areas, water boils quickly because the gas there is liquid. Since there is no air behind the atmosphere, the boiling point becomes lower. That is why being in a vacuum is so dangerous for a person; his blood can simply boil in his veins. This explains the fact that it contains mainly solid bodies.
People who make movies, writers who write fantastic works, with their works they are trying to set an example for mere mortals. That as soon as a person enters the space environment, he immediately dies. This is due to the temperature that exists in this environment. What is the temperature in space?
Film directors and science fiction writers claim that the temperature in the space environment is such that not a single living creature is able to withstand it without a special suit. Arthur Clarke described the presence of a person in outer space in a very interesting way. In his work, as soon as a person got into outer space, he immediately died due to terrible frost and severe internal pressure. What do scientists say about this?
First, let's define the concepts. Temperature is the movement of atoms and molecules. They move without a specific direction. That is, chaotic. Absolutely any body has this value.
It depends on the intensity of movement of molecules and atoms. If there is no substance, then we cannot talk about this quantity. This is exactly the kind of place the space environment is.
There is very little matter here. Those bodies that live in the intergalactic environment have different thermal indices. These figures depend on many other factors.
How are things really going?
In fact, outer space is truly incredibly cold. Degrees in this space represent -454 degrees Celsius. In outer space important role It's the temperature that plays a role.
In general, open outer space is an emptiness; there is nothing at all there. An object that enters space and remains there acquires the same temperature as in its environment.
 Air does not exist in this space. All the heat that is present here circulates thanks to infrared rays. The heat received from these infrared rays, is slowly being lost. What does it mean? That an object in space ends up having a temperature of just a couple of degrees Kelvin.
Air does not exist in this space. All the heat that is present here circulates thanks to infrared rays. The heat received from these infrared rays, is slowly being lost. What does it mean? That an object in space ends up having a temperature of just a couple of degrees Kelvin.
However, it is also fair to note that this object does not freeze overnight. And this is exactly how it is filmed in films and described in fiction. In reality, it is a slow process.
It will take several hours to completely freeze. But the thing is that this low temperature, this is not the only danger. There are other factors that can affect viability. Various objects are located and constantly moving in outer space.
Since they have been moving there for some time, their temperature regime is also very low. If a person comes into contact with one of these objects, he will instantly die from frostbite. Because such an object will take away all the heat from him.
Wind
 Despite the cold, the wind in outer space can be quite hot. The degrees at the top of the sun are approximately 9,980 degrees Fahrenheit. The sun planet itself produces infrared rays. There are gas clouds between the stars. They also have a fairly high temperature regime.
Despite the cold, the wind in outer space can be quite hot. The degrees at the top of the sun are approximately 9,980 degrees Fahrenheit. The sun planet itself produces infrared rays. There are gas clouds between the stars. They also have a fairly high temperature regime.
There’s also this danger. The temperature may be critical. It can exert enormous pressure on objects. They are not only located within the boundaries of the atmosphere and convection. An orbit that faces the sun can have a temperature of 248 degrees Fahrenheit.
And its shadow side can have a temperature of -148 degrees Fahrenheit. It turns out that the difference in temperature conditions is large. At one moment it can be very different. The human body simply cannot tolerate such a difference in temperature conditions.
Temperature of other items

The degrees of other objects in space depend on various factors. From how much they are reflected, from how close they are to the sun. Their shape and weight category also matter. It is important how long they are in this place.
Let's take smooth type aluminum for example. It faces the sun and is at the same distance from the sun as planet Earth. It heats up to 850 degrees Fahrenheit. But material that is painted with white paint cannot have a temperature regime greater than -40 degrees Fahrenheit. Increase these degrees in in this case Facing the sun won't help either.
All these factors need to be taken into account. There is no way for a person to enter outer space without special equipment.
Space suits are specially designed. To have a slow rotation to one side long time I haven't been in the sun. And also so that she does not remain in the shadow part for too long.
Boiling in this space
Perhaps you are also interested in the question, at what degrees does liquid begin to boil in the cosmic kingdom? In fact, the temperature at which liquids begin to boil is a relative value. It depends on other quantities.
From quantities such as pressure that acts on the liquid. This is why water comes to boil much faster in higher areas. This is because the air in such areas is more liquid. Accordingly, beyond the boundaries of the atmosphere, where air is not present, the temperature at which boiling begins will be lower.
In a vacuum, the degrees at which water begins to boil will be lower than the temperature in the room. It is for this reason that exposure to the space environment poses a danger. IN human body at the same time, the blood in the veins boils.
It is for this reason that the following are quite rarely present in this environment:
- liquids;
- solid bodies;
- gases.
On April 1, it is customary to deceive or make fun of everyone, but I will go against tradition. Even today I cannot afford to deceive my readers. So I'll tell you about real facts, which caused my surprise. Of course, these facts will not be news to some, but I hope that at least something will be of interest to everyone. And I also hope that many, like me, and contrary to the precepts of Sherlock Holmes, drag into their brain attic not only what is necessary, but also what is simply interesting. I would be glad if this April Fool's selection will force someone to dig deeper into the sources and double-check my statements.
The temperature in space, in Earth's orbit, is +4°C
To be precise, not in the Earth’s orbit, but at a distance from the Sun equal to the distance of the Earth’s orbit. And for an absolutely black body, i.e. one that will completely absorb Sun rays without reflecting anything back.
It is believed that the temperature in space tends to absolute zero. Firstly, this is not entirely true, since the entire known Universe is heated to 3 K, cosmic microwave background radiation. Secondly, the temperature increases near stars. And we live quite close to the Sun. Strong thermal protection is needed for spacesuits and spaceships because they enter the shadow of the Earth, and our luminary can no longer warm them to the indicated +4°C. In the shade, the temperature can drop to -160° C, for example at night on the Moon. It's cold but up absolute zero still far.
Here, for example, are the readings of the onboard thermometer of the TechEdSat satellite, which was orbiting in low Earth orbit:

He was also influenced by earth's atmosphere, but in general the graph does not show the terrible conditions that are commonly imagined in space.
There is leaden snow in places on Venus

This is probably the most amazing fact about space, which I learned not so long ago. The conditions on Venus are so different from anything we could imagine that Venusians could easily fly to hell on earth to relax in the mild climate and comfortable conditions. Therefore, no matter how fantastic the phrase “lead snow” may seem, for Venus it is reality.
Thanks to the radar of the American Magellan probe in the early 90s, scientists discovered a certain coating on the tops of the Venusian mountains that is highly reflective in the radio range. At first, several versions were assumed: a consequence of erosion, deposition of iron-containing materials, etc. Later, after several experiments on Earth, they came to the conclusion that this is the most natural metallic snow, consisting of bismuth and lead sulfides. IN gaseous state they are released into the planet's atmosphere during volcanic eruptions. Thermodynamic conditions at 2600 m then favor condensation of compounds and precipitation at higher elevations.
There are 13 planets in the solar system... or more

When Pluto was demoted from the planets, the rule of good form was to know that in solar system only eight planets. True, at the same time, they introduced new category celestial bodies- dwarf planets. These are “subplanets” that have a round (or close to it) shape, are not anyone’s satellites, but at the same time cannot clear own orbit from less massive competitors. Today it is believed that there are five such planets: Ceres, Pluto, Hanumea, Eris and Makemake. The closest one to us is Ceres. In a year, we will know much more about it than now, thanks to the Dawn probe. So far we only know that it is covered with ice and water evaporates from two points on its surface at a rate of 6 liters per second. We will also learn about Pluto in next year, thanks to the New Horizons station. In general, just as 2014 will be the year of comets in astronautics, 2015 promises to be the year dwarf planets.
The remaining dwarf planets are located beyond Pluto, and we will not learn any details about them soon. Just the other day, another candidate was found, although it was not officially included in the list of dwarf planets, just like its neighbor Sedna. But it is possible that several larger dwarfs will be found, so the number of planets in the solar system will further increase.
The Hubble telescope is not the most powerful

Thanks to the colossal volume of images and impressive discoveries made by the Hubble telescope, many people have the idea that this telescope has the most high resolution and is able to see details that cannot be seen from Earth. For some time this was true: despite the fact that large mirrors can be assembled on telescopes on Earth, the atmosphere introduces significant distortion into the images. Therefore, even a “modest” mirror by earthly standards with a diameter of 2.4 meters in space can achieve impressive results.
However, over the years since the launch of Hubble and terrestrial astronomy has not stood still, several technologies have been developed that make it possible, if not to completely get rid of the distorting effect of air, then to significantly reduce its impact. Today, the most impressive resolution is provided by the Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory in Chile. In optical interferometer mode, with four main and four auxiliary telescopes working together, it is possible to achieve a resolution of about fifty times greater than Hubble's.

For example, if Hubble gives a resolution of about 100 meters per pixel on the Moon (shoutout to everyone who thinks this is how the Apollo landers can be viewed), then VLT can distinguish details down to 2 meters. Those. in its resolution, American landers or our lunar rovers would look like 1-2 pixels (but they won’t look because of the extreme high cost working hours).
A pair of Keck telescopes, in interferometer mode, can exceed Hubble's resolution by ten times. Even individually, each of the ten-meter Keck telescopes, using adaptive optics technology, is capable of outperforming Hubble by a factor of two. For an example photo of Uranus:

However, Hubble is not left without work, the sky is large, and the breadth of coverage of the space telescope camera exceeds ground-based capabilities. And for clarity, you can look at a rather complex, but informative
Film directors and science fiction writers are constantly trying to prove to us that a person who suddenly finds himself in outer space without a spacesuit will die in a split second. According to them, the temperature in space is such that not a single Living being without special equipment, he is unable to stay in the open space of the Universe for more than a second. For example, this is quite interestingly and vividly written about in one of Arthur C. Clarke’s works: a hero who finds himself in open space instantly dies due to severe frost and internal pressure. However, according to the theoretical calculations of modern scientists, the death of a person in such conditions does not occur instantly.
It is often suggested that a person who finds himself in the open space of space will be torn apart from the inside by a sharply increased pressure. Space is a perfect vacuum, and the human body maintains a pressure of approximately one atmosphere. At first glance, it may seem quite enough for a living creature to instantly die from an “explosion.”
In fact, no “explosion” will occur - the body tissues are characterized by sufficient strength and are able to cope with pressure of one atmosphere. Instead of the expected reaction, something completely different happens: the capillaries that supply the skin with blood burst, this is a rather unpleasant phenomenon, but not at all fatal.
Another reason why a person can die very quickly in the open space of the Universe is the very temperature of Space, which, according to some data, reaches Kelvin (-273.15 ° C). To be more precise, people who know nothing about the temperature characteristics of interplanetary space think so. Temperature in open space, strange as it may sound, is the absence of any temperature. Outer space, according to researchers, has no temperature; accordingly, it cannot in any way heat or cool the living organism located in it.
What is traditionally meant by a term such as “temperature”? Firstly, the chaotic movement of atoms or molecules that make up absolutely all bodies. The more intense the molecules move, the correspondingly higher the thermometer reading. Where there is no substance as such, there can be no talk of such a concept as temperature. Outer space is just such a place where there is very little matter. That's why they say that temperature in Space is its complete absence. However, the bodies that are in have very different thermal indicators, which depend on many different parameters.
Outer space is filled with radiation from sources of the most varied intensities and frequencies. And temperature in Space, from this point of view, is understood as the total energy of radiation in a certain place in space.
A thermometer in open space will first show the temperature that was characteristic of the environment from which it was removed, for example, from internal space. Over time, the device will heat up, and very much so. Indeed, in conditions where there is convective heat transfer, objects lying in direct sunlight become hot enough that it is impossible to touch them. In space, such heating will be much stronger, since vacuum is an ideal heat insulator.
Thus, temperature in Space is a relative concept, however, depending on what point in space a body is located, it can heat up or cool down. Far from the stars, where they practically do not penetrate heat flows, the temperature of such a body will be approximately 2.725 degrees Kelvin, since it extends throughout the entire part of the Universe known to astronomers, however, as the body approaches any star, it will gradually increase.
April 1, 2014 at 06:33Facts about space that are hard to believe
- Photographic equipment,
- Cosmonautics,
- Physics
On April 1, it is customary to deceive or make fun of everyone, but I will go against tradition. Even today I cannot afford to deceive my readers. Therefore, I will tell you about the real facts that caused my surprise. Of course, these facts will not be news to some, but I hope that at least something will be of interest to everyone. And I also hope that many, like me, and contrary to the precepts of Sherlock Holmes, drag into their brain attic not only what is necessary, but also what is simply interesting. I would be glad if this April Fool's selection will force someone to dig deeper into the sources and double-check my statements.
The temperature in space, in Earth's orbit, is +4°C
To be precise, not in the Earth’s orbit, but at a distance from the Sun equal to the distance of the Earth’s orbit. And for an absolutely black body, i.e. one that will completely absorb the sun's rays without reflecting anything back.
It is believed that the temperature in space tends to absolute zero. Firstly, this is not entirely true, since the entire known Universe is heated to 3 K by cosmic microwave background radiation. Secondly, the temperature increases near stars. And we live quite close to the Sun. Strong thermal protection is needed for spacesuits and spacecraft because they enter the Earth's shadow, and our luminary can no longer warm them to the specified +4°C. In the shade, the temperature can drop to -160° C, for example at night on the Moon. It's cold, but still a long way from absolute zero.
Here, for example, are the readings of the onboard thermometer of the TechEdSat satellite, which was orbiting in low Earth orbit:

It was also influenced by the earth’s atmosphere, but overall the graph does not show the terrible conditions that are commonly imagined in space.
There is leaden snow in places on Venus

This is probably the most amazing fact about space that I learned recently. The conditions on Venus are so different from anything we could imagine that Venusians could easily fly to hell on earth to relax in a mild climate and comfortable conditions. Therefore, no matter how fantastic the phrase “lead snow” may seem, for Venus it is reality.
Thanks to the radar of the American Magellan probe in the early 90s, scientists discovered a certain coating on the tops of the Venusian mountains that is highly reflective in the radio range. At first, several versions were assumed: a consequence of erosion, deposition of iron-containing materials, etc. Later, after several experiments on Earth, they came to the conclusion that this is the most natural metallic snow, consisting of bismuth and lead sulfides. In a gaseous state, they are released into the planet's atmosphere during volcanic eruptions. Thermodynamic conditions at 2600 m then favor condensation of compounds and precipitation at higher elevations.
There are 13 planets in the solar system... or more

When Pluto was demoted from the planets, it became a rule of good manners to know that there are only eight planets in the solar system. True, at the same time, they introduced a new category of celestial bodies - dwarf planets. These are “subplanets” that have a round (or close to it) shape, are not anyone’s satellites, but at the same time cannot clear their own orbit from less massive competitors. Today it is believed that there are five such planets: Ceres, Pluto, Hanumea, Eris and Makemake. The closest one to us is Ceres. In a year, we will know much more about it than now, thanks to the Dawn probe. So far we only know that it is covered with ice and water evaporates from two points on its surface at a rate of 6 liters per second. We will also learn about Pluto next year, thanks to the New Horizons station. In general, just as 2014 will be the year of comets in astronautics, 2015 promises to be the year of dwarf planets.
The remaining dwarf planets are located beyond Pluto, and we will not learn any details about them soon. Just the other day, another candidate was found, although it was not officially included in the list of dwarf planets, just like its neighbor Sedna. But it is possible that several larger dwarfs will be found, so the number of planets in the solar system will further increase.
The Hubble telescope is not the most powerful

Thanks to the enormous volume of images and impressive discoveries made by the Hubble telescope, many people have the idea that this telescope has the highest resolution and is able to see details that cannot be seen from Earth. For some time this was true: despite the fact that large mirrors can be assembled on telescopes on Earth, the atmosphere introduces significant distortion into the images. Therefore, even a “modest” mirror by earthly standards with a diameter of 2.4 meters in space can achieve impressive results.
However, over the years since the launch of Hubble and terrestrial astronomy has not stood still, several technologies have been developed that make it possible, if not to completely get rid of the distorting effect of air, then to significantly reduce its impact. Today, the most impressive resolution is provided by the Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory in Chile. In optical interferometer mode, with four main and four auxiliary telescopes working together, it is possible to achieve a resolution of about fifty times greater than Hubble's.

For example, if Hubble gives a resolution of about 100 meters per pixel on the Moon (shoutout to everyone who thinks this is how the Apollo landers can be viewed), then VLT can distinguish details down to 2 meters. Those. in its resolution, American landers or our lunar rovers would look like 1-2 pixels (but they won’t look at it due to the extremely high cost of working time).
A pair of Keck telescopes, in interferometer mode, can exceed Hubble's resolution by ten times. Even individually, each of the ten-meter Keck telescopes, using adaptive optics technology, is capable of outperforming Hubble by a factor of two. For an example photo of Uranus:

However, Hubble is not left without work, the sky is large, and the breadth of coverage of the space telescope camera exceeds ground-based capabilities. And for clarity, you can look at a rather complex, but informative
 The problem of the teacher's influence on the student
The problem of the teacher's influence on the student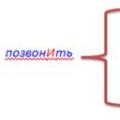 In which word is the letter denoting the stressed vowel sound correctly highlighted?
In which word is the letter denoting the stressed vowel sound correctly highlighted? The best historical novels What historical novels
The best historical novels What historical novels