Basic properties of ocean water. Oceans of our planet
IN open ocean the water is clearer than near the shores, since there are more impurities in the water near the shores. Depending on the type of impurities, water may have different shade. For example, water Yellow Sea have a yellow tint due to silt of this color, which enters the sea along with the waters of the rivers flowing into it.
Compared to land, water heats up more slowly and cools down more slowly. Its heat capacity is greater. During warm times, ocean water accumulates great amount heat and, cooling down in cold times, gives it away. Therefore, the World Ocean significantly influences the temperature of land when winds blow from it to the continents.
With depth, the temperature of ocean waters drops and already deeper than 200 m it can be around zero or even lower.
The temperature of the upper layers of the waters of the World Ocean, as well as on land, depends on the latitude of the area. It is much warmer at the equator than at the poles. In temperate zones, water is warmer in summer than in winter. The average temperature of the surface waters of the World Ocean is about +17 °C.
Important property The ocean is its salinity. In fact, sea water is bitterly salty. Various salts are dissolved in it. Salinity shows how many grams of salts are dissolved in 1 liter of water. Salinity is measured in ppm (‰). The average salinity of the waters of the World Ocean is about 35‰. This means that in 1 liter ocean water 35 grams of various salts are dissolved.
There are many dissolved in the oceans various substances, but most of all it contains table salt.
The salinity of ocean waters is not the same everywhere. This is not how the rivers entering the seas influence it. They desalinate nearby waters. Melting ice also makes the water less salty. Currents transport water and affect salinity. Salinity is especially affected by precipitation. Where there is a lot of rain, the salinity is less. In those places where heat and little precipitation, high salinity, since at high temperatures water evaporates more.
Salinity and temperature affect the density of water. Cold water heavier than warm, more salty water is heavier than less salty. Various densities water causes it to move.
The amount of substances dissolved in water affects its freezing point. The more there are, the lower the temperature the water freezes. So on average, ocean water freezes at a temperature of –2 °C.
Living organisms living in the seas and oceans are adapted to a certain salinity.
Gases are also dissolved in water. So the amount of oxygen in water decreases with increasing temperature. Therefore, in warm waters the number of living organisms is less than in relatively colder ones. With depth, the amount of oxygen also decreases.
Salinity is most important feature ocean water. This solution contains almost all known on Earth chemical elements. Total salts 50-10 16 tons. They can cover the bottom of the ocean with a layer, they can cover the bottom of the ocean with a layer of 60 m, the entire Earth - 45 m, land - 153 m. The ratio of salts in ocean water remains constant, this is ensured by the high dynamics of ocean waters. The composition is dominated by NaCl (77.8%), MgCl (10.9%), etc.
The average salinity of ocean water is 35 0/00. Deviation from the average salinity in one direction or another is caused by changes in the incoming and outgoing balance of fresh water. Thus, precipitation, water from glaciers, and runoff from land reduce salinity; Evaporation increases salinity.
There are both zonal and regional features in the distribution of salinity in the ocean. Zonal features are associated with climatic conditions(distribution of precipitation and evaporation). In the equatorial zone, the waters are slightly saline (O>E), in tropical and subtropical latitudes (E>O) the maximum salinity for surface ocean waters is 36-37 0 / 00, to the north and south of this zone the salinity decreases. Melting ice contributes to a decrease in salinity in high latitudes.
The latitudinal zonality in the distribution of salinity on the ocean surface is disrupted by currents. Warm ones increase salinity, cold ones decrease them. The average salinity of the oceans at the surface varies. The Atlantic Ocean has the highest salinity - 35.4 0 / 00, the lowest is the North Arctic Ocean– 32 0 / 00 (the desalination role of Siberian waters is great). Changes in salinity are associated mainly with surface layers that directly receive fresh waters and determined by the mixing depth. All changes in salinity occur in the upper layers to depths of 1500 m; deeper salinity does not change.
Water temperature of the World Ocean.
Changes in the course of heat balance elements determine the course of water temperature. Daily amplitudes of water temperature fluctuations on the ocean surface do not exceed on average 0.5 0 C. The largest daily amplitude is in low latitudes (up to 1 0 C), the smallest in high latitudes (up to 0 0 C). Daily temperature fluctuations in the ocean play a subordinate role.
The annual amplitudes of temperature fluctuations on the ocean surface are greater than the daily ones. Annual temperature fluctuations are small at low (1 0) and high (2 0) latitudes. In the first case, a large amount is evenly distributed throughout the year, in the second - over short summer The water doesn't have time to get very hot. The largest annual amplitudes (from 10 0 to 17 0) are observed in temperate latitudes. The highest average annual water temperatures (27-28 0) are observed in equatorial and tropical latitudes, to the north and south of them the temperature drops to 0 0 C and lower in polar latitudes. The thermal equator is located approximately at 5 0 C north latitude. Ocean currents disrupt the zonal temperature distribution. Currents that transport heat towards the poles (for example, the Gulf Stream) are identified as positive temperature anomalies. Therefore, in tropical latitudes, under the influence of currents, the water temperature on the eastern shores is higher than on the western shores, and in temperate latitudes, on the contrary, on the western shores it is higher than on the eastern shores. In the southern, more seaward hemisphere, the zonality in the distribution of water temperatures is almost unchanged. The highest temperature on the ocean surface (+32 0 C) was observed in August in Pacific Ocean, the lowest in February in the Arctic Ocean (-1.7 0 C). On average per year, the ocean surface is southern hemisphere colder than in the north (influence of Antarctica). The average annual temperature on the ocean surface is +17.4 0 C, which is higher than the annual air temperature of +14 0. The warmest is the Indian Ocean - about +20 0 C. Warm solar radiation heating the upper layer of water, it is extremely slowly transferred to the underlying layers. Heat redistribution in the ocean water occurs due to convection and mixing by waves and currents. Hence, the temperature decreases with depth. At a depth of somewhere around 100-200 m, the temperature drops sharply. A layer of sharp drop in water temperature with depth is called a thermocline.
Thermocline in the ocean from the equator to 50-60 0 s. and S. exists constantly at depths from 100 to 700 m. In the Arctic Ocean, the water temperature drops to a depth of 50-100 m, and then increases, reaching a maximum at a depth of 200-600 m. This increase in temperature is caused by the penetration of warm waters from temperate latitudes, more salty, than the upper layers of water.
Ice in the ocean appears at high latitudes when the water temperature drops below freezing point. The freezing point depends on its salinity. The higher the salinity, the lower the freezing point. Ice has a lower density than fresh ice. Salt ice is less durable than fresh ice, but more plastic and viscous. It doesn't break in the swell ( slight excitement). Takes on a greenish tint, unlike blue color at fresh ice. Ice in the ocean can be either stationary or floating. Fixed ice is a continuous sheet of ice associated with land or shoals. Usually this is fast ice. floating ice(drifting) is not connected to the shore and moves under the influence of wind and currents.
The temperature of the entire mass of ocean water is about 4 °C. Water is the most heat-capacity body on Earth. Therefore, the ocean slowly warms up and slowly releases heat, serving as a heat accumulator. Since the oceans make up 71% of the surface globe, then it accounts for more than 2/3 of the absorbed solar radiation. It is spent on evaporation, heating the upper layer of water to a depth of approximately 300 m, and also heating the air. It’s not for nothing that the ocean is called the kitchen of the weather.
The average temperature of surface ocean waters is more than +17 °С, Moreover, in the northern hemisphere it is 3° higher than in the southern. The highest water temperatures in the northern hemisphere are observed in August, the lowest in February, and vice versa in the southern hemisphere. Daily and annual fluctuations in water temperature are insignificant: daily fluctuations do not exceed 1°, annual maximum 5...10° in temperate latitudes.
Surface water temperatures are zonal. In the equatorial latitudes the temperature is 27...28 °C all year round, in tropical areas in the west of the oceans it is 20...25 °C, in the east it is 15...20 °C (due to currents). In temperate latitudes, the water temperature gradually decreases from 10 to 0° - in the southern hemisphere, in the northern hemisphere with the same trend in western shores continents are warmer than the eastern ones, also due to currents. In the polar regions, the water temperature all year round is O... -2 °C; in the center of the Arctic, multi-year ice thickness up to 5-7 m.
Maximum temperatures surface waters are observed in tropical seas and bays: in the Persian Gulf more than 35 ° C, in the Red Sea 32 ° C. In the bottom layers of the World Ocean, temperatures at all latitudes are low - from + 2 ° at the equator to - 2 ° C in the Arctic and Antarctic .
Freezing sea water occurs at negative temperatures: with an average salinity of about -2°C. The higher the salinity, the lower the freezing point. Sea ice is brackish, but its salinity is several times less than the salinity of the water from which it was formed. Ice covers about 15% of the world's oceans. In addition to lightly salted sea ice The oceans contain freshwater river and continental (iceberg) ice. Under the influence of winds and currents, ice from the polar regions is carried to temperate latitudes and melts there. Ice makes navigation difficult. Ship disasters are associated with icebergs.
Ocean water contains salts, gases, and solid particles of organic and inorganic origin. By weight they make up only 3.5%, but certain properties of water depend on them.
An important property of ocean water is salinity. Salinity is the amount of salts in grams dissolved in 1 kg (liter) of sea water. It is designated by the symbol S and is expressed in ppm, i.e. in thousandths (°/oo). Average salinity of ocean water S=35°/oo (35 g/l).
Ocean water has a bitter-salty taste, determined by the chlorides (more than 88%) and sulfates (about 11%) dissolved in it. Gives salty taste to water salt, bitter - magnesium salts. For ocean water characterized by constant percentage various salts, despite the different salinity. Salts, like the water of the oceans themselves, came to earth's surface, primarily from the bowels of the Earth, especially at the dawn of its formation. Salts are also brought to the ocean by river waters rich in carbonates (more than 60%). However, the amount of carbonates in ocean water does not increase and is only 0.3%. This is explained by the fact that they precipitate, and are also spent on the skeletons and shells of animals, and are consumed by algae, which, after dying, sink to the bottom.
The distribution of surface water salinity shows zonality, which is primarily determined by the ratio of precipitation and evaporation. Salinity is reduced by river runoff and melting icebergs. In subequatorial latitudes, where more precipitation falls than evaporates, and river flow, - salinity 34-35 °/oo. In tropical latitudes there is little precipitation, but evaporation is high, so the salinity is 37 °/oo. In temperate latitudes, salinity is close to 35°7оо. In the subpolar latitudes, salinity is the lowest (32-33°/oo), since the amount of precipitation here is greater than evaporation, the river flow is high, especially in Siberian rivers, and there are many icebergs, mainly around Antarctica and Greenland.
The latitudinal pattern of salinity is disrupted by sea currents. For example, in temperate latitudes, salinity is greater on the western coasts of the continents, where tropical waters flow, and less on the eastern coasts, washed by polar waters. Coastal waters near river mouths have the lowest salinity. Maximum salinity is observed in tropical inland seas surrounded by deserts. For example, in the Red Sea the salinity is more than 42 °/oo, in the Persian Gulf - 39 °/oo. Salinity affects other properties of water, such as density, freezing point, etc.
Our Earth appears to be a blue planet from space. This is because ¾ of the surface of the globe is occupied by the World Ocean. He is united, although greatly divided.
The surface area of the entire World Ocean is 361 million square meters. km.
Oceans of our planet
Ocean - water shell earth, the most important component of the hydrosphere. Continents divide the World Ocean into parts.
Currently, it is customary to distinguish five oceans:

. - the largest and oldest on our planet. Its surface area is 178.6 million square meters. km. It occupies 1/3 of the Earth and makes up almost half of the World Ocean. To imagine this magnitude, it is enough to say that the Pacific Ocean can easily accommodate all the continents and islands combined. This is probably why it is often called the Great Ocean.
The Pacific Ocean owes its name to F. Magellan, who during his trip around the world crossed the ocean under favorable conditions.
The ocean has oval shape, its widest part is located near the equator.
The southern part of the ocean is an area of calm, light winds and a stable atmosphere. To the west of the Tuamotu Islands, the picture changes dramatically - here is an area of storms and squalls that turn into fierce hurricanes.
In the tropical region, the waters of the Pacific Ocean are clean, transparent and have deep Blue colour. Formed near the equator favorable climate. The air temperature here is +25ºC and practically does not change throughout the year. Winds are moderate and often calm.
The northern part of the ocean is similar to the southern one, as if in mirror image: in the west there is unstable weather with frequent storms and typhoons, in the east there is peace and quiet.
The Pacific Ocean is the richest in the number of animal and plant species. Its waters are home to over 100 thousand species of animals. Almost half of the world's fish catch is caught here. Through this ocean are laid the most important sea routes, connecting 4 continents at once.

. occupies an area of 92 million square meters. km. This ocean, like a huge strait, connects the two poles of our planet. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, famous for its instability, runs through the center of the ocean. earth's crust. Individual peaks This ridge rises above the water and forms islands, the largest of which is Iceland.
The southern part of the ocean is influenced by trade winds. There are no cyclones here, so the water here is calm, clean and clear. Closer to the equator, the Atlantic changes completely. The waters here are muddy, especially along the coast. This is explained by the fact that large rivers flow into the ocean in this part.
Northern tropical zone The Atlantic is famous for its hurricanes. Two major currents meet here - the warm Gulf Stream and the cold Labrador Stream.
The northern latitudes of the Atlantic are the most picturesque area with huge icebergs and powerful ice tongues protruding from the waters. This area of the ocean is dangerous for shipping.

. (76 million sq. km) - region ancient civilizations. Navigation began to develop here much earlier than in other oceans. The average depth of the ocean is 3700 meters. Coastline slightly indented, with the exception of the northern part, where most of the seas and bays are located.
Water Indian Ocean more salty than others, since many fewer rivers flow into it. But thanks to this, they are famous for their amazing transparency and rich azure and blue color.
The northern part of the ocean is a monsoon region; typhoons often form in autumn and spring. Closer to the south, the water temperature is lower, due to the influence of Antarctica.

. (15 million sq. km) is located in the Arctic and occupies vast areas around north pole. Maximum depth— 5527m.
The central part of the bottom is a continuous intersection of mountain ranges, between which there is a huge basin. The coastline is heavily dissected by seas and bays, and in terms of the number of islands and archipelagos, the Arctic Ocean ranks second after such a giant as the Pacific Ocean.
The most characteristic part of this ocean is the presence of ice. The Arctic Ocean remains the least studied today, since research is hampered by the fact that most of ocean is hidden under ice cover.

. . The waters washing Antarctica combine signs. Allowing them to be separated into a separate ocean. But there is still debate about what should be considered boundaries. If the borders from the south are marked by the mainland, then the northern borders are most often drawn at 40-50º south latitude. Within these limits, the ocean area is 86 million square meters. km.
The bottom topography is indented by underwater canyons, ridges and basins. The fauna of the Southern Ocean is rich, here is the most a large number of endemic animals and plants.
Characteristics of the oceans

The world's oceans are several billion years old. Its prototype is the ancient ocean Panthalassa, which existed when all the continents were still a single whole. Until recently, it was assumed that the ocean floors were level. But it turned out that the bottom, like the land, has a complex topography, with its own mountains and plains.
Properties of the world's oceans

Russian scientist A. Voyekov called the World Ocean a “huge heating battery” of our planet. The fact is that the average water temperature in the oceans is +17ºC, and the average air temperature is +14ºC. Water takes much longer to heat up, but it also consumes heat more slowly than air, while having high heat capacity.
But not all water in the oceans has the same temperature. They only get warm under the sun surface water, and with depth the temperature drops. It is known that at the bottom of the oceans the average temperature is only +3ºC. And she remains like this because high density water.

It should be remembered that the water in the oceans is salty, which is why it freezes not at 0ºC, but at -2ºC.
The degree of water salinity varies depending on geographical latitude: in temperate latitudes the waters are less saline than, for example, in the tropics. In the north, the waters are also less saline due to the melting of glaciers, which greatly desalinize the water.
Ocean waters also vary in transparency. At the equator the water is clearer. As you move away from the equator, water becomes more quickly saturated with oxygen, which means more microorganisms appear. But near the poles, due to low temperatures, the waters become clearer again. Thus, the waters of the Weddell Sea near Antarctica are considered the most transparent. Second place belongs to the waters of the Sargasso Sea.
The difference between the ocean and the sea

The main difference between the sea and the ocean is its size. Oceans are much larger, and seas are often only part of the oceans. Seas also differ from the ocean to which they belong by a unique hydrological regime (water temperature, salinity, transparency, distinctive composition of flora and fauna).
Ocean climate

Pacific climate infinitely diverse, since the ocean is located in almost all climatic zones: from equatorial to subarctic in the north and Antarctic in the south. 5 circulate in the Pacific Ocean warm currents and 4 cold ones.
The greatest amount of precipitation falls in the equatorial belt. The amount of precipitation exceeds the share of water evaporation, so the water in the Pacific Ocean is less salty than in others.

Atlantic Ocean Climate determined by its large extent from north to south. The equator zone is the most narrow part ocean, so the water temperature here is lower than in the Pacific or Indian.
The Atlantic is conventionally divided into northern and southern, drawing the border along the equator, and South part much colder due to its proximity to Antarctica. Many areas of this ocean are characterized by dense fogs and powerful cyclones. They are strongest near the southern tip North America and in the Caribbean region.

For formation Indian Ocean climate provides a huge impact the proximity of two continents - Eurasia and Antarctica. Eurasia actively participates in the annual change of seasons, bringing dry air in winter and filling the atmosphere with excess moisture in summer.
The proximity of Antarctica causes a decrease in water temperature in the southern part of the ocean. Frequent hurricanes and storms occur north and south of the equator.

Formation climate of the Arctic Ocean is determined by it geographical location. Arctic air masses dominate here. Average air temperature: from -20 ºC to -40 ºC, even in summer the temperature rarely rises above 0ºC. But the ocean waters are warmer due to constant contact with the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Therefore, the Arctic Ocean warms a significant part of the land.
Strong winds are rare, but fog is common in summer. Precipitation falls mainly in the form of snow.

It is influenced by the proximity of Antarctica, the presence of ice and the absence of warm currents. The Antarctic climate prevails here with low temperatures, cloudy weather and light winds. Snow falls throughout the year. Distinctive feature climate of the Southern Ocean - high activity cyclones.
The influence of the ocean on the Earth's climate

The ocean has a tremendous influence on climate formation. It accumulates huge reserves heat. Thanks to the oceans, the climate on our planet becomes softer and warmer, since the temperature of the waters in the oceans does not change as sharply and quickly as the air temperature over land.
Oceans promote better circulation air masses. And this is the most important a natural phenomenon, like the water cycle, provides the land with a sufficient amount of moisture.
 Battleship “Victory” – Legendary sailing ships
Battleship “Victory” – Legendary sailing ships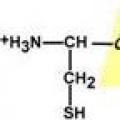 Formation of a peptide bond Two equivalent forms
Formation of a peptide bond Two equivalent forms Kasatkin Mikhail Alexandrovich (1902–1974) M Kasatkin
Kasatkin Mikhail Alexandrovich (1902–1974) M Kasatkin