Bacteria that help humans. Beneficial and harmful microorganisms
Rice. 1. The human body consists of 90% microbial cells. It contains from 500 to 1000 different types of bacteria or trillions of these amazing residents, which amounts to up to 4 kg of total weight.

Rice. 2. Bacteria inhabiting the oral cavity: Streptococcus mutants ( green color). Bakteroides gingivalis, causes periodontitis ( purple colour). Candida albicus (yellow color). Causes candidiasis of the skin and internal organs.





Rice. 7. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bacteria have been causing diseases in humans and animals for many millennia. The tuberculosis bacillus is extremely stable in the external environment. In 95% of cases it is transmitted by airborne droplets. Most often affects the lungs.

Rice. 8. The causative agent of diphtheria is corynebacteria or Leffler's bacillus. It most often develops in the epithelium of the mucous layer of the tonsils, less often in the larynx. Swelling of the larynx and enlarged lymph nodes can lead to asphyxia. The pathogen's toxin is fixed on the membranes of the cells of the heart muscle, kidneys, adrenal glands and nerve ganglia and destroys them.

Rice. 9. Causative agents of staphylococcal infection. Pathogenic staphylococci cause extensive damage to the skin and its appendages, damage to many internal organs, foodborne toxic infection, enteritis and colitis, sepsis and toxic shock.

Rice. 10. Meningococci are the causative agents of meningococcal infection. Up to 80% of cases are children. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets from sick and healthy carriers of bacteria.

Rice. 11. Bordetella pertussis.

Rice. 12. The causative agent of scarlet fever is streptococcus pyogenes.
Harmful bacteria of water microflora
Water is the habitat for many microbes. In 1 cm3 of water you can count up to 1 million microbial bodies. Pathogenic microorganisms enter water from industrial enterprises, settlements and livestock farms. Water containing pathogenic microbes can become a source dysentery, cholera, typhoid fever, tularemia, leptospirosis, etc. Vibrio cholerae and can remain in water for quite a long time.
Rice. 13. Shigella. Pathogens cause bacillary dysentery. Shigella destroys the epithelium of the colon mucosa, causing severe ulcerative colitis. Their toxins affect the myocardium, nervous and vascular systems.

Rice. 14. . Vibrios do not destroy the cells of the mucous layer of the small intestine, but are located on their surface. They secrete a toxin called choleragen, the action of which leads to disruption of water-salt metabolism, causing the body to lose up to 30 liters of fluid per day.

Rice. 15. Salmonella is the causative agent of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. The epithelium and lymphoid elements of the small intestine are affected. With the bloodstream they enter the bone marrow, spleen and gall bladder, from which the pathogens again enter the small intestine. As a result of immune inflammation, the wall of the small intestine ruptures and peritonitis occurs.

Rice. 16. Causative agents of tularemia (coccobacteria blue color). They affect the respiratory tract and intestines. They have the ability to penetrate the human body through intact skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, nasopharynx, larynx and intestines. The peculiarity of the disease is damage to the lymph nodes (primary bubo).

Rice. 17. Leptospira. They affect the human capillary network, often the liver, kidneys and muscles. The disease is called infectious jaundice.
Harmful bacteria of soil microflora
Billions of “bad” bacteria live in the soil. In a 30-centimeter thickness of 1 hectare of land there are up to 30 tons of bacteria. Possessing a powerful set of enzymes, they break down proteins into amino acids, thereby taking Active participation in the processes of decay. However, these bacteria bring a lot of trouble to humans. Thanks to the activity of these microbes, food spoils very quickly. Man has learned to protect shelf-stable foods by sterilizing, salting, smoking and freezing. Some types of these bacteria can spoil even salted and frozen foods. enter the soil from sick animals and humans. Some types of bacteria and fungi stay in the soil for decades. This is facilitated by the ability of these microorganisms to form spores, which protect them from unfavorable environmental conditions for many years. They cause the most dangerous diseases - anthrax, botulism, and tetanus.
Rice. 18. Pathogen anthrax. It remains in the soil in a spore-like state for decades. A particularly dangerous disease. Its second name is malignant carbuncle. The prognosis of the disease is unfavorable.

Rice. 19. The causative agent of botulism produces a powerful toxin. 1 microgram of this poison kills a person. Botulinum toxin affects nervous system, oculomotor nerves, up to paralysis and cranial nerves. The mortality rate from botulism reaches 60%.

Rice. 20. The causative agents of gas gangrene multiply very quickly in the soft tissues of the body without air access, causing severe lesions. In a spore-like state, it persists in the external environment for a long time.

Rice. 21. Putrefactive bacteria.

Rice. 22. Damage to food products by putrefactive bacteria.
Harmful bacteria that damage wood
A number of bacteria and fungi intensively decompose fiber, playing an important sanitary role. However, among them there are bacteria that cause serious illnesses animals. Molds destroy wood. Wood staining mushrooms paint wood in different colors. House mushroom leads the wood to a rotten state. As a result of the vital activity of this fungus, wooden buildings are destroyed. The activity of these fungi causes great damage in the destruction of livestock buildings.
Rice. 23. The photo shows how the house fungus destroyed the wooden floor beams.

Rice. 24. Spoiled appearance logs (blue staining) affected by wood staining fungus.

Rice. 25. House mushroom Merulius Lacrimans. a – cotton wool mycelium; b – young fruiting body; c – old fruiting body; d – old mycelium, cords and wood rot.
Harmful bacteria in food
Products contaminated with dangerous bacteria become a source of intestinal diseases: typhoid fever, salmonellosis, cholera, dysentery etc. Toxins that are released staphylococci and botulism bacilli, cause toxic infections. Cheeses and all dairy products may be affected butyric acid bacteria, which cause butyric acid fermentation, resulting in products appearing bad smell and color. Vinegar sticks cause acetic fermentation, which leads to sour wine and beer. Bacteria and micrococci that cause rotting contain proteolytic enzymes, which break down proteins, giving foods a foul-smelling odor and bitter taste. Products become covered in mold as a result of damage to mold fungi.
Rice. 26. Bread affected by mold.

Rice. 27. Cheese affected by mold and putrefactive bacteria.

Rice. 28. “Wild yeast” Pichia pastoris. The photo was taken with 600x magnification. The worst pest of beer. Found everywhere in nature.
Harmful bacteria that decompose dietary fats
Butyric acid microbes are everywhere. 25 of their species cause butyric acid fermentation. Life activity fat-digesting bacteria leads to rancidity of the oil. Under their influence, soybean and sunflower seeds become rancid. Butyric acid fermentation, which is caused by these microbes, spoils the silage, and it is poorly eaten by livestock. And wet grain and hay, infected with butyric acid microbes, self-heats. The moisture contained in butter is a good environment for reproduction. putrefactive bacteria and yeast fungi. Because of this, the oil deteriorates not only outside, but also inside. If the oil is stored for a long time, then it can settle on its surface. molds.
Rice. 29. Caviar oil affected by fat-splitting bacteria.
Harmful bacteria affecting eggs and egg products
Bacteria and fungi penetrate into eggs through the pores of the outer shell and its damage. Most often, eggs are infected with salmonella bacteria and molds, egg powder - salmonella and .
Rice. 30. Spoiled eggs.
Harmful bacteria in canned food
for humans are toxins botulinum bacillus and perfringens bacillus. Their spores exhibit high heat resistance, which allows microbes to remain viable after pasteurization of canned food. Being inside the jar, without access to oxygen, they begin to multiply. At the same time, it stands out carbon dioxide and hydrogen, which causes the can to swell. Eating such a product causes severe food toxicosis, which is characterized by an extremely severe course and often ends in the death of the patient. Canned meat and vegetables are amazing acetic acid bacteria, As a result, the contents of the canned food sour. Development does not cause bloating of canned food, since staphylococcus does not produce gases.
Rice. 31. Canned meat affected by acetic acid bacteria, as a result of which the contents of the cans turn sour.

Rice. 32. Swollen canned food may contain botulinum bacilli and perfringens bacilli. The jar is inflated by carbon dioxide, which is released by bacteria during reproduction.
Harmful bacteria in grain products and bread
Ergot and other molds that infect grains are the most dangerous for humans. The toxins of these mushrooms are heat stable and are not destroyed by baking. Toxicoses caused by the use of such products are severe. Torment, stricken lactic acid bacteria, has an unpleasant taste and specific smell, lumpy in appearance. Already baked bread is affected Bacillus subtilis(Bac. subtilis) or "gravitating disease." The bacilli secrete enzymes that break down bread starch, which is manifested, first, by an odor not characteristic of bread, and then by the stickiness and viscousness of the bread crumb. Green, white and capitate mold affects already baked bread. It spreads through the air.
Rice. 33. In the photo there is purple ergot. Low doses of ergot cause severe pain, mental disorders and aggressive behavior. High doses of ergot cause painful death. Its action is associated with muscle contraction under the influence of fungal alkaloids.

Rice. 34. Mold mycelium.

Rice. 35. Spores of green, white and capitate molds can fall from the air onto already baked bread and infect it.
Harmful bacteria that affect fruits, vegetables and berries
Fruits, vegetables and berries are seeded soil bacteria, molds and yeast, which cause intestinal infections. The mycotoxin patulin, which is secreted mushrooms of the genus Penicillium, can cause cancer in humans. Yersinia enterocolitica causes the disease yersiniosis or pseudotuberculosis, which affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract and other organs and systems.
Rice. 36. Damage to berries by mold fungi.

Rice. 37. Skin lesions due to yersiniosis.
Harmful bacteria enter the human body through food, air, wounds and mucous membranes. The severity of diseases caused by pathogenic microbes depends on the poisons they produce and the toxins that arise when they die en masse. Over the course of thousands of years, they have acquired many adaptations that allow them to penetrate and remain in the tissues of a living organism and resist immunity.
Study the harmful effects of microorganisms on the body and develop preventive actions- this is the task of man!
The entire set of bacteria that live in the human body is called microbiota. Healthy intestinal microflora consists of many bacteria. There are more than a million of them. Every microorganism plays huge role in normalizing the functioning of the whole organism. If the balance is disturbed and there is a lack of any bacteria, this leads to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The pathogenic process begins to develop rapidly. All beneficial microorganisms are found mostly in the intestines, as well as on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. The immune system is able to regulate required amount beneficial bacteria.
The microflora of the human body is populated by both beneficial and pathogenic organisms. At a certain concentration this is considered normal. There are beneficial and pathogenic bacteria. Of course, there are many more beneficial microorganisms in the intestines. Balance is only achieved when good microflora constitutes more than 95 percent of all microorganisms. There are the following types of bacteria that live in the human body:
- lactobacilli;
- bifidobacteria;
- enterococci;
- coli.
Bifidobacteria
They are the most common type of bacteria. They are directly involved in the formation of lactic acid and acetate. Bifidobacteria contribute to the creation acidic environment, which helps to neutralize almost all pathogenic bacteria. In this case, the pathogenic flora can no longer develop further. The processes of decay and fermentation stop in the body.
Bifidobacteria are very important for child's body. They are responsible for allergic reactions to various foods. They also have a good antioxidant effect and prevent the development of tumors.
This type of bacteria takes part in the synthesis of vitamin C. They help the rapid absorption of vitamins B and D, which take part in the formation of the child’s body. If there are few bifidobacteria in the body, then even synthetic vitamins will not be able to fully replenish their required amount.
Lactobacilli
These microorganisms also play a fairly important role in the normal functioning of the body. They are able to interact with other good bacteria that inhabit the intestines. At the same time, they block the development of pathogenic microflora and suppress the vital activity of bacteria, causing diseases intestines.
Lactobacilli take part in the formation of lysozyme, lactic acid and some vitamins. They are excellent helpers for the immune system. A deficiency of these bacteria almost always leads to the development of dysbacteriosis.
Lactobacilli can often be found not only in the intestines, but also on the mucous membranes. This is a very important factor, especially for women's health. With their help, the necessary acidity in the vagina is maintained. This helps prevent the development of diseases such as bacterial vaginosis.
Enterococci
Appear in the human body in the first days after birth. Promotes good absorption of sucrose. Most often, enterococci are found in the small intestine. By interacting with other good bacteria, they protect the body from the development of pathogenic microflora. However, this type of microorganism is considered to be conditionally safe. If their concentration is exceeded, intestinal diseases develop.
Escherichia coli
Many types of such microorganisms do not contribute to the development of any diseases. In some cases they also perform protective function. Their usefulness lies in the synthesis of cocilin, which creates an obstacle to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Escherichia coli takes part in the synthesis of many vitamins, as well as nicotinic and folic acid. This is very important because folic acid is responsible for the formation of red blood cells in the body, which helps maintain hemoglobin levels.
Positive effects of bacteria on the human body
Good bacteria have a lot of useful and necessary properties. The body is able to function normally as long as it maintains the necessary balance between the bacteria that inhabit the intestines and mucous membranes. A lot of them are involved in the most important process synthesis of vitamins. B vitamins cannot be absorbed normally without exposure to beneficial bacteria. Because of this, the level of hemoglobin in the blood may decrease, the skin may suffer, and disorders of the nervous system may occur.
Bacteria are able to break down undigested food components that reach the large intestine. Beneficial microorganisms help maintain water-salt balance in the body.
The intestinal microflora takes part in the formation of local immunity. Helps block the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, people do not feel bloating and flatulence. An increase in the number of lymphocytes provokes the work of phagocytes, which consists of fighting harmful microbes. At the same time, some bacteria actively participate in the synthesis of immunoglobulin A.
Beneficial microorganisms have a positive effect on the functioning of the large and small intestines. With their help, it is possible to maintain the necessary acidity, as a result of which the epithelium becomes more resistant to the effects of harmful factors. Intestinal motility also depends on microorganisms. Bifidobacteria take part in blocking the processes of decay and fermentation in the body. Many bacteria are constantly in symbiosis with pathogens, controlling their effect on the body.
The overall balance of the body is maintained by biochemical reactions occurring in the body with the participation of bacteria. At the same time, it stands out thermal energy. The basis of nutrition for beneficial bacteria is the remains of undigested food.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is usually called changes in the quantity and quality of bacteria. In this case, a large number good bacteria They simply die, and the bad ones begin to multiply quickly. Dysbacteriosis in many cases affects not only the intestines. It can appear in the oral cavity or on mucous membranes. Strepto- and staphylococci can be detected in the tests.
In the normal state of the body, beneficial bacteria are able to completely regulate the proliferation of pathogens. Usually the airways and skin are protected. But if the balance is imbalanced, a person begins to feel some symptoms of a developing disease. Abdominal pain, bloating, and possible development of flatulence and diarrhea. Later, vitamin deficiency and anemia begin. Due to lack of appetite, weight rapidly decreases. Women may develop sexual dysfunction. Copious vaginal discharge appears. They often have an unpleasant odor. The skin becomes dry. You can find roughness and cracks on it. In almost all cases, dysbiosis is one of the manifestations of long-term use of antibiotics.
At the first signs of illness, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will prescribe all the necessary examinations, on the basis of which the maximum effective treatment dysbacteriosis. Various probiotics are most often used for medicinal purposes.
The most ancient living organism on our planet. Not only have its members survived for billions of years, but they are also powerful enough to wipe out every other species on Earth. In this article we will look at what types of bacteria there are.
Let's talk about their structure, functions, and also name some useful and harmful types.
Discovery of bacteria
Let's begin our excursion into the kingdom of microorganisms with a definition. What does "bacteria" mean?
The term comes from the ancient Greek word for "stick". Christian Ehrenberg introduced it into the academic lexicon. These are nuclear-free microorganisms that do not have a nucleus. Previously, they were also called “prokaryotes” (nuclear-free). But in 1970 there was a division into archaea and eubacteria. However, this concept is still more often used to mean all prokaryotes.
The science of bacteriology studies what types of bacteria there are. Scientists say that given time About ten thousand different types of these living creatures have been discovered. However, it is believed that there are more than a million varieties.
Anton Leeuwenhoek, Dutch naturalist, microbiologist and fellow of the London Royal Society, in 1676, in a letter to Great Britain, describes a number of protozoan microorganisms that he discovered. His message shocked the public, and a commission was sent from London to double-check this data.
After Nehemiah Grew confirmed the information, Leeuwenhoek became a world-famous scientist, a discoverer. But in his notes he called them “animalcules.”
Ehrenberg continued his work. It was this researcher who coined the modern term “bacteria” in 1828.

Microorganisms are also used for military purposes. By using various types a deadly one is created. To do this, not only the bacteria themselves are used, but also the toxins released by them.
In a peaceful way, science uses single-celled organisms for research in the field of genetics, biochemistry, genetic engineering And molecular biology. With the help of successful experiments, algorithms for the synthesis of vitamins, proteins and other necessary for a person substances.
Bacteria are used in other areas as well. With the help of microorganisms, ores are enriched and water bodies and soils are cleaned.
Scientists also say that the bacteria that make up the microflora in the human intestine can be called a separate organ with its own tasks and independent functions. According to researchers, there is about one kilogram of these microorganisms inside the body!
In everyday life, we encounter pathogenic bacteria everywhere. According to statistics, the largest number of colonies are found on the handles of supermarket trolleys, followed by computer mice in Internet cafes, and only in third place are the handles of public restrooms.
Beneficial bacteria
Even at school they teach what bacteria are. Grade 3 knows all kinds of cyanobacteria and other single-celled organisms, their structure and reproduction. Now we will talk about the practical side of the issue.
Half a century ago, no one even thought about such an issue as the state of microflora in the intestines. Everything was OK. Eating more natural and healthy, less hormones and antibiotics, less chemical emissions into the environment.
Today, in conditions of poor nutrition, stress, and an overabundance of antibiotics, dysbiosis and related problems are taking leading positions. How do doctors propose to deal with this?

One of the main answers is the use of probiotics. This is a special complex that repopulates the human intestines with beneficial bacteria.
Such an intervention can help with such unpleasant issues as food allergies, lactose intolerance, gastrointestinal disorders and other ailments.
Let's now touch on what beneficial bacteria there are, and also learn about their effect on health.
Most thoroughly studied and widely used for positive impact There are three types of microorganisms on the human body - acidophilus, Bulgarian bacillus and bifidobacteria.
The first two are designed to stimulate the immune system, as well as reduce the growth of some harmful microorganisms such as yeast, E. coli, and so on. Bifidobacteria are responsible for digesting lactose, producing certain vitamins and lowering cholesterol.
Harmful bacteria
Earlier we talked about what types of bacteria there are. The types and names of the most common beneficial microorganisms were announced above. Further we'll talk about the “single-cell enemies” of humans.
There are some that are harmful only to humans, while others are deadly for animals or plants. People have learned to use the latter, in particular, to destroy weeds and annoying insects.
Before delving into what types there are, it is worth deciding on the ways of their distribution. And there are a lot of them. There are microorganisms that are transmitted through contaminated and unwashed food, by airborne droplets and contact, through water, soil or through insect bites.
The worst thing is that just one cell, once in favorable environment human body, is capable of multiplying to several million bacteria in just a few hours.

If we talk about what types of bacteria there are, the names of pathogenic and beneficial ones are difficult for a layman to distinguish. In science, Latin terms are used to refer to microorganisms. In common parlance, abstruse words are replaced by concepts - “Escherichia coli”, “pathogens” of cholera, whooping cough, tuberculosis and others.
Preventive measures to prevent the disease are of three types. These are vaccinations and vaccinations, interruption of transmission routes (gauze bandages, gloves) and quarantine.
Where do bacteria in urine come from?
Some people try to monitor their health and get tested at the clinic. Very often the cause of poor results is the presence of microorganisms in the samples.
We'll talk about what bacteria are in urine a little later. Now it is worthwhile to dwell separately on where, in fact, single-celled creatures appear there.
Ideally, a person's urine is sterile. There cannot be any foreign organisms there. The only way bacteria can enter waste is at the site where waste is removed from the body. In particular, in in this case this will be the urethra.
If the analysis shows a small number of inclusions of microorganisms in the urine, then everything is normal for now. But when the indicator increases above the permitted limits, such data indicate the development of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. This may include pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urethritis and other unpleasant ailments.
Thus, the question of what types of bacteria are in the bladder is completely incorrect. Microorganisms do not enter the discharge from this organ. Scientists today have identified several reasons leading to the presence of single-celled creatures in urine.
- Firstly, this is promiscuous sex life.
- Secondly, diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Thirdly, neglect of personal hygiene rules.
- Fourthly, decreased immunity, diabetes and a number of other disorders.
Types of bacteria in urine
Earlier in the article it was said that microorganisms in waste are found only in cases of disease. We promised to tell you what bacteria are. The names will be given only of those species that are most often found in the analysis results.

So, let's begin. Lactobacillus is a representative of anaerobic organisms, a gram-positive bacterium. She must be in digestive system person. Its presence in the urine indicates some malfunctions. Similar event uncritical, but it is an unpleasant wake-up call that you should take serious care of yourself.
Proteus is also a natural inhabitant of the gastrointestinal tract. But its presence in the urine indicates a failure in the excretion of feces. This microorganism passes from food into urine only in this way. A sign of presence large quantity proteus in the waste is a burning sensation in the lower abdomen and painful urination with dark-colored liquid.
Enterococcus fecalis is very similar to the previous bacterium. It gets into the urine the same way, multiplies quickly and is difficult to treat. In addition, enterococcus microorganisms are resistant to most antibiotics.
Thus, in this article we have figured out what bacteria are. We talked about their structure and reproduction. You have learned the names of some harmful and beneficial species.
Good luck, dear readers! Remember that following the rules of personal hygiene is the best prevention.
Bacteria are the most ancient organism on earth, and also the simplest in its structure. It consists of just one cell, which can only be seen and studied under a microscope. A characteristic feature bacteria is the absence of a nucleus, which is why bacteria are classified as prokaryotes.
Some species form small groups of cells; such clusters may be surrounded by a capsule (case). The size, shape and color of the bacterium are highly dependent on the environment.
Bacteria are distinguished by their shape into rod-shaped (bacillus), spherical (cocci) and convoluted (spirilla). There are also modified ones - cubic, C-shaped, star-shaped. Their sizes range from 1 to 10 microns. Selected species bacteria can actively move using flagella. The latter are sometimes twice the size of the bacterium itself.
Types of forms of bacteria
To move, bacteria use flagella, the number of which varies—one, a pair, or a bundle of flagella. The location of the flagella can also be different - on one side of the cell, on the sides, or evenly distributed throughout the entire plane. Also, one of the methods of movement is considered to be sliding thanks to the mucus with which the prokaryote is covered. Most have vacuoles inside the cytoplasm. Adjusting the gas capacity of the vacuoles helps them move up or down in the liquid, as well as move through the air channels of the soil.
Scientists have discovered more than 10 thousand varieties of bacteria, but according to scientific researchers, there are more than a million species in the world. general characteristics bacteria makes it possible to determine their role in the biosphere, as well as to study the structure, types and classification of the kingdom of bacteria.
Habitats
Simplicity of structure and speed of adaptation to environmental conditions helped bacteria spread over a wide range of our planet. They exist everywhere: water, soil, air, living organisms - all this is the most acceptable habitat for prokaryotes.
Bacteria were found both on south pole, and in geysers. They are found on the ocean floor, as well as in the upper layers air envelope Earth. Bacteria live everywhere, but their number depends on favorable conditions. Eg, large number species of bacteria live in open water bodies, as well as soil.
Structural features
A bacterial cell is distinguished not only by the fact that it does not have a nucleus, but also by the absence of mitochondria and plastids. The DNA of this prokaryote is located in a special nuclear zone and has the appearance of a nucleoid closed in a ring. In bacteria, the cell structure consists of a cell wall, capsule, capsule-like membrane, flagella, pili and cytoplasmic membrane. Internal structure formed by cytoplasm, granules, mesosomes, ribosomes, plasmids, inclusions and nucleoid.

The cell wall of a bacterium performs the function of defense and support. Substances can flow freely through it due to permeability. This shell contains pectin and hemicellulose. Some bacteria secrete a special mucus that can help protect against drying out. Mucus forms a capsule - a polysaccharide in chemical composition. In this form, the bacterium can tolerate even very high temperatures. It also performs other functions, such as adhesion to any surfaces.
On the surface of the bacterial cell there are thin protein fibers called pili. There may be a large number of them. Pili help the cell transmit genetic material, and also provide adhesion to other cells.
Under the plane of the wall there is a three-layer cytoplasmic membrane. It guarantees the transport of substances and also plays a significant role in the formation of spores.
The cytoplasm of bacteria is 75 percent made from water. Composition of the cytoplasm:
- Fishsomes;
- mesosomes;
- amino acids;
- enzymes;
- pigments;
- sugar;
- granules and inclusions;
- nucleoid.
Metabolism in prokaryotes is possible both with and without the participation of oxygen. Most of them feed on ready-made nutrients of organic origin. Very few species are able to synthesize themselves organic matter from inorganic. These are blue-green bacteria and cyanobacteria, which played a significant role in the formation of the atmosphere and its saturation with oxygen.
Reproduction
In conditions favorable for reproduction, it is carried out by budding or vegetatively. Asexual reproduction occurs in the following sequence:
- The bacterial cell reaches its maximum volume and contains the necessary supply of nutrients.
- The cell lengthens and a septum appears in the middle.
- Nucleotide division occurs inside the cell.
- The main and separated DNA diverge.
- The cell divides in half.
- Residual formation of daughter cells.
With this method of reproduction there is no exchange genetic information, so all daughter cells will be an exact copy of the mother cell.
The process of bacterial reproduction under unfavorable conditions is more interesting. Scientists learned about the ability of sexual reproduction of bacteria relatively recently - in 1946. Bacteria do not have division into female and reproductive cells. But their DNA is heterogeneous. When two such cells approach each other, they form a channel for the transfer of DNA, and an exchange of sites occurs - recombination. The process is quite long, the result of which is two completely new individuals.
Most bacteria are very difficult to see under a microscope because they do not have their own color. Few varieties are purple or green in color due to their bacteriochlorophyll and bacteriopurpurin content. Although if we look at some colonies of bacteria, it becomes clear that they release colored substances into their environment and acquire a bright color. In order to study prokaryotes in more detail, they are stained.

Classification
Classification of bacteria can be based on indicators such as:
- Form
- way to travel;
- method of obtaining energy;
- waste products;
- degree of danger.

Bacteria symbionts live in community with other organisms.
Bacteria saprophytes live on already dead organisms, products and organic waste. They promote the processes of rotting and fermentation.
Rotting cleanses nature of corpses and other organic waste. Without the process of decay there would be no cycle of substances in nature. So what is the role of bacteria in the cycle of substances?
Rotting bacteria are an assistant in the process of breaking down protein compounds, as well as fats and other compounds containing nitrogen. Having carried out a difficult chemical reaction, they break the bonds between the molecules of organic organisms and capture molecules of protein and amino acids. When the molecules break down, they release ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and other harmful substances. They are poisonous and can cause poisoning in people and animals.
Rotting bacteria multiply quickly in conditions favorable to them. Since these are not only beneficial bacteria, but also harmful ones, in order to prevent premature rotting of products, people have learned to process them: drying, pickling, salting, smoking. All these treatment methods kill bacteria and prevent them from multiplying.
Fermentation bacteria with the help of enzymes are able to break down carbohydrates. People noticed this ability back in ancient times and still use such bacteria to make lactic acid products, vinegars, and other food products.
Bacteria, working together with other organisms, do very important chemical work. It is very important to know what types of bacteria there are and what benefits or harm they bring to nature.
Meaning in nature and for humans
It was already noted above great importance many types of bacteria (during the processes of decay and various types fermentation), i.e. fulfilling a sanitary role on Earth.
Bacteria also play a huge role in the cycle of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and other elements. Many types of bacteria contribute to the active fixation of atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into organic form, helping to increase soil fertility. Of particular importance are those bacteria that decompose cellulose, which is the main source of carbon for the life of soil microorganisms.
Sulfate-reducing bacteria are involved in the formation of oil and hydrogen sulfide in medicinal mud, soils and seas. Thus, the layer of water saturated with hydrogen sulfide in the Black Sea is the result of the vital activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria. The activity of these bacteria in soils leads to the formation of soda and soda salinization of the soil. Sulfate-reducing bacteria convert nutrients in rice plantation soils into a form that becomes available to the roots of the crop. These bacteria can cause corrosion of metal underground and underwater structures.
Thanks to the vital activity of bacteria, the soil is freed from many products and pests and is filled with valuable nutrients. Bactericidal preparations are successfully used to combat many types of insect pests (corn borer, etc.).
Many types of bacteria are used in various industries to produce acetone, ethyl and butyl alcohols, acetic acid, enzymes, hormones, vitamins, antibiotics, protein-vitamin preparations, etc.
Without bacteria, the processes of tanning leather, drying tobacco leaves, producing silk, rubber, processing cocoa, coffee, soaking hemp, flax and other bast-fiber plants, sauerkraut, and cleaning are impossible. Wastewater, metal leaching, etc.
Most people associate the word “bacteria” with something unpleasant and a threat to health. At best, fermented milk products come to mind. At worst - dysbacteriosis, plague, dysentery and other troubles. But bacteria are everywhere, they are good and bad. What can microorganisms hide?
What are bacteria
Bacteria means “stick” in Greek. This name does not mean that harmful bacteria are meant.
They were given this name because of their shape. Most of these single cells look like rods. They also come in squares and star-shaped cells. For a billion years, bacteria do not change their appearance; they can only change internally. They can be movable or immobile. Bacteria On the outside it is covered with a thin shell. This allows it to maintain its shape. There is no nucleus or chlorophyll inside the cell. There are ribosomes, vacuoles, cytoplasmic outgrowths, and protoplasm. The largest bacterium was found in 1999. It was called the "Grey Pearl of Namibia". Bacteria and bacillus mean the same thing, they just have different origins.
Man and bacteria
In our body there is a constant battle between harmful and beneficial bacteria. Thanks to this process, a person receives protection from various infections. Various microorganisms surround us at every step. They live on clothes, fly in the air, they are omnipresent.

The presence of bacteria in the mouth, and this is about forty thousand microorganisms, protects the gums from bleeding, from periodontal disease and even from sore throat. If a woman’s microflora is disturbed, she may develop gynecological diseases. Compliance elementary rules personal hygiene will help avoid such failures.
Human immunity completely depends on the state of the microflora. Almost 60% of all bacteria are found in the gastrointestinal tract alone. The rest are located in the respiratory system and in the reproductive system. About two kilograms of bacteria live in a person.
The appearance of bacteria in the body
A newly born baby has a sterile intestine.

After his first breath, many microorganisms enter the body with which he was previously unfamiliar. When the baby is first put to the breast, the mother transfers beneficial bacteria with milk, which will help normalize the intestinal microflora. It is not for nothing that doctors insist that the mother immediately after the birth of her child breastfeed him. They also recommend extending this feeding as long as possible.
Beneficial bacteria

Beneficial bacteria There are: lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria, E. coli, streptomycents, mycorrhizae, cyanobacteria.
They all play an important role in human life. Some of them prevent infections, others are used in production medicines, still others maintain balance in the ecosystem of our planet.
Types of harmful bacteria
Harmful bacteria can cause a number of serious illnesses in humans. For example, diphtheria, sore throat, plague and many others. They are easily transmitted from an infected person through air, food, or touch. It is the harmful bacteria, the names of which will be given below, that spoil food. They give off an unpleasant odor, rot and decompose, and cause diseases.
Bacteria can be gram-positive, gram-negative, rod-shaped.
Names of harmful bacteria
| Titles | Habitat | Harm |
| Mycobacteria | food, water | tuberculosis, leprosy, ulcer |
| Tetanus bacillus | soil, skin, digestive tract | tetanus, muscle spasms, respiratory failure |
Plague stick (considered by experts as a biological weapon) | only in humans, rodents and mammals | bubonic plague, pneumonia, skin infections |
| Helicobacter pylori | human gastric mucosa | gastritis, peptic ulcer, produces cytoxins, ammonia |
| Anthrax bacillus | the soil | anthrax |
| Botulism stick | food, contaminated dishes | poisoning |
Harmful bacteria can stay in the body for a long time and absorb beneficial substances from it. However, they can cause an infectious disease.
The most dangerous bacteria
One of the most resistant bacteria is methicillin. It is better known as Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus). can cause not one, but several infectious diseases. Some types of these bacteria are resistant to powerful antibiotics and antiseptics. Strains of this bacterium can live in the upper respiratory tract, open wounds and urinary tract of every third inhabitant of the Earth. For a person with a strong immune system, this does not pose a danger.

Harmful bacteria to humans are also pathogens called Salmonella typhi. They are the causative agents of acute intestinal infections and typhoid fever. These types of bacteria, harmful to humans, are dangerous because they produce toxic substances which are extremely life-threatening. As the disease progresses, intoxication of the body occurs, very high fever, rashes on the body, and the liver and spleen enlarge. The bacterium is very resistant to various external influences. Lives well in water, on vegetables, fruits and reproduces well in milk products.
To the very dangerous bacteria also includes the bacterium Clostridium tetan. It produces a poison called tetanus exotoxin. People who become infected with this pathogen experience terrible pain, seizures and die very hard. The disease is called tetanus. Despite the fact that the vaccine was created back in 1890, 60 thousand people die from it every year on Earth.
And another bacterium that can lead to the death of a person is It causes tuberculosis, which is resistant to drugs. If you do not seek help in a timely manner, a person may die.
Measures to prevent the spread of infections
Harmful bacteria and the names of microorganisms are studied by doctors of all disciplines from their student days. Healthcare annually seeks new methods to prevent the spread of life-threatening infections. If you follow preventive measures, you will not have to waste energy on finding new ways to combat such diseases.
To do this, it is necessary to timely identify the source of the infection, determine the circle of sick people and possible victims. It is imperative to isolate those who are infected and disinfect the source of infection.

The second stage is the destruction of pathways through which harmful bacteria can be transmitted. For this purpose, appropriate propaganda is carried out among the population.
Food facilities, reservoirs, and food storage warehouses are taken under control.
Every man can resist harmful bacteria, strengthening your immunity in every possible way. Healthy image life, observing basic hygiene rules, protecting oneself during sexual contact, using sterile disposable medical instruments and equipment, completely limiting communication with people in quarantine. If you enter an epidemiological area or a source of infection, you must strictly comply with all the requirements of sanitary and epidemiological services. A number of infections are equated in their effects to bacteriological weapons.
 See what “Legion (number)” is in other dictionaries
See what “Legion (number)” is in other dictionaries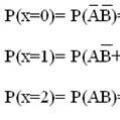 Examples of solving problems on the topic “Random variables”
Examples of solving problems on the topic “Random variables” I’m reading the poem “Frost, Red Nose” by Nekrasov
I’m reading the poem “Frost, Red Nose” by Nekrasov