Description of the results of professional pedagogical activity. The effectiveness of educational activities
Description of the results of professional pedagogical activity in accordance with the main educational program of the educational institution of the educator of the municipal budgetary preschool educational institution kindergarten "Zvezdochka"
IN modern world comprehensive development of children is impossible without the use of modern technologies. In order to achieve new educational results, I use the following modern educational technologies:
Health-saving, personality-oriented, TRIZ technologies, game learning technologies.Thanks to the systematic use of gaming technologies, the pace has increased in the immediate educational activities increased cognitive activity of pupils.
The purpose of using health-saving technologies is to create conditions for optimizing the workload of children in order to strengthen and maintain their mental and physical health.
I use methods such as dynamic pauses, outdoor and sports games, relaxation, gymnastics (finger, for the eyes, breathing, invigorating, physical education, game massage), thereby increasing the effectiveness of the educational process, forming value orientations among pupils aimed at maintaining and strengthening health.
The introduction of health-saving technologies contributes to raising a child's interest in the learning process, increases cognitive activity and, most importantly, improves psycho-emotional well-being and health. The average attendance of children has increased, absenteeism due to illness has decreased.
As a result of my systematic use of gaming technologies, children have developed the ability to analyze, compare, independently organize different types of games, and build relationships with peers. The pace, interest in educational activities has increased, the activity of children has increased, therefore, cognitive activity.
One of important directions I consider the development of fine motor skills of preschoolers to be my activity, therefore, since 2017, I have been working in depth on the topic: “Development of fine motor skills of preschool children”. The objectives of this work are: development of fine motor skills and coordination of hand movements in preschool children through various activities, improving conditions for development of fine motor skills of the fingers of preschool children.
For the successful implementation of the tasks set, I developed an individual educational plan:
1. Study the literature on the topic.
2. Implement in work with children.
3. Make a card file of games for fine motor skills development.
4. Consultation for parents " Development of fine motor skills of hands in children
preschool age».
5. Consultation for educators “What is fine motor skills and why it is important to develop it.”
6. Exercises to improve the statistical and dynamic coordination of finger movements.
This plan is implemented by me through the following forms work: joint activities of the educator with children; individual work with pupils; free independent activities of the children themselves. Working methods and techniques:
Hand massage
Finger gymnastics, physical education
Finger games with verses, with tongue twisters
Finger theater
Modeling from plasticine and salt dough using natural material(seeds, cereals, shells, etc.)
Non-traditional drawing techniques: brush, plastic fork, finger, toothbrush, candle, etc.
Construction: from paper using origami technique, work with LEGO constructor
Various types of applications
Stencil drawing
Hatching
Finishing (according to the principle of symmetry)
labyrinths
Didactic games
Lacing
Games with small items
Puzzles, mosaic.
Expected result of this activity:work on the development of fine motor skillsand coordination of hand movements should be an important part development of children's speech, skills formation self-service and preparation for writing. On how deftly the child learns to control his fingers, his further development depends. Along with the development of fine motor skills develop memory, attention, and vocabulary.
Pupils show a steady interest in creative activities, become more proactive and independent in the game, communication, possess developed imagination, which is implemented in various types of children's activities, can express their thoughts and desires.
In accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, DO updated the developing subject-spatial environment. In addition, I divided the entire space in the group into certain zones or centers, which, if desired and necessary, can be easily transformed. They are equipped with a large number of educational materials (books, toys, creative materials, educational equipment, etc.). All items are accessible to children. The equipment of the centers changes in accordance with thematic planning educational process: artistic and creative center, security center, musical and theatrical, nature center, experimentation center, design center, cognitive speech.
As a result: children accompany playing and everyday activities with speech, play with pleasure on a noise orchestra, own a finger, puppet theater; learn the rules of the road faster.
great attention I devote myself to creating conditions for independent productive activity. In the art center she placed colored pencils, felt-tip pens, stencils, coloring books, albums for free drawing at the request of children. Everything is in a place accessible to children. This contributes to the ability to freely hold a pencil, felt-tip pen, arouses interest in visual activity.
Created conditions for gaming activities, including manuals, attributes, substitute items, toys, soft play modules, various layouts. The equipment in the group is placed taking into account children's interests, individual needs, gender approach. There are materials relevant to the interests of boys and girls. I am constantly transforming the developing subject-spatial environment, taking into account the Federal State Educational Standard.
I provide the necessary conditions for self-realization of pupils with different levels development in cognitive activity:
prepared a series of consultations for parents and educators on cognitive development; issued didactic games and manuals that promote cognitive activity and cognitive interest of preschoolers, a card index of proverbs, rhymes, sayings, riddles.
Result: children show interest and cognitive activity in research, constructive and communicative activities.
In my work with children, I use not an authoritarian, but a personality-oriented model of education.
A positive result in mastering the initial information of a social nature was achieved through the development of games: "Family", "Shop", "Beauty Salon", "Magic Ball"; viewing drawings and photographs; reading works of art; writing stories; playing problem situations; leisure: "Road safety" - according to traffic rules.
Result: children began to better control their behavior, express their attitude, comment on their actions, establish contacts, keep up the conversation using the norms of communication. To a lesser extent, such qualities as aggression, shyness, and isolation began to appear.
To cultivate respect for the traditions of moral values, love for the Motherland and knowledge of its history, I use small folklore forms: with the help of Russian fairy tales, ditties, jokes, I introduce children to folk culture. She held thematic entertainments “Maslenitsa”, “Red Summer” with round dance songs, “Children of Russia for Peace”. As a result, increased interest folk traditions, children manifest themselves in productive activities - they love to draw, sculpt, design - they reflect impressions. I also use elements of folklore in educational activities:
child and the world: theme "Family" - Russian folk proverbs;
Communication - "Russian folklore" children expressively read nursery rhymes.
I organize educational activities in the form of role-playing games, excursions, quizzes; I use various forms of organizing children; I include elements of TRIZ, modeling of educational games, children's experimentation, solving problem-game situations, which allows me to help each child rise to a new level of development.
I actively use the methods of non-traditional drawing techniques by G.N. Davydova in joint and independent activities.
In order for the child to be healthy, I use the games: “I know myself”, classes from the “Health” series on life safety - methods of exposure through gymnastics for the eyes, after sleep, finger, respiratory, walking along ribbed paths; manuals and materials for improving the health of children, made by parents. For parents I hold meetings, conversations, questionnaires, consultations: “Prevention of scoliosis, flat feet, posture defects”, family sports leisure: “Dad, mom, I am a sports family”. Photo exhibition of physical culture and health improvement direction. I consider the use of such a health-saving technology to be effective, since the ability to take care of maintaining health has been formed in children from an early age. I use modern health-saving programs in my work: E.I. Podolskaya "Forms of rehabilitation of children 3-7 years old"; I.M. Novikova "Formation of ideas about healthy way life of preschoolers. Results in the field of health saving:
The sports team of the group in 2016 took 1st place in the inter-district Olympiad in kindergarten;
For two years, the incidence of colds in children has decreased;
According to the results of monitoring the individual physical training of children, there is an increase in the number of children with a high level of physical development.
Diagnostics of the development of cognitive and emotional spheres in children by specialists of the psychological, medical and pedagogical commission, by definition school maturity 2016 graduates showed 89% school readiness.
In the course of my work, I constantly introduce children to the surrounding beauty, form the ability to independently plan their actions, bring the work started to the end, develop accuracy and diligence. All graduates of my group were included in different forms additional education, 50% were engaged in the circle of the DPI "Magic Basket".
Such coverage of children with additional education allows you to maintain a positive emotional background in the group, helps to increase the activity of the families of pupils in creative endeavors. The result of this activity is the design of the portfolio of each preschooler.
With the transition to the Federal State Educational Standard, the relationship has changed kindergarten and families. Parents are not outside observers, but active participants in the educational process. With this in mind, I involve parents in all the activities of the group: the joint creation of a developing subject-spatial environment, the production of handouts and demo material, registration of photo exhibitions and exhibitions of children's works, preparation for the OD. I try to achieve positive results in my work by working in close contact with parents. I provide advisory support to parents, develop and bring to their attention methodological recommendations, advice from specialists in the field of preschool psychology and pedagogy on organizing children's activities at home. When working with parents, I try to take into account their interests and wishes. In joint events, I use such forms of work as thematic conversations, meetings -discussions, round tables, photo exhibitions, consultations, questionnaires,which contributes to the establishment of trusting relationships with the families of pupils. She designed an information stand for parents in an original way, where there are sliding folders, memos with constantly updated information on the development of speech, the improvement of children, artistic creativity, which increases the competence of parents in the field of preschool education. I also post information about the topic of the current week, about the upcoming joint activities teachers and children, about the planned final event. I conduct consultations: “Each child is an individuality”, “Age psychological characteristics of preschoolers 6-7 years old”, “Children's games are a serious matter”, etc. It should be noted that parents are interested in the recommendations , tips, reminders.
Joint work with parents gave the following results: parents assist in the design of the group, in the creation of attributes for games, take an active part in the "weekend campaigns" for the improvement and landscaping of the territory of the kindergarten.
To ensure the greatest effectiveness of work with parents, I conduct a survey in order to identify the most appropriate and effective forms of work with the parent community. According to the results of the survey, 95% of the parents of my group are satisfied with the quality of the educational process.
I constantly improve my teaching skills, study novelties of special literature, attend advanced training courses, seminars and workshops, both on the basis of our kindergarten and regional ones, use the Internet and CERs in my pedagogical activities in order to find additional material for OD, broaden the horizons of children. In relations with colleagues, I am balanced, conflict-free, willingly respond to requests for help.
On topical issues of education and upbringing, I share my experience of working with kindergarten colleagues and parents, repeatedly spoke at teachers' councils, methodological associations, gave open events: "Road Safety" (according to traffic rules) -2017, "Earth Day" -2016, " Mini-Miss "-2015," Journey to the world of magic soap "-2018, multi-plot role-playing game" To the store for gifts "-2017.
"___" ________________2018 Sviridova Oksana Stepanovna
Results of pedagogical activity
Ivanov Nikolai Nikolaevich, teacher of biology and chemistry.
Ivanov Nikolai Nikolaevich, teacher of biology and chemistry at MBOU Tatar-Saiman secondary school, Nikolaevsky district, Ulyanovsk region.
Born in the Nikolaevsky district of the Ulyanovsk region. For 10 years he studied at the Baranovskaya secondary school. In 1980, after receiving secondary education, he entered the Ulyanovsk State Order of the Badge of Honor. pedagogical institute to the Faculty of Natural Geography with a degree in geography and biology.
In 1985 he received a diploma of graduation from the institute and was hired at the Pospelovsky secondary school in the Nikolaevsky district. Currently I work at the MBOU of the Tatar-Saiman secondary school. 32 years of teaching experience.
My professional credo: from information to knowledge, from fantasy to creativity, from craft to mastery.
Over the years of my teaching experience, I have developed certain system which reveals the diversity of the child's possibilities in creative development and aims only at success. This is important condition in achieving results, including educational orientation.
The activity of the teacher in teaching.
In my work I have stable positive results of learning by students educational program in accordance with the requirements of the federal state educational standard.
I plan work according to educational programs that correspond to educational kit. The purpose of the work is the self-realization of the student through his education.
Working at school, I am constantly in search of new forms and methods of working with students, I use new technologies in the learning process. It is important for me that every student feels comfortable in the lessons of biology and chemistry. To achieve these goals, I use various methods in my lessons. organizational forms work: individual, group. In the lessons I use such teaching methods as reproductive, research, and partially search.
In my work, I systematically use the following ICT technologies, as well as materials from the following educational resources:
United Collection digital educational resources ( http:// school- collection. edu. en);
We study biology ( http:// learnbiology. people. en/ );
International Social and Ecological Union ( www. sea.ru)
Web-atlas "Environment and health of the population of Russia" ( www. sci.aha.ru/ATL/raOO.htm)
Journal "Ecology and Life" ( www. eco life. en/ index. shtml) and others.
The use of a computer in the educational process contributes to the improvement of teaching methods to a greater extent. First of all, the computer greatly expands access to the sources of information that I use in preparing for classes. The computer replaces the main part visual aids and models.
In order to instill in students an interest in subjects, I try to diversify the types of lessons, I hold conferences, quizzes. Students often, at their own request, prepare messages and abstracts for the lesson. Thus, they extract a lot of information from additional literature, the Internet.
Given the multi-level composition of the classes, in order to develop the skills of solving problems in chemistry, I give algorithms for solving them.
At the beginning of each lesson, I clearly state the topic and goals. In the lessons of studying new material, I assign a large role to exercises and assignments for updating the knowledge of students, contributing to the development of the relationship between theoretical and practical material, a more holistic perception of the topic. I present the new material in a form that is understandable to students, I teach to see the main thing, to make generalizations and conclusions, theoretical material confirm with examples.
The main indicator of the effectiveness of educational work, proceeding on general didactic principles, is the successful mastery by students of a certain complex of ZUN. I diagnose the results, make adjustments to the teaching process, plan individual work with students who have difficulty learning the material.
Some work is being done on self-education. My theme of self-education: "The use of digital educational resources in pedagogical activity." The main goal is to promote the activation of the cognitive activity of students in biology lessons and extracurricular activities with the help of information technologies. The use of information technology makes it possible to use the universal features of the child's personality to a greater extent. When planning a self-education program, I was guided by the fact that self-education is not a control of the results achieved, but an analysis of my activities, identifying directions for its development.
In order to obtain additional knowledge in the field of biology and at the request of students of the educational process, a circle " Entertaining biology» in the 9th grade.
The level of progress and quality of knowledge of all students over the past three years in biology and ecology is optimal (75-100%). When comparing the progress in the dynamics of the same classes, we can say that in comparison there is a positive dynamics in the results of students mastering educational programs and a stable high level.
Such results are an indicator of an individual and differentiated approach, the use of a system-activity approach and health-saving technologies in the classroom, combined with multi-level education and the systematic use of modern educational technologies in the work.
Every year my graduates participate in the state final certification in USE form in biology and chemistry. Students gain the minimum number of points established by Rosobrnadzor.
In 2017, 5th grade students took part in the All-Russian Biology Test. Completion of tasks in % of the number of participants is high. Evaluation criterion "5" - 50%, "4" - 50%
Graduates continue to study at universities and colleges, where the core subjects are biology and chemistry.
I hold traditional school Olympiads, prepare students to participate in district olympiads. The effectiveness of students' participation in various stages of the All-Russian Olympiad for schoolchildren and in other events
| Name of the event | F.I. participant | Results of participation |
||
| Municipal | Murtazina Lilia | Diploma, prize-winner |
||
| All-Russian Olympiad biology students | Municipal | Barinova Alena | Diploma, prize-winner |
|
| All-Russian Olympiad for Students in Biology | Municipal | 1. Alena Barinova 2. Abdulmyanova Guzal | Diploma, prize-winner Award, winner |
|
| Participant of the action "Earth Hour -2016" and concern for the future of our planet | Russian | Alshina Elvira | Certificate |
There is a positive dynamics of special achievements of students in the subject. Students are participants, winners, prize-winners.
Extracurricular activities of the teacher in academic subjects.
Training and education are based on the development of the personality of students. And in school, development should be comprehensive and complete. I, as a teacher, besides learning activities I also organize extracurricular work in subjects in various forms (games, quizzes, olympiads, competitions accompanied by presentations, awards and prizes) in order to attract interest in subjects and the school. Every year the school holds a holiday "Day of Birds", in which the children take part with pleasure. I conduct quizzes, KVN, conferences.
Behind creativity in the organization of educational work with students was awarded the Diploma of the school director.
The activity of the teacher in the field of health saving.
I work in the field of health saving on the basis of school curriculum health. I spend physical education sessions, control the study load, the total amount of homework, adjust the timing of verification and control work. I monitor the posture of students during the lessons. The classroom has a health corner where students can find information on strengthening and maintaining health.
The activity of the teacher in the field of education.
An important competence of a teacher is the ability to master educational technologies, establish contact with children, select material that is appropriate age characteristics. As an educator I find and use different approaches in this process. Encouraged students to take part in school, district competitions. Students, in 100% of the composition, take part in competitions and events. We participated in the cleaning of the school territory, we spend weeks of kindness.
Spiritual and moral position of the teacher.
IN moral education very relevant is the formation of humane relations between children, the education of effective moral feelings. The teacher is an example for the student.
In this regard, many different events are held at school with children: conversations on ethical topics, reading fiction, discussion of positive and negative actions children, adults.
I treat every student with respect. Relations in the team are conflict-free, kind. Parents of students provide support and help. On their part, there were no complaints, dissatisfaction with the teacher in terms of teaching methods, in terms of relationships with students.
Teacher activities in the field of professional development
Now it is very important for the teacher to navigate the new didactic achievements and use them. I try to work creatively, use the best teaching methods and techniques. In my lessons I use tests, multi-level cards.
In the lessons, the children fill in the tables on their own, make up judgment questions, draw up diagrams, working from the textbook and additional material.
Students do it on their own experimental tasks, as a result of which they themselves make analyzes and conclusions. When consolidating the studied material, the guys perform creative homework: make a collection, crossword puzzles, prepare an essay, a message. In preparation for the lessons of biology and natural history, experiments made by the children at home are used.
I improve my professional level by self-training. I study new technologies in teaching biology, chemistry. Continuously, systematically improve my skills, take courses, participate in seminars and improve my professional growth.
| Name of the educational organization | Form of advanced training, name of the educational program | Date of advanced training | ID/Certificate No. |
| Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "UlSPU" named after I.N. Ulyanov | Advanced training courses for the program: " Topical issues teaching chemistry, biology, geography in the context of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard "in the amount of 108 hours | certificate №731800803952 |
Generalization and dissemination of their own pedagogical experience and skills.
In April, it is planned to speak at the RMS of biology teachers with a report from the courses.
Every year I hold educational events for the parent community and teachers.
Effective social experience.
I have the respect of the school administration, parents, students and residents of the settlement. I participate in the beautification of the village. We plant trees with students near the school. We are planning to take part in the Obelisk action with the students of the school.
awarded Honorary diploma Ministry of Education and Science of the Ulyanovsk Region (2017), Honorary Diploma of the Administration municipality"Nikolaevsky district" of the Ulyanovsk region (2016)
Participated in various webinars at the Russian, interregional level. There are incentives.
| event title | Result |
|||
| Russian Federation for the Development of Education | Active participant in a series of webinars on the preparation and conduct of the USE-2016 | |||
| Webinar on the preparation and conduct of the USE-2016 | Interregional Center for Quality and Innovation of the Russian Federation | Participant of a series of webinars on the preparation and conduct of the USE-2016 | Certificate |
|
| SAOU "Center pedagogical excellence» | Participation in the conduct and verification of the All-Russian verification work of 4 classes around the world (VPR) | Gratitude |
||
| All-Russian verification work (VPR) | Participation in the conduct and verification of the All-Russian verification work - VPR-2017 5th grade in biology | Gratitude |
||
| All-Russian verification work (VPR) | Moscow Center for Continuous mathematics education | Participation in the conduct and verification of the All-Russian verification work - VPR-2017 11th grade in chemistry | Gratitude |
I systematically improve my qualifications in the form of certification.
| Document |
||
Teacher of biology and chemistry Ivanov Nikolay Nikolaevich
How to design an experiment program?Sidenko Alla Stepanovna, cand. ped. Sci., Head of the Regional Scientific and Methodological Center of the Institute for Advanced Studies and Retraining of Public Education Workers of the Moscow Region
"I almost always go to school with joy. School for me is interest, knowledge and, of course, joy. In the lessons, when the topics are interesting, I like to argue. After the lessons, the door swings wide open, and cheerful schoolchildren run out of there, even if in the morning at They came to school sad. When I go on vacation, I look at the sign "School" Eureka ", and I get a little sad."(Alesha Bezborodov, 5th grade) "I like the fact that in our school we study on our own, and if someone does not understand something, we can explain it to each other. I go to school with joy, because I know that this day will again be interesting. "(Kapustin Misha, 5th grade).
Before talking about how to develop an experiment program, I would like to specify a number of preliminary steps that are necessary for teachers who have embarked on the path of experimentation.
First, I advise you to figure out whether an experiment is needed and what do teachers expect from experimental activities? Educators answer these questions in different ways. Some are waiting for a status upgrade; others - social security; still others - scientific confirmation of innovative teaching methods; qualitatively different learning outcomes; solving specific pedagogical problems and difficulties, and so on.
And although the motives that prompt the teacher to start the experiment are very different, having decided on it, everyone must act professionally, be a Master of their craft. As you know, any master in the manufacture of his product, uses a tool. And the more complex the manufacturing process, the thinner and more elegant the product, the more accurate and complex tool the Master will need.
Likewise, the teacher-experimenter, striving to obtain the planned result of his activity, must possess a kind of a tool for designing and analyzing pedagogical actions - set of special professional concepts. What is this tool and how to use it when developing an experiment program?
As the practice of experimentation shows, experimental programs can be very different, both in the direction of the content (which is natural), and in the number and complexity of the tools used to describe the program. The question arises: what does it depend on? When should a program be very complete and detailed, and when should it not?
There are several factors that affect the level of requirements for the experimental program (and, consequently, the completeness and breadth of its components). These factors are both objective and subjective. Among the subjective ones is the inner self-determination of the experimenter, the level of his personality. The objective ones are social norms for experimental activities. Thus, the level of requirements depends on type experiment (stating, searching, forming); status (experimental platform of the federal level, regional, municipal city or district; interschool or intraschool; individual or collective); from scale experiment (duration in time, coverage in terms of the volume of material - several lessons of the topic, a quarter, a year, several years), etc.
This, of course, must be taken into account when developing a program. For now, I will only note that the higher, for example, the status or scale of the experiment, the more detailed and complexly organized its program should be.
As the varied experience of unfolding (launching) an experiment at school shows, the best result is achieved when the teacher has the freedom of choice, the opportunity to decide for himself and decide whether he needs an experiment and which one. In this case, one can hope for greater success than when the experiment is lowered “from above”. But at the same time, it is important to create conditions for teachers to develop an inner installations, a kind of relationship to own development. This is not a formality and not beautiful words. Behind them is the huge work of the administration of the educational institution (together with the leader of the experiment, if he is, or without him, if he is not) to create a desire among teachers, a desire to start an experiment, an understanding of the need to master its technique and methodology. Since the desire of the teacher, his special training and personal responsibility for the reliability of the result of the experimental activity are important for the success of the experiment, it is desirable that the deployment of the experiment in an educational institution be consistent and very gradual. There is no need to rush and force things here. Therefore, a good director, a smart administrator - a strategist for the development of his educational institution, develops a whole range of conditions for the success of the first steps of his educational institution in the experimental mode.
Thus, the development of motivational conditions helps to interest, involve the teacher in the experiment; legal (legal) - to protect all participants in the educational process (children, parents, teachers) from possible negative manifestations of the experiment; normative - to present some system of requirements to the participants of the experiment and, in particular, to the teacher. I would like to dwell on the last position in particular. When formulating a system of norms, it is desirable not to frighten the teacher with complexity, additional work, excessive demands on him as an experimenter, not to accidentally push formalities and replies about the results of supposedly experimental activity “into the ravine”. And at the same time, it is very important to be able to maintain a clear position that defines rather stringent requirements for all levels of the experiment. What are these requirements?
1. Before the start of the experiment need to develop a program, in which the plans, expectations of the teacher, diagnostic tools are assembled into a kind of integrity that will help manage the pedagogical process, make, if necessary, correction (controlled changes) in the educational process.
2. Upon completion a certain stage of the experiment is necessary analyze the results, which are usually issued in the form of a reflective report, certificate of results, report, notes, articles, etc. All this is not “excessive writing”, as teachers sometimes think. The results obtained in the experiment must be conclusive, and the actions of the experimenter must be perceived by him as special, located in the space of research. Without reflection, the teacher will not be able to understand and clearly answer the questions: “What does he do as an experimenter? Why does it work like that? What is expected to be received and how is the result going to be checked? What happened in the end? Were expectations confirmed? Therefore, try to make the first step in unfolding the experiment - motivational, the second - self-determining, and the third - design, associated with the development of the experiment program.
How to approach the development of the program? It is possible to distinguish the stages of professional growth of a teacher-experimenter (and, accordingly, the levels of experiment within an educational institution), for the development of which the teacher is self-determined.
Level I experiment - experimental work; II level - experimental activity; III level - experimental and search activity; IV level: experimental research activity.
The basis for the division into levels is the degree of reliability and reproducibility of the result of the experiment. The more evidence-based and reasoned is the result of the experiment, the higher its level. The more technological and possible to repeat the result of the experiment, the higher its level again. The most complete program in terms of content and structure is being developed for the IV level of the experiment. It can contain about 25 positions and be from 7-8 to 50 pages of text and be very close to the fact that the teacher could describe the results of his experimental research (if desired) in a dissertation. (The structure of such a program is described in more detail in the journal “School Technologies” 1997, No. 1, pp. 76-79).
Yes, for I level of experiment - experimental work the teacher should be able to answer in writing the questions of the three groups (on any chosen question from each group).
I group of questions - “feature of pedagogical activity”:what is the peculiarity of his pedagogical activity, due to which he expects to get a positive result in the educational process? or What is the totality of pedagogical techniques, techniques, methods or technologies used to achieve the planned result of education (or education)? or What is the difference between the pedagogical influences on the student, carried out in the course of the experiment, and the traditional ones? or What is the “highlight” of his teaching experience, which helps to get positive changes in the state of students?
II group of questions - “pedagogical goal”: What changes in the state of the student are planned (or already achieved)? or What is the pedagogical goal? or What are the planned results of training (education)? What personality traits and abilities are developed by the experimental activity of the teacher? or What is the distinguishing feature that characterizes the knowledge or skills of the student, which he acquires (acquires) during the experiment?
III group of questions - "performance": how will the teacher distinguish (fix, determine, notice), (or already distinguish) that these changes in students have occurred? or By what signs, changes in the state of the student was (or will be) assessed the effectiveness of pedagogical activity?
Thus, first level experiment involves the development of the ability to awareness (designing and reflection) of their own pedagogical actions . The key questions that the experimenter learns to answer at this stage are: “What am I doing as an educator-experimenter? How do I do it? Why and what result do I get?
Level II of the experiment - experimental is based on the first and differs from it in the completeness and depth of answers to the selected questions, the development of an experiment program in a certain form.
The structure of the experiment program (II level)
|
ITEM OF THE PROGRAM |
QUESTION TO ANSWER |
|
|
1. Performer of the experiment |
Surname, name, patronymic, position | |
|
2. Pedagogical goal |
The expected result of pedagogical activity, expressed in positive changes in students that have appeared due to experimental development |
What do you want to change in a student? What personality traits do you want to cultivate in a student through experimental actions? What skills would you like to develop? What changes do you expect in student learning? ... |
|
3. Purpose of the experiment |
The expected result of the experimenter's activity, expressed in obtaining new knowledge about pedagogical reality and designed in the form of experimental materials. |
What do you want to develop and test? What (what experimental developments) will you introduce into the educational process and test? What will be tested: the program, syllabus, concept, methodology, etc. |
|
4. Hypothesis |
A logically based assumption, a set of pedagogical influences |
What do you suppose? What is the totality of pedagogical actions aimed at achieving the goal? What will you check?... |
|
5. Diagnostic tools |
Means for evaluating the results of the experiment: tests, questionnaires, tests, transcripts of lessons ... |
How will results be monitored? What type of task or task for students will be used to test the effectiveness of the experiment? |
|
6. Criteria for evaluating expected results |
Signs on the basis of which the effectiveness of experimental development is evaluated |
With the help of what signs in the change in the state of students will the effectiveness of experimental materials be assessed? How do you propose to fix, diagnose, what changes have occurred in students? |
When developing an experiment program of this level, some difficulties may arise. So, the first difficulty may be the teacher's misunderstanding that the result (product) of the activity of the teacher-practitioner and the experimenter is different. Their goals are different.
Pedagogical purpose and purpose of the experiment- it's not the same thing. This is the first "underwater reef". As already mentioned in the correspondence seminar, (see // National Education, 1997. - No. 7, 8), the experimental teacher works in two spaces: research and practical, i.e. actually teaching. Simultaneous stay in these two positions is quite difficult for a teacher who is not specially prepared for this. That is why the gradual development of the position of an experimenter-researcher is important. If the result of the activity of a teacher-practitioner (pedagogical purpose) are positive changes in the student that appeared due to a complex of pedagogical influences (although it would be better to say - pedagogical co-creation, collaboration, community), then the result of the activity of a teacher-experimenter ( purpose of the experiment) is the answer to the question: how and due to what did such a result succeed?
In other words, the result of the teacher-practitioner is expressed in a change in the state of the student: the development of the need-motivational, emotional-volitional, cognitive spheres of the personality. Usually the teacher describes this as: “the student became interested in learning”, “the student got a motive for learning activities”, “the student became persistent, assiduous”, “the student’s knowledge became systemic”, “the student developed the ability to ...”, etc. And the experimental teacher achieves the real result of his activity as new knowledge about pedagogical reality, about the method and way of obtaining the result of pedagogical activity. Therefore, such a teacher is in a reflective (research) space. There are great difficulties in understanding this difference. And it is desirable for the head of the school (experiment) to remember this and, if possible, help the teacher in understanding the difference in goals.
The next "underwater reef" - hypothesis. It can be successfully developed if the teacher at the I level of the experiment has determined the peculiarity of pedagogical influences, due to which he receives (or wants to) receive the planned result of the student's education. Having predicted the final result and looking into the future, planning steps to achieve the goal, the teacher puts forward hypothesis, logically justified an assumption that includes a set of pedagogical influences, a system of measures, aimed at achieving the expected pedagogical result.
The question now being answered by the experimenter is: “What control actions are supposed to implement the objectives of the experiment?” or “What is the system of measures, the totality of pedagogical influences, with the help of which it is expected to obtain a certain effectiveness of the educational process?”
Hypotheses can be general and particular, intuitive and logically substantiated, working and scientifically substantiated. It will help to formulate the hypothesis of the existence of the so-called hypothesis formulas , which looks like this: "if...then..., because". For example, a hypothesis may sound like this: “if the content of lectures, laboratory and practical classes, the topics of seminars and scientific and practical abstract works are directed to the development of cognitive activity of high school students in teaching subjects of the natural and mathematical cycle; if the forms and methods of organizing training sessions and independent to direct the work of students to the development of their cognitive activity, this will help to form the ability to independently acquire knowledge, to self-study.The next possible difficulty in writing an experiment program is the development of criteria.
Criteria for evaluating expected results experiment - the most important component necessary for the implementation of experimental activities. Without criteria, it is impossible to assess the truth or falsity of the hypothesis put forward, to check the effectiveness of developments, the reliability of the results and the validity of the tools. When developing the criteria for the experiment, the teacher answers the question: “What signs will be used to track changes in students that occur due to the experimental materials used by the teacher (programs, methods, didactic principles, a set of pedagogical techniques, etc.)? By what parameters will the effectiveness of the developed experimental materials be evaluated?”
For example, the criteria for the formation of aesthetic taste in the study of literature in the creative activity of adolescents can be an emotional and personal attitude to the fate of the characters, a sense of empathy for the world of beauty. With the development of figurative thinking of younger students, the criteria may be the ability to create associations, the ability to find signs or properties similar to those studied in the course by association.
Having developed the criteria by which you will evaluate the expected result, proceed to the development diagnostic tools - means of evaluating the results of the experiment. These means can be: questionnaires, tests, tests, questions for interviews, etc., the content of which is the previously identified criteria. You have to answer the question: “How will results be monitored?”
For example, if you set a pedagogical goal to develop in schoolchildren the ability to perform complex mental operations (induction, deduction, argumentation, proof, transfer of knowledge from one subject area to another, etc.), a diagnostic tool can be a test that includes the following tasks: explain the meaning; reveal the value; prove; why do you think that...” Now let's move on to the next level of program structure.
Level III of the experiment - experimental and search. It is based on the first and second levels of the experiment and is distinguished by a greater depth of answers to the questions posed above, the completeness of the tools used. The structure of the experiment program includes, in addition to positions I and II levels of the experiment, such components as: contradiction, problem, object, subject of experiment, experimental idea. the idea, purpose and objectives of the experiment, its stages.
An experiment of this level is distinguished by a greater degree of reproducibility of results, manufacturability, evidence of results, which is why the program of the experiment includes components that describe the cycle of experimental research, from the analysis of practice and the birth of the idea of the experiment to testing the effectiveness of the hypothesis in teaching practice. We already know that the need for a pedagogical experiment arises every time a problematic situation arises in pedagogical practice, manifests itself contradiction interfering with the activities of the teacher, not allowing him to achieve the desired result.
A situation arises in which professional knowledge is not enough to resolve the problem. Problems. You have to look for the answer to the question: What needs to be learned from what has not been studied before? The answer to this question gives rise to the idea of the experiment. experimental idea- this is a general idea of the intended direction of the teacher's activity in the created problem situation, some idea of the desired result. For example, the idea of advanced learning, the idea of multi-level classes, conducting binary lessons, enhancing learning activities using game modeling, etc., can be tested.
According to Professor V.I. Zagvyazinsky, the idea contains an idea, an assumption about an expedient way to organize the activities of students, about the combination of the known and the new in it, about the originality of pedagogical assistance.
So, you have an idea. The next step is its specification. The idea of the experiment is specified in its intent, which involves a description of the process of implementing the idea. The main question in the development of the plan - how to put the idea of experiment into practice?
Intention experiment transforms the idea into concrete forms, requires certain methods her incarnation. The idea may contain a logical scheme for unfolding actions; principles of selection of educational material; highlighting the central thoughts, leading positions, methods, organizational forms. All this, taking into account the specific conditions in which the experimental idea arose, the parameters of the state of educational practice, limited by the problem situation. Therefore, the idea and concretizes the idea, linking it with the methods of implementation.
The idea and design of the experiment allow the teacher-experimenter to determine the boundaries of the study, changes in practice. In other words, the teacher determines an object experimentation is a pedagogical space, an area within the boundaries of which is what will be studied. Here's the main question: what is being researched ?
For example, the object can be: the educational process in the subject "Economics"; interaction between kindergarten and school; teaching high school students the basics of computer science, etc. The object of the experiment is rather complicated. In order to concretize what exactly the pedagogical influence is aimed at, - on what properties, connections, relationships - it is necessary to highlight item experimentation. His research will provide new knowledge about the factors influencing the change in the state of the student (his development, learning, upbringing).
For example, the educational process as a whole can be considered as the object of the experiment, and the forms of its organization can be considered as the subject. The object can be the teaching of high school students in the methods of mental activity, and the subject can be the process of forming the ability to compare, analyze, generalize. The object is the formation of an information-value attitude to reading among younger students, the subject is a pedagogical technology that forms the motivation for reading, effective techniques reading. The object is the system of educational work of the school, the subject is the process of its optimization, and so on.
Item, thus answers the question: how the object is considered: what properties, relations, functions are distinguished in the object; what reality, what part of the object will be revealed in this experimental study? The function of the subject of the experiment - fixation, holding the boundaries of influence. Target experimental answers the question: what does the teacher-experimenter want to create and test as a result of the experiment?
For example, the following provisions can be formulated as a goal: to develop and test a set of pedagogical techniques aimed at developing the communicative abilities of schoolchildren or a set of psychological and pedagogical conditions for introducing the methodology of S.I. Lysenkova in an ungraded rural school; develop and test a system of forms of educational work aimed at the socialization of the individual, its adaptation to market conditions of management, etc. In addition to the goal in the program of the experiment, it is determined tasks. They require an answer to the question: what intermediate results need to be obtained in order to achieve the goal and what steps need to be taken to achieve this?
The tasks of the experiment act as more specific in relation to the general goal of the experiment, particular goals. They can be defined as Steps to achieve the goal. They define a set of sub-problems to be solved during the experiment. For example, the tasks may be as follows: Analyze current trends in the development of methods for teaching physics. To identify and differentiate a set of pedagogical techniques, methods that determine the effectiveness of teaching physics. Develop and test a set of techniques for teaching physics in the humanities classes in order to develop cognitive interest to this course. The experiment is quite long and extended in time, so there is a need to identify the stages of the experiment.
Stages experiment determine some parts, intermediate results and the sequence of their achievement. Parts allow, at certain time intervals, to successively implement the system of measures laid down in the hypothesis. Stages serve to fix intermediate results, their evaluation and adjustment . When highlighting the stages of the experiment, the teacher answers the question: What are the intermediate results and in what sequence are they supposed to achieve the goal? The program also indicates the start time of the experiment and the expected end, that is - terms experiment. We stopped at some of the most significant components of the experiment program, made an attempt to introduce the content of the experiment program item and give a small illustration of each item.
This approach contains some minus, and we apologize in advance to the strict reader, since from a methodological point of view, it is not advisable to consider the components of the program separately. The program must have meaningful logical continuity and the connection of each part with the whole. Therefore, examples of program components should be (according to this position) taken from one of the experiment programs. But in this case, only possible illustrations of the formulations were important to us. Thus, completing the acquaintance with the provisions of the development of the experiment program and their illustrations, we can conclude for any level of the experiment, which is as follows: for the successful conduct of a pedagogical experiment, it is important for the teacher-experimenter:
Develop an inner mindset for gradual development steps professional excellence teacher-experimenter, on “peculiar growth” in the field of experiment (“today I can do one thing, tomorrow I will master and do something else in the field of experiment...”);
Motivation.
Pedagogical goals and tasks.
The subject of pedagogical activity.
Pedagogical means and ways to solve the tasks.
Product and result of pedagogical activity.
Each type of activity has its own subject, just like pedagogical activity has its own.
Subject pedagogical activity is the organization of educational activities of students, aimed at the development of subject socio-cultural experience by students as the basis and conditions for development.
means pedagogical activities are:
Scientific (theoretical and empirical) knowledge, with the help and on the basis of which the conceptual and terminological apparatus of students is formed;
- "carriers" of knowledge - texts of textbooks or knowledge reproduced by the student during observation (on laboratory, practical exercises etc.), organized by the teacher, behind the mastered facts, patterns, properties of objective reality;
Auxiliaries- technical, computer, graphic, etc.
Ways transfer of social experience in pedagogical activity are:
Explanation;
Display (illustration);
Collaboration;
Direct practice of the student (laboratory, field);
Trainings, etc.
Product pedagogical activity - the individual experience formed by the student in the totality of axiological, moral and ethical, emotional and semantic, subject, evaluative components. The product of this activity is evaluated at the exam, tests, according to the criteria for solving problems, performing educational and control actions.
result pedagogical activity as the fulfillment of its main goal is the development of the student:
His personal development;
Intellectual improvement;
His formation as a person, as a subject of educational activity.
The concept of abilities in psychology
Capabilities- individual psychological characteristics of a person, manifested in the activity and are a condition for the success of its implementation. The speed, depth, ease and strength of the process of mastering knowledge, skills and abilities depend on abilities, but they themselves are not reduced to them. Based on the analysis of psychological literature on the problem of abilities, the following signs of the presence of abilities for any type of activity can be distinguished.
Usually, types of abilities are distinguished by their focus, or specialization. In this regard, we can highlight:
General abilities - such individual personality traits that provide relative ease and productivity in mastering knowledge and implementing various kinds activities;
Special abilities- a system of personality traits that help to achieve high results in any field of activity. Special abilities are organically connected with general ones.
The essence of pedagogical abilities
Pedagogical abilitiescalled a set of individual psychological characteristics of a teacher's personality that meet the requirements of pedagogical activity and determine success in mastering this activity.
The difference between pedagogical abilities and pedagogical skills lies in the fact that pedagogical abilities are personality traits, and pedagogical skills are separate acts of pedagogical activity carried out by a person at a high level.
Each ability has its own structure, it distinguishes between leading and auxiliary properties.
The leading properties in pedagogical abilities are:
Pedagogical tact;
Observation;
Love for children;
The need for knowledge transfer.
Pedagogical tact- this is the observance by the teacher of the principle of measure in communicating with children in a wide variety of fields of activity, the ability to choose the right approach to students.
Pedagogical tact involves:
Respect for the student and exactingness to him;
Development of students' independence in all types of activities and firm pedagogical guidance of their work;
Attentiveness to the mental state of the student and the reasonableness and consistency of the requirements for it;
Trust in students and systematic verification of their academic work;
A pedagogically justified combination of the business and emotional nature of relations with students, etc.
Pedagogical observation- this is the ability of the teacher, manifested in the ability to notice the essential, characteristic, even subtle properties of students.
In another way, we can say that pedagogical observation is a quality of the teacher's personality, which consists in a high level of development of the ability to concentrate attention on one or another object of the pedagogical process.
Basic teaching abilities
Domestic researchers of pedagogical abilities based on the provisions of S.L. Rubinstein, B.M. Teplov in the 60s. of the last century identified a whole set of pedagogical abilities. The circle of pedagogical abilities is very wide. It covers the entire structure of pedagogical activity. Psychologists and educators who have studied the teacher's professiogram identify various teacher abilities.
In the studies of N.V. Kuzmina revealed such abilities as pedagogical observation, pedagogical imagination, pedagogical tact, distribution of attention, and organizational skills.
F.N. Gonobolin enumerates and reveals The following skills are required for a teacher :
The ability to understand the student;
The ability to easily impose material;
Ability to develop student interest;
Pedagogical tact;
Anticipating the results of your work, etc.
In general, the group of pedagogical abilities primarily includes:
Pedagogical observation;
pedagogical imagination;
Demandingness as a character trait;
Pedagogical tact;
Organizational skills;
Simplicity, clarity and persuasiveness of speech.
The listed pedagogical abilities allow to successfully carry out all aspects of pedagogical activity.
So, pedagogical imagination especially significant for constructive activity - it is expressed in the "projection" of students' future knowledge, the ability to find suitable methods and techniques in advance. It is also expressed in the "projection" of the character, habits of students both in the educational and in educational work, in the formation of the team as a whole. It is the pedagogical imagination that helps the teacher to carry out developmental education and upbringing.
Pedagogical tact manifests itself in the communicative side of pedagogical activity. As we noted above, this is the ability to establish right relationship with students, teachers, parents, a sense of proportion in relationships (moderately exacting, moderately kind), which allows you to eliminate and prevent conflict situations.
Organizational skills are also needed for the activities of the teacher, since all pedagogical activity is of an organizational nature.
N.D. Levitov identifies the following as the main pedagogical abilities:
The ability to transfer knowledge to children in a concise and interesting way;
The ability to understand students based on observation;
Independent and creative way of thinking;
Resourcefulness or quick and accurate orientation;
Organizational skills necessary both to ensure the work systems of the teacher himself, and to create a good student team.
In the most generalized form, pedagogical abilities were presented by V.A. Krutetsky, who gave them the corresponding general definitions.
1. Didactic ability- the ability to transfer students educational material, making it accessible to children, presenting the material or problem to them clearly and understandably, arousing interest in the subject, arousing active independent thought in students.
2. Academic ability- ability in the relevant field of science (mathematics, physics, biology, literature, etc.).
3. Perceptual abilities- the ability to penetrate the inner world of the student, pupil, psychological observation associated with a subtle understanding of the personality of the student and his temporary mental states.
4. Speech abilities- the ability to clearly and clearly express their thoughts, feelings through speech, as well as facial expressions and pantomime.
5. Organizational skills- this is, firstly, the ability to organize a student team, rally it, inspire it to solve important problems and, secondly, the ability to properly organize one's own work.
7. Communication skills- the ability to communicate with children, the ability to find the right approach to students, to establish with them expedient, from a pedagogical point of view, relationships, the presence of pedagogical tact.
8. Pedagogical imagination (or predictive ability)- this is a special ability, expressed in anticipation of the consequences of one's actions, in the educational design of the student's personality, associated with the idea of \u200b\u200bwhat the student will become in the future, in the ability to predict the development of certain qualities of the student.
9. The ability to distribute attention simultaneously between several types of activity; It has special meaning for the teacher's work.
Introspection Materials
pedagogical activity
primary school teachers
Lutovina Oksana Gennadievna
2015
Update process primary education orients me to an active search for a new content of education, changes in learning priorities. School education should be structured in such a way that graduates can independently set and achieve serious goals, skillfully respond to different life situations. The scientific and methodological program for the development of our school is as follows: “Formation educational environment providing accessibility, high quality education and upbringing of a socially adapted personality”, therefore, I consider the purpose of my work not only to give the student a certain amount of knowledge, but also to teach to learn, to develop interest in learning.
The fundamental difference between the standards of the new generation is their focus on the result of education. The development of the student's personality comes to the fore on the basis of mastering the methods of activity and the development of competencies. Along with general literacy, such qualities of the child as the ability for self-development, the formation of purposeful cognitive activity and motivation, as well as social and interpersonal relationships, that is, an individual development trajectory is being built.
The purpose of my professional activity is directly consistent with the activities of the educational institution. It aims to create conditions conducive to the formation and development core competencies in terms of integrating general and additional education, improving the quality of student learning.
To achieve this goal, I set the following tasks:
Identification and development of students' intellectual, creative and communicative abilities, accumulating experience in collective creative affairs;
Continued work on the implementation of the principle of an individual approach in training and education;
Formation in students of the need for self-control and self-esteem;
Identification and implementation of the educational potential of students;
The use of modern educational technologies, a variety of variable approaches to the creative activity of students;
Involvement of primary school students in the system of additional education;
Implementation of health-saving technologies in the educational process;
Continuous improvement of the level of their pedagogical skills, erudition and competence in the professional field.
During the inter-certification period, I worked on the problem “Technology of problem-dialogical learning in primary school". The result of this work was speeches at meetings of the regional methodological association, pedagogical councils, school problem group, parent meetings: "Technology of problem-dialogical learning as a means of realizing the modern goals of educating a younger student" (RMO, 2014), "How to cultivate a love of reading in a child" (parent meeting, 2013), "The subject-developing environment in the context of the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard" ( teachers' council, 2013), "Evaluation and mark: incentive or alienation"(school problem group, 2013), “How to conduct lessons of different themes in integrated classes” (school problem group, 2012), “Creating a health-saving environment at the initial stage general education”(RMO, 2011), “The activity of a primary school teacher in the context of the formation of a new model of education” (pedagogical council, 2011).
I have repeatedly shared my work experience not only at the school level, but also at the district level.
Combined lesson on teaching literacy on the topic "Sounds "n", "n", "r", "r". Letters H, R. (SHMO, 2011)
Russian language lesson in grade 1 on the topic “Repetition. Offer. Intonation. Punctuation marks at the end of a sentence” (RMO, 2012)
Mathematics lesson in grade 3 on the topic "Multiplication and division three-digit numbers". (SHMO, 2013)
The school is working on the topic "Formation of an educational environment that ensures accessibility, high quality education and the upbringing of a socially adapted personality."
My main goal of learning is studying modern pedagogical technologies. In my work, I use the following educational technologies that contribute to the formation of key competencies in children, leading to the success of students in modern society:
1.problem-dialogical training
I consider this technology to be the central point in the process of cognition and learning, since students do not receive ready-made knowledge, but extract it own efforts. I create a problem situation at various stages of the lesson: determining the topic of the lesson, updating knowledge, explaining new material, consolidating, independent work. At the lesson of explaining new material, I offer tasks that allow students to independently derive a rule. At the stage of consolidation, the main means of creating a problem situation is the integration of questions and practical methods, allowing to find an invariant solution of the problem. I include problem tasks in independent work, taking into account a differentiated approach;
2.research activities
One of the main problems modern education on which I am working during the lessons and outside, is the organization of research activities with primary school students.
Children are explorers by nature, discovering the world around them with joy and surprise. They are interested in everything. I maintain this interest in the lessons of the surrounding world and in extracurricular activities at the “I am a researcher” circle, where I work according to a modified program. The organization of research activities of schoolchildren allows students to develop cognitive interests, independence, a culture of educational work, allows them to systematize, generalize, deepen knowledge in a certain area of the subject and teaches them to apply them in practice.
To develop the skills of exploratory behavior in children in the classroom, I teach to see the problem, ask questions, put forward hypotheses, classify, observe, conduct an experiment, draw conclusions and conclusions, structure the material, prove and defend their ideas.
At the lessons of the surrounding world, studies were carried out: “Do shrubs and trees die in winter”, “The influence of alcohol on a growing organism”, “Connection of generations”, “The big history of a small village”, etc. The results of the study “The influence of alcohol on a growing organism” were reflected in project and presented at the annual school scientific-practical conference "Through search and creativity to perfection." In addition, every year we take part in the regional scientific and practical conference "The Edge of Creativity".
3.information and communication technologies
I pay much attention to solving the problem of using information and communication technologies in the classroom in the elementary grades.
The use of ICT in teaching allows me to:
Provide positive motivation for learning;
Conduct lessons at a high aesthetic level (music, animation);
Increase the volume of work performed in the lesson;
Improve knowledge control;
Rationally organize the educational process, increase the effectiveness of the lesson;
To form research skills;
Provide access to various help systems, electronic libraries, other information resources.
Educational electronic resources I use as:
1. Illustrations of educational material (tables, diagrams, experiments, video clips, musical works, multimedia presentations);
2. Support for educational material (assignments, tests, texts of presentations, etc.)
3. Source of educational material ( electronic textbook, development of tasks for independent work of the student).
To do this, I use ready-made Internet resources, learning programs, self-created ESM.
Usage various tests is of particular relevance in connection with the need to prepare students for school testing, monitoring studies.
To obtain new information and expand the horizons of students in the classroom and after school hours, I use presentations , which I compose myself with the involvement of material taken from the resources of the Internet.
In modern information society each student should be able to work on a computer, namely, to find the necessary information in various information sources (electronic encyclopedias, the Internet), process it and use the acquired knowledge and skills in life. I teach this at technology lessons in the Computer Science block and in extracurricular activities at the Me and the Computer circle, where I work according to the author's program. In the classroom, the children get to know the main components of a computer: monitor, system unit, keyboard; about their purpose and structure; are learning work with programs Word, Paint, P ower Point, create files, save them to your hard drive, copy, cut, move, create folders and work with them.
Active use information and communication technologies allows my students to successfully achieve common goals education, forms their competence in the field of communication (the ability to collect facts, compare them, organize, express their thoughts, reason logically, listen and understand oral and written speech, discover something new, make choices and make decisions). The children have an increased interest in the subjects they study.
4.technology for forming the type of correct reading activity(I use it in the process of explaining new material, working out basic concepts and controlling knowledge);
5. technology of multi-level education;
6. individual and differentiated approaches learning;
7. health-saving technologies(use of dynamic pauses, physical exercises, training of emotions, finger gymnastics);
8. gaming technology help to make the learning process interesting, exciting, to awaken curiosity among students.
The use of the above technologies in the learning process helps:
To ensure a high level of knowledge of students, the ability to independently acquire and apply them in practice, to involve each younger student in an active learning process;
Create conditions for search and research activities, develop practical thinking, provide the possibility of self-knowledge;
To cultivate a culture of work, collectivism, humanity and mercy, spirituality, a culture of behavior and conflict-free communication, respect for the world around us;
Collaborate with parents and other agencies that influence intellectual development children and their upbringing.
I try to make all my classes interesting, informative, developing the thinking of children, their ability to assess their psycho-emotional state. At each lesson, I teach students to meaningful work at all its stages. This activates attention, contributes to the education of industriousness and respect for working time in children, teaches children to appreciate the results of their work, the work of their classmates and adults.
I believe that the effectiveness of learning is high when the student is an active participant in the process. Therefore, I organize the educational process in such a way that there are methods in the lessons that activate the initiative and creative self-expression of the students themselves: work in groups of constant and variable composition, discussion in pairs, role-playing and business games, discussion methods (round table, brainstorming), design . Group learning increases the activity of students, involves both strong and weak students in the work, fosters mutual support, a culture of communication, creates a broad visual-sensory basis for theoretical generalization, provides conditions for students to master such complex skills as goal-setting, control, evaluation. I create an atmosphere of interest for each student in the work of the class. Immersing in the lesson in the learning environment, students have the opportunity to organize their learning activities.
I encourage the student to find his own way of doing independent work. We analyze with the class various ways performing tasks, choose and master the most rational ones. I create pedagogical situations of communication in the classroom, allowing each student to show initiative, independence, and find self-expression. I often suggest that children themselves choose tasks that are different in content, type and form. A differentiated approach creates a situation of success in the learning and development of each student.
The quality of the result of such work equally depends both on the activity of each student and on the coherence of the actions of the whole class as a whole. When checking the knowledge of students, I organize self-control, mutual control, analysis of the response of a friend and its evaluation.
In my work I use not only classical, but also non-traditional forms of lessons: a lesson-journey, a lesson-competition, a lesson of open thoughts, a lesson-tournament, a lesson-protection of projects and others.
For the effective use of schoolchildren's time and my own time, I try to make the most of the opportunities, knowledge, and interests of the students themselves in order to increase productivity and reduce costs in the learning process.
To this end, I plan my activities: I draw up work programs, calendar and thematic planning, lesson plans.
Planning helps to select material, balance the teaching load, clearly identify the stages of the lesson, organize differentiated work, select tasks at different levels, determine the degree of assimilation of the material, think over the control of monitoring, and most importantly, organize learning activities so that each student acts in the lesson: is in search, solved problems, suggested solutions, etc.
I try to build interaction with students on the principles of cooperation pedagogy. Analyzing my professional activities, I came to the conclusion about the effectiveness and efficiency of communication and learning based on joint creative activity.
I organize interaction with the class in the classroom and after school hours on the principles of respect, mutual trust and cooperation. I organize the educational process on the basis of interaction, dialogue, during which students learn to think critically, solve complex problems, weigh and defend alternative opinions, make thoughtful decisions, participate in discussions, and communicate with other children. To do this, I organize pair and group work, role-playing and business games, various creative work. When checking the knowledge of students, I organize self-control, mutual control and analysis of the response of a friend with his assessment.
I consider that the cognitive interest in my lessons is rated as above average. Active Forms, methodological techniques used by me in the classroom, contribute to the improvement of the necessary skills and abilities of students, the development of sustainable interest in subjects, cognitive activity, creativity, optimization of the learning process. Interest is lost if learners are unable to cope or find it difficult. To avoid this, I spend with children individual sessions which help me to keep younger students interested in learning activities. For the formation of communicative and social competence I use work in small groups, which is an effective form of instilling interest in subjects. A game also helps to arouse interest in educational activities, with the help of which younger students easily and quickly learn educational material, learn to think logically and fantasize. Using a wide variety of games in my practice (crossword puzzles, mathematical lotto, magic squares, riddles, etc.), I noticed that children's motivation for learning increases. Games help us to repeat and consolidate, generalize and systematize the knowledge gained in the learning process, make the learning process interesting and exciting.
My children are active participants and winners of school, municipal, All-Russian competitions and olympiads.
Gorelkina Daria - winner of the school competition of crafts "Santa Claus' Toy Factory" (2013)
Fateeva Daria - winner of the school drawing competition " Christmas story» (2013)
Petrov Dmitry - winner of the school poetry competition "Teacher, in front of your name ..." (2013)
Fateeva Daria - winner of the regional competition "Live Classics" (2013)
Kochergin Nikita, Egorov Nikita, Yakunina Nastya - 1st place in the regional competition "The second life of unnecessary things" (2013)
Gurova Victoria - participant of the regional competition "Star Ground" in the nomination "Theater of one actor" (2012)
Miloserdov Vadim, Gurova Victoria - participants of the International Competition-Festival of Children's Arts and Crafts "Easter Egg 2012" (2012)
Dolgushin Nikita - 1st place, Mountain biking competition among juniors (2014)
Ulyanov Maxim - 1st place, All-Russian marathon "Favorite fairy tales" (2013)
Ulyanov Maxim - 2nd place, All-Russian marathon "ABC of the animal world" (2013)
Kochergin Nikita, Sharshnev Vadim - 2nd place, All-Russian marathon "Merry Mathematics" (2013)
Fateeva Daria - 3rd place, All-Russian marathon "Merry Mathematics" (2013)
two students took part in the All-Russian competition "Russian Bear" (2012);
five students took part in the All-Russian math competition"Kangaroo" (2014)
In extracurricular activities, I also encourage children to be active. I conduct additional developmental events in subjects: intellectual tournaments, subject weeks, literary games, health holidays, competitions, quizzes. We participate in all school activities with the class. In the current academic year the students themselves proposed the numbers of the concert program for Mother's Day, the Autumn Ball. Last academic year, they took patronage over the kids of the kindergarten: students played outdoor games with him on the street, prepared a performance for the harvest festival, held a competition in Russian folk tales and riddles.
Active participation the guys took part in such events as "Autumn Ball", "Mother's Day" (songs and poems), "New Year's Tale" (staging); designed an exhibition of drawings "How beautiful this world is." A concert program was prepared for the day of honoring veterans.
I maintain close ties with the rural House of Culture. So, for the Victory Day, students under my guidance made congratulatory letters-triangles for veterans of the Great Patriotic War and home front workers and prepared a literary and musical composition.
Based on the school development program on the importance of education and upbringing of a Russian citizen based on the development of the initiative and creativity of the teacher using modern methods, I strive to ensure the satisfaction of the educational needs of individual students through classes in the classroom and after school hours. The combination of various forms of learning activity makes it possible to identify students with different abilities and inclinations. This allows you to create an educational field around each student. In my work, the main goal is to work for a strong student and the desire to "pull up" everyone else to this level.
This approach makes it possible to achieve a positive attitude towards the Russian language, mathematics, literature among children and parents, contributes to the formation of a benevolent microclimate in the classroom and extracurricular activities, creates a situation of success.
The effectiveness of the use of these teaching and upbringing technologies is confirmed by the results of the educational activities of children.
Information about the quality of knowledge and the level of students' learning in dynamics for 3 years
2011 – 2012 academic year
4th grade(4 students)
2012 - 2013 academic year
1 class
2013 – 2014 academic year
Grade 2(12 students)
The modern reform of the education system and the realities of our life require the improvement of the methodology and methodology for assessing the personal and educational achievements of students. In my teaching activities, I use the following forms and methods of control:
1. Current certification: oral surveys, written independent work, dictations, control cheating, test tasks, graphic works, presentations, compositions, reports, creative works.
2. final examination(for a quarter, half a year, a year): diagnostic - tests, tests, tasks of a partially search character, dictations, presentations, essays, control of reading technique, control of computational skills, complex tests).
3. Individual student rating as the main indicator of learning success ( rating system control of learning gives rise to competition in learning, positively affects the motivation of students, minimizes randomness in assessment).
4. Computer testing.
Other forms of accounting for achievements:
1. Lesson activity (analysis of the dynamics of current performance).
2. Extracurricular activities (participation in exhibitions: "Skillful Hands", "Gifts to Moms"; thematic exhibitions: "On the Conquest of Space", "On the Battlefields"; presentations; competitions; Olympiads; competitions; activity in projects and programs of extracurricular activities; creative report).
3. Portfolio - a method of cumulative assessment (allows you to maintain a high learning motivation for my students, encourages their activity, independence, expands the possibilities of learning and self-learning, develops the skills of reflective and evaluative activity).
4. Analysis of psychological and pedagogical research.
In the first class there is a non-judgmental system. From the second grade, I evaluate students on a five-point system. In my work, the following types of assessment take place:
Internal (assessment by a teacher, school) and external assessment (monitoring studies of educational achievements of students, certification of an educational institution).
Subjective or expert (observations, self-assessment, self-analysis, etc.) and objective (based on the analysis of written answers and students' work).
A variety of forms of assessment, the choice of which is determined by the stage of training, general and special learning objectives, current learning objectives, the purpose of obtaining information (mutual assessment, group assessment, etc.).
Quantitative and qualitative assessments.
Integral assessment (portfolio, exhibitions, presentations, differentiated assessment of individual aspects of education).
To record the results of the assessment, I use the sheets of achievements, cool magazines, electronic forms of documentation, diaries of students, personal diary of observations, certificates on the results of intra-school control, characteristics of students.
The class is a living organism mental health which depends on the mood, academic success, mutual understanding in the team. Great experience as a teacher taught me to assess the psychological state of the student at first sight.
I know that nothing unites the guys like a common cause, which helps to evoke positive emotions in students. I’m in a bad mood, I “treat” failure with a responsible assignment, a request: to help a classmate, check the work of a neighbor, pick up entertaining tasks for elementary grades, etc.
Relationships with students are trusting and respectful. Micro-research on the problem of “Teacher-Student Relationships” shows that in mathematics lessons, according to students, understanding reigns, and the teacher and student work in commonwealth.
Ideally, parents should be active participants in the educational process, working closely with the teacher.
Interaction with parents is traditionally carried out through school-wide, classroom parent meetings. On them I report the general class achievements of students, the successes of individual students. Problematic issues We decide in an individual conversation. This helps develop trusting relationships with parents.
Not all parents adequately perceive the quantitative assessments of their children. The so-called evidence base helps to dissuade them of this. I conduct micro-studies of student learning:
The level of memory development;
The level of development of thinking.
In the classroom, a survey was conducted among parents on the topic "The emotional and psychological state of the child in the classroom." Based on the results of the survey, it can be seen that parents are satisfied with the living conditions of the class team. Children feel comfortable in the classroom and school.
Our school has developed good tradition- Organize open days. I invite parents to the lessons so that they can see the work of the children, I give them to look through notebooks for tests and speech development. Together we identify problems, outline solutions to improve academic performance, intellectual level schoolchildren. I am sensitive to the opinions, requests and wishes of parents. I never leave them unattended. As a sign of gratitude, the parents of 4th grade students congratulated me this year on Teacher's Day through the regional newspaper Trudovaya Nov.
The psychological atmosphere in our team of teachers is friendly, I enjoy communicating with colleagues, I am always ready to help, help with advice, a kind word, if you need to print something, instructed and helped in compiling work programs, filling out electronic diary etc.
By nature, I am a non-conflict, sociable person, so I rate my relationships in the team as good. Our teaching staff is a team of like-minded people, which allows us to achieve one of the highest quality of knowledge in the region, one hundred percent training.
I am constantly improving my professional skills. A large role in this is given to self-education and the exchange of pedagogical experience. For these purposes, I:
1) I am taking advanced training courses (2011 “Formation of the professional competence of a primary school teacher in the context of the implementation of the new generation of the Federal State Educational Standards”);
2) I am currently taking courses in the program professional retraining"Teaching a foreign language in the context of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard of Basic General Education"
3) participate in school and district methodological events;
4) participated in the municipal scientific and practical conference "The living secret of education, or lessons for the soul"(2013)
5) I take part in network professional competitions, online forums, network teachers' councils, in competitions of professional skills;
6) I place my materials in the media ( collection "IMC Rasskazovsky district"), on Internet sites, in network professional communities;
7) developed work programs in all disciplines, the author's program of extracurricular activities "I and the computer", a modified program of extracurricular activities "I am a researcher";
8) exchange experience with colleagues on the methodology of teaching individual subjects;
9) in accordance with the work plan of the school, I carry out a diagnosis of the individual educational needs of students.
Awarded in the last 5 years:
Year of awardThe demographic situation in the village has led to a sharp reduction in the number of classes (once best school in the district became a branch) and as a result of this, the association into classes-sets. Happensdifficulty in organizing the lesson, it is necessary to think over the lesson so that all the children work.
In classes 3 - 13 students. If someone thinks that 3-4 students are good for a teacher, then this person is deeply mistaken. It is very difficult to motivate children for productive work, there is nowhere to “turn around”, and sometimes there is no one to ask. I want to immerse myself in the lesson, in this childish “fuss”, work, in this light working noise, in this thick of questions and even some misunderstandings, I want to argue, even make a mistake, and not in front of anyone and with no one.
Unfortunately, the understanding that the main child's work - education should be treated responsibly and with full dedication, comes to some children and parents late.
I believe that the individualization of education, the more active introduction of information and communication technologies, design methodologies help to overcome these difficulties.
The main direction of its future activities I see in improving the quality of education through the maximum use of research, information and communication technologies in the classroom, preserving and strengthening the health of students with the help of health-saving technologies.
So I'm planning to:
to develop tasks aimed at the formation of universal educational activities for all academic subjects;
continue work on the use of information and communication technologies in educational activities;
continue studying pedagogical technologies, contributing to the activation of students in the process of speech development;
develop indicators, criteria, tools for tracking organizational, informational, intellectual skills;
create conditions for the research work of students in the classroom and in extracurricular activities (mini-projects; research in more deep sense words);
to continue work on revealing the creative abilities of children;
contribute to the development of the child's personality through participation in competitions, seminars, olympiads, including remote ones.
Municipal budgetary educational institution
Platonic mean comprehensive school
Rasskazovsky district, Tambov region
Reflective materials
practical results
pedagogical activity
primary school teachers
Lutovina Oksana Gennadievna
2015
 Converting a decimal fraction to an ordinary fraction and vice versa: a rule, examples
Converting a decimal fraction to an ordinary fraction and vice versa: a rule, examples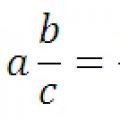 Converting decimal numbers to common fractions
Converting decimal numbers to common fractions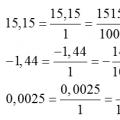 Converting an ordinary fraction to a decimal fraction and vice versa, rules, examples
Converting an ordinary fraction to a decimal fraction and vice versa, rules, examples